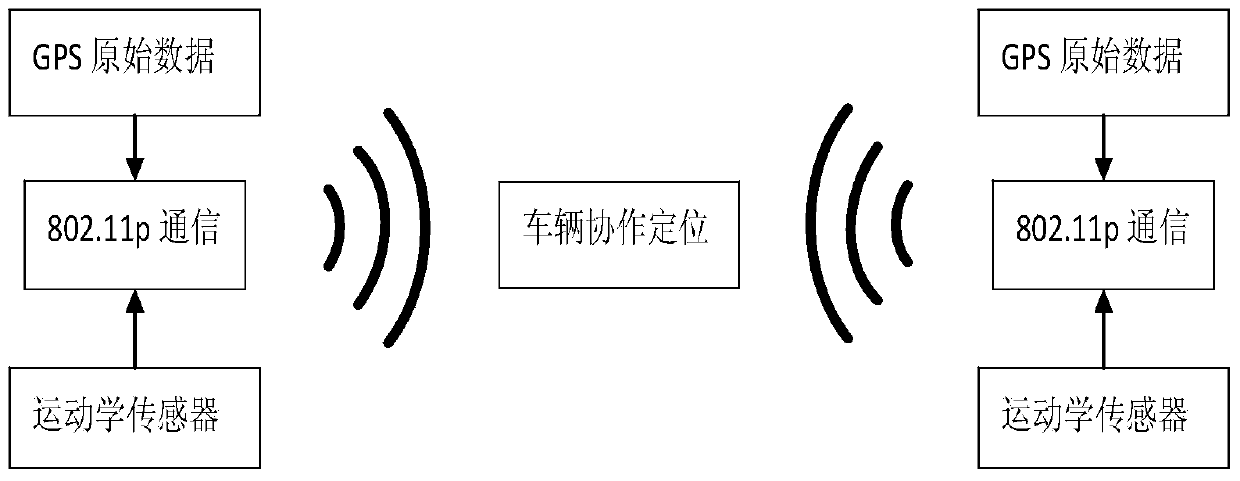
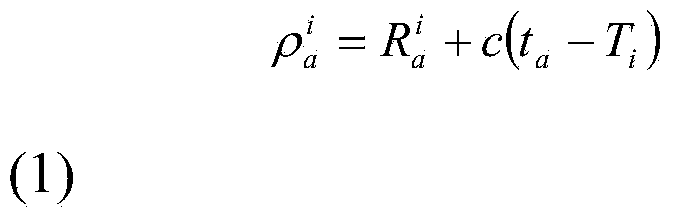GPS (Global Positioning System)-pseudo-range-differential-based cooperative positioning method for vehicles
A collaborative positioning and pseudo-range difference technology, applied in the field of Internet of Vehicles, can solve the problems of improving the absolute accuracy of positioning to the lane level, failing to meet reliability requirements, and not suitable for long-term independent positioning.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
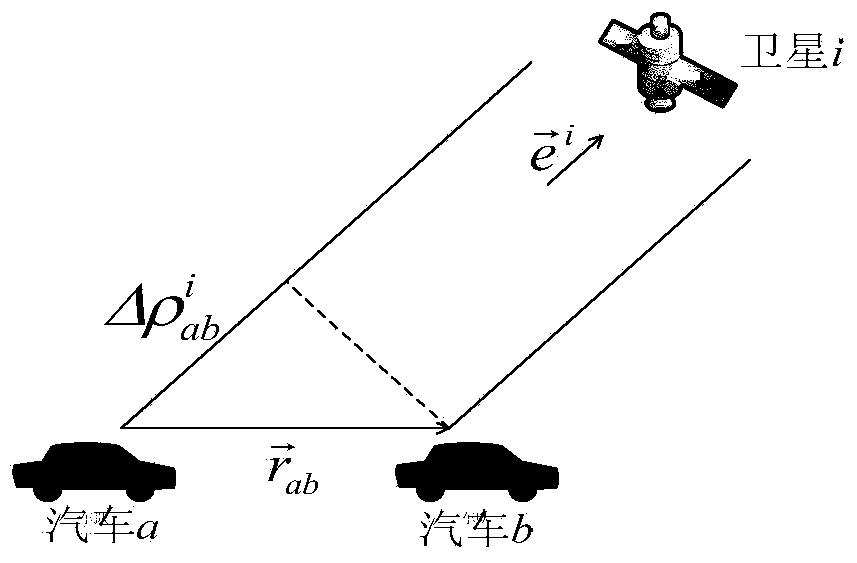
[0060] By differencing the pseudorange measurements of car a's GPS receiver and car b's GPS receiver relative to the same satellite i, the common error due to satellite i can be canceled out:
[0061] Δρ ab i = ρ a i - ρ b i
[0062] = R a i - R b i + c ( t a - t b )
[0063] = ΔR ab i + c · Δt ab
[0064] In the formula, is the pseudorange difference value, is the actual distance difference between c...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com