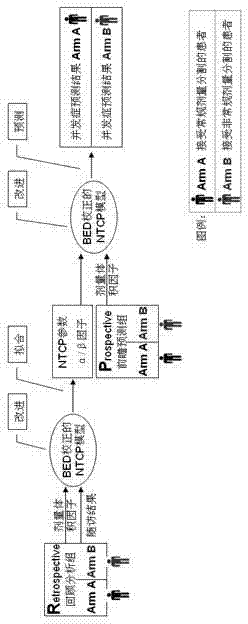
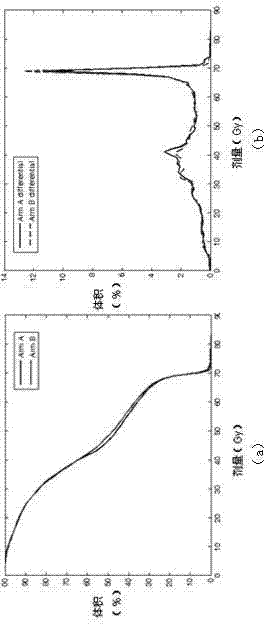
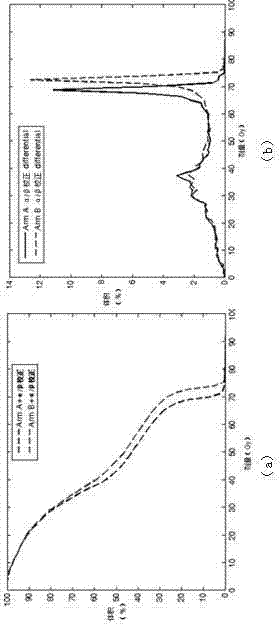
BED (biological effective dose)-based prediction method for complications caused by tumor radiotherapy
A biological effect and tumor radiation technology, applied in X-ray/γ-ray/particle irradiation therapy, special data processing applications, instruments, etc., can solve the problem of not considering the impact, the inability to see the difference of bladder complications, and the probability of complications To improve the survival rate, reduce the probability of complications, and improve the quality of life
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0043] The method of the present invention will be described in further detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings.
[0044] (1) Improve the traditional NTCP model
[0045] 1) After a certain volume of a normal organ receives a certain radiation dose, the probability of complication (NTCP) is as follows:
[0046] (Formula 4)
[0047] in,
[0048] (Formula 5)
[0049] (Formula 6)
[0050] (Formula 7)
[0051] in formula 7 and patients respectively The irradiated volume element and the corresponding dose element of the organ, , and are the three parameters of the NTCP model;
[0052] 2) For the maximum dose in Equation 5 and each dose element in Equation 7 , respectively using formula 1 to convert the physical dose into biological dose, and correspondingly get and ;
[0053] 3) with and Replace in Equation 5 and Equation 7 res...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com