Breeding method of predatory natural enemies using eggs of wax moth
A technology of large wax moth and natural enemies, which is applied in the breeding field of predatory natural enemies, can solve the problems of artificial feed pollution, high manufacturing and feeding costs, low efficiency of bait, etc., and achieve the effects of fast growth, high utilization and more eggs
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0029] Embodiment 1: Utilize the rearing of the predatory natural enemy of wax moth egg
[0030] 1-1: Breeding of wax moth and collection of eggs
[0031] The large wax moth was obtained from the Rural Development Agency, and then multiplied in artificial feed. Select the varieties with superior fertility from the large wax moths raised through generations and subcultures, and raise and keep them in feeders (11cmx17cmx6cm).
[0032] The artificial diet for raising the wax moth was composed of 200mL honeycomb, 1200mL wheat bran, 1200mL rice bran, 200mL glycerin, 0.8mL multivitamin, and 100mL water. Use after sterilizing by pressure for 15 minutes.
[0033] In the feeder made of four-corner transparent plastic, spread 3 cm to 5 cm high sterilized artificial feed, put 30 large wax moth pupae, and then cover with artificial feed.
[0034] In addition, take two rolls of toilet paper, fold them 4 to 5 times to form a square egg-laying board with a size of 5cmx3cm, make about 10 a...
experiment example 1
[0055] Experimental Example 1: Determination of the 1-day predation amount of small flower bugs on cotton aphids according to age
[0056] Investigate the 1-day predation amount of cotton aphids by the small flower bugs reared by the method of embodiment 1-2 according to the age, and the results are shown in Table 4.
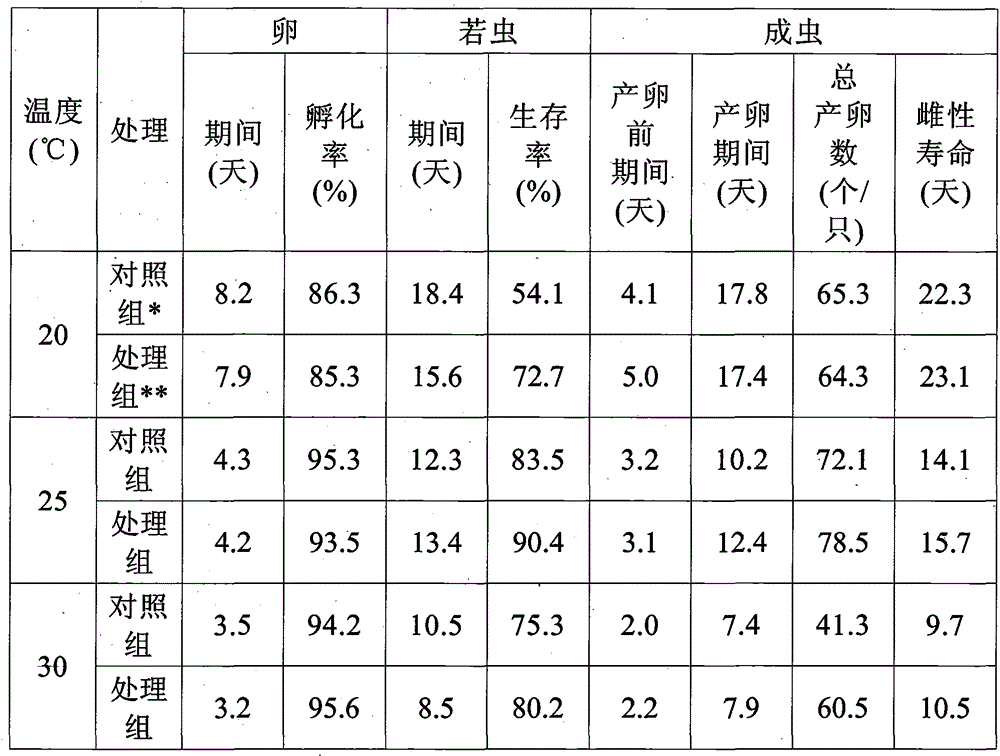
[0057] Table 4
[0058]
[0059]
[0060] *Control group: flower stinkbugs reared with the eggs of the spotted borer moth
[0061] **Treatment group: small flower stink bugs reared with the eggs of the wax moth
[0062] It can be seen from Table 4 that the 1-day predation amount of cotton aphids by nymphs and adults of the small flower stinkbug fed with the eggs of the wax moth was more than that of the control group.
experiment example 2
[0063] Experimental Example 2: Determination of the 1-day predation amount of Heterochromia on cotton aphids by age
[0064] The 1-day predation amount of H. gossypii by age survey by the method of embodiment 1-3 rearing of H. gossypiae is shown in Table 5.
