NMOS transistor and formation method thereof, and SRAM memory cell circuit
A MOS transistor and transistor technology, applied in transistors, circuits, electrical components, etc., can solve the problems of reduced operating voltage and increased threshold voltage changes, and achieve the effect of improving write margin and read and write stability.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
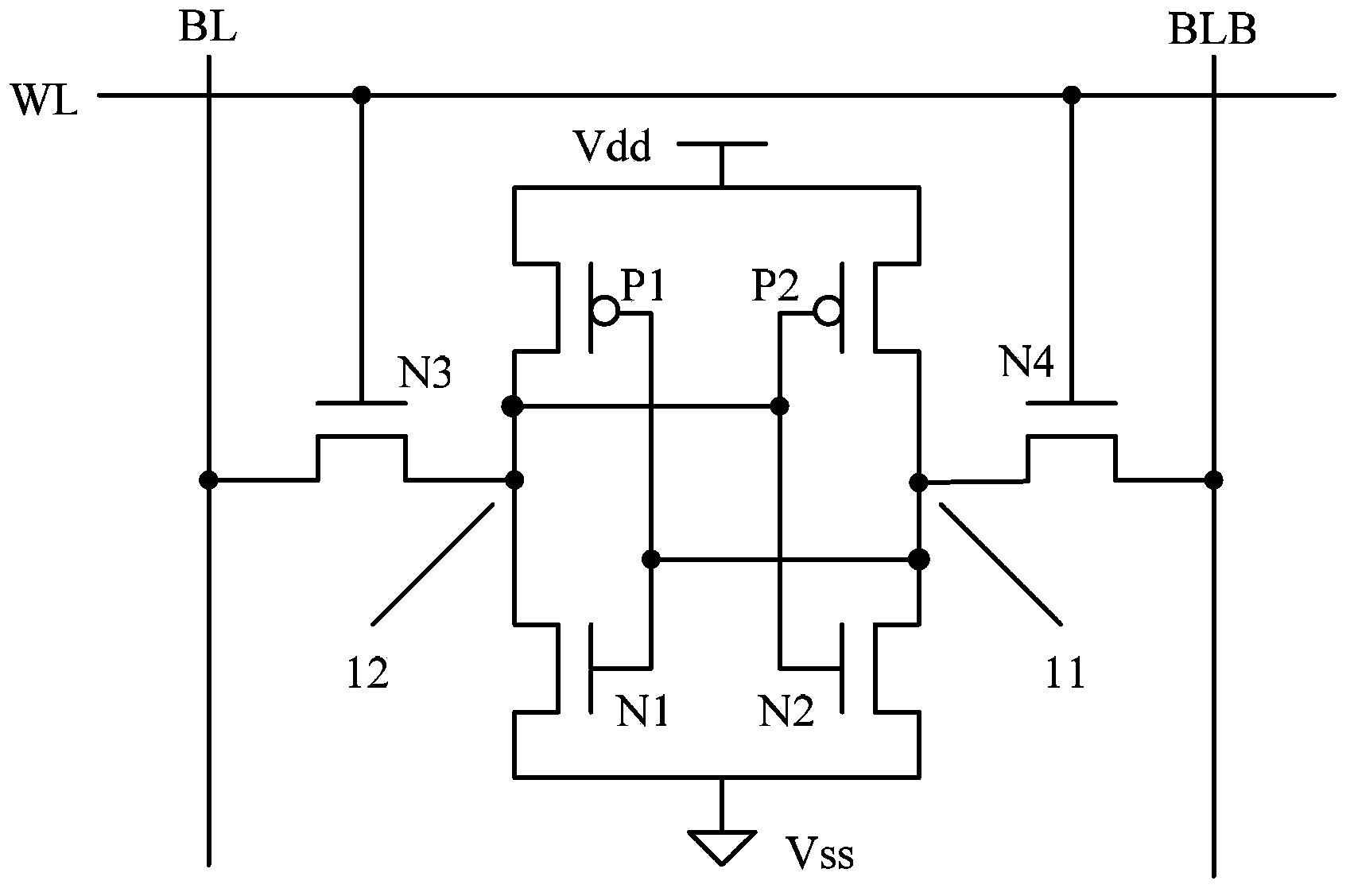
[0038] The read and write stability of SRAM memory is mainly measured by the two parameters of read margin and write margin. The read margin is the maximum noise voltage that the SRAM memory can withstand without changing the storage state during the read operation. , the write margin is the maximum noise voltage that the SRAM memory can withstand without changing the storage state during the write operation. The higher the read margin and the write margin, the better the read and write stability of the SRAM memory. Among them, the read margin is related to the ratio between the saturated source-drain current value of the pull-down NMOS transistor and the saturated source-drain current value of the pass NMOS transistor; the write margin is related to the saturated source-drain current value of the pass NMOS transistor and the pull-up PMOS The transistor's saturation source-drain current value is related to the ratio.
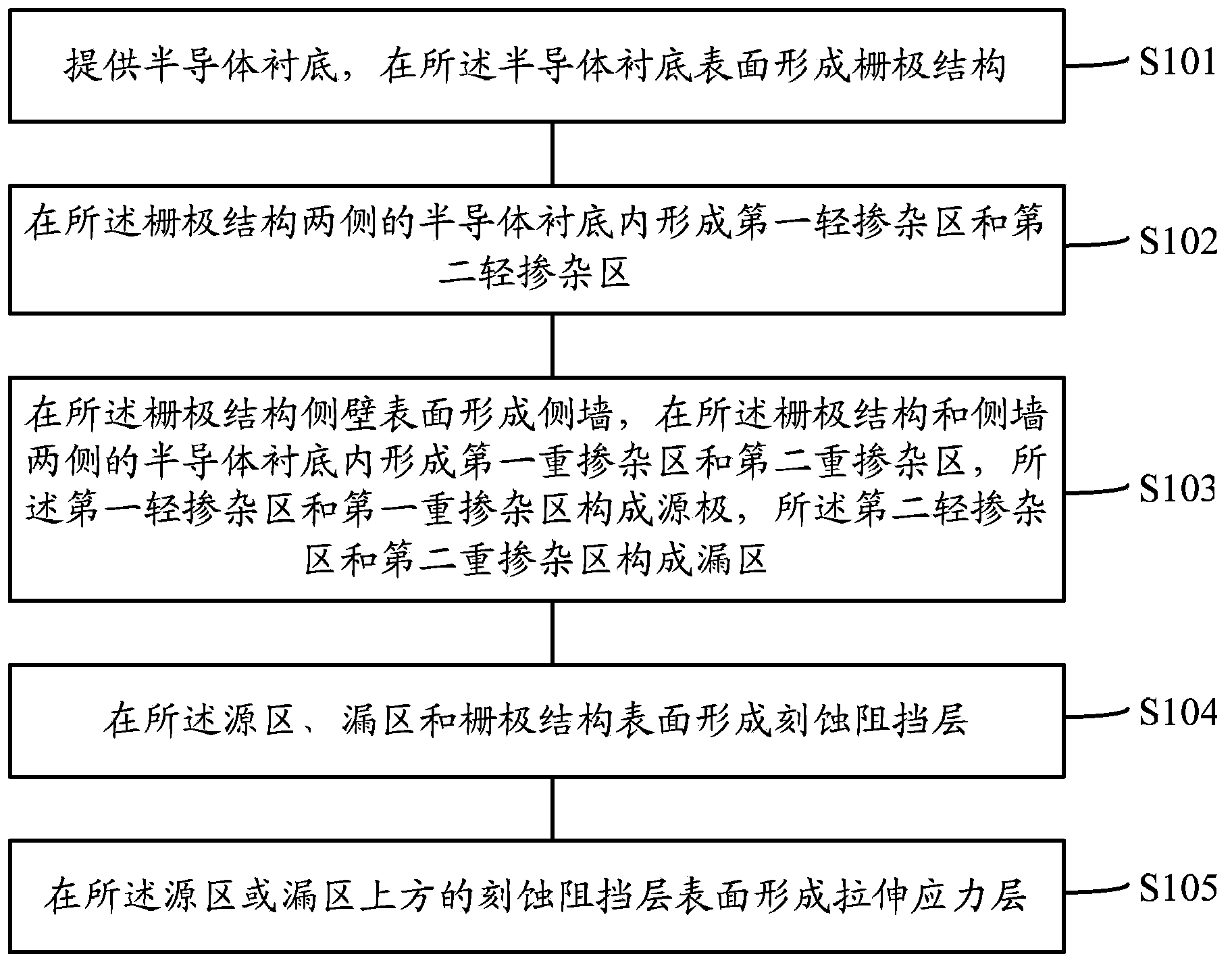