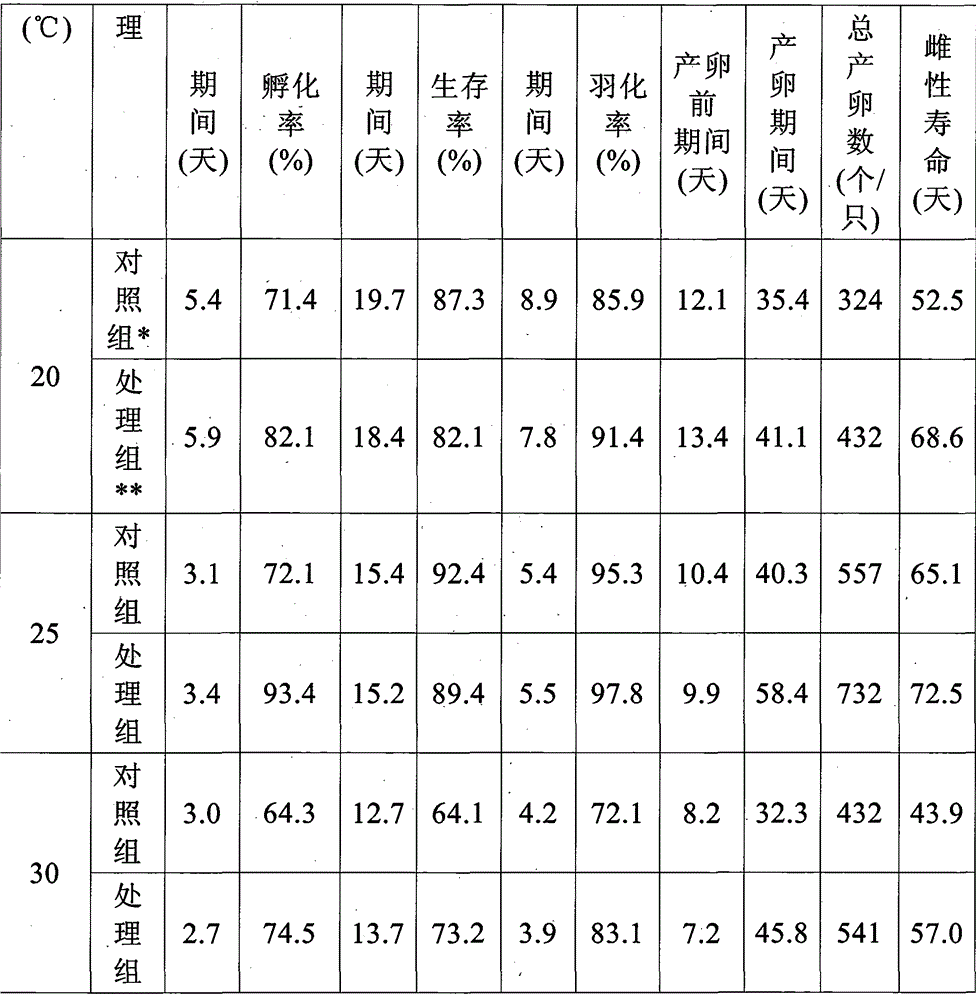
[0065] table 5
[0066]
[0067] *Control group: Heterochromia reared with cotton aphids
[0068] **Treatment group: Heterochromia reared on the eggs of the wax moth
[0069] It can be seen from Table 5 that the 1-day predation amount of H. gossypii by the nymphs and adults of H. gossypii raised by the eggs of the wax moth was greater than that of the control group.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com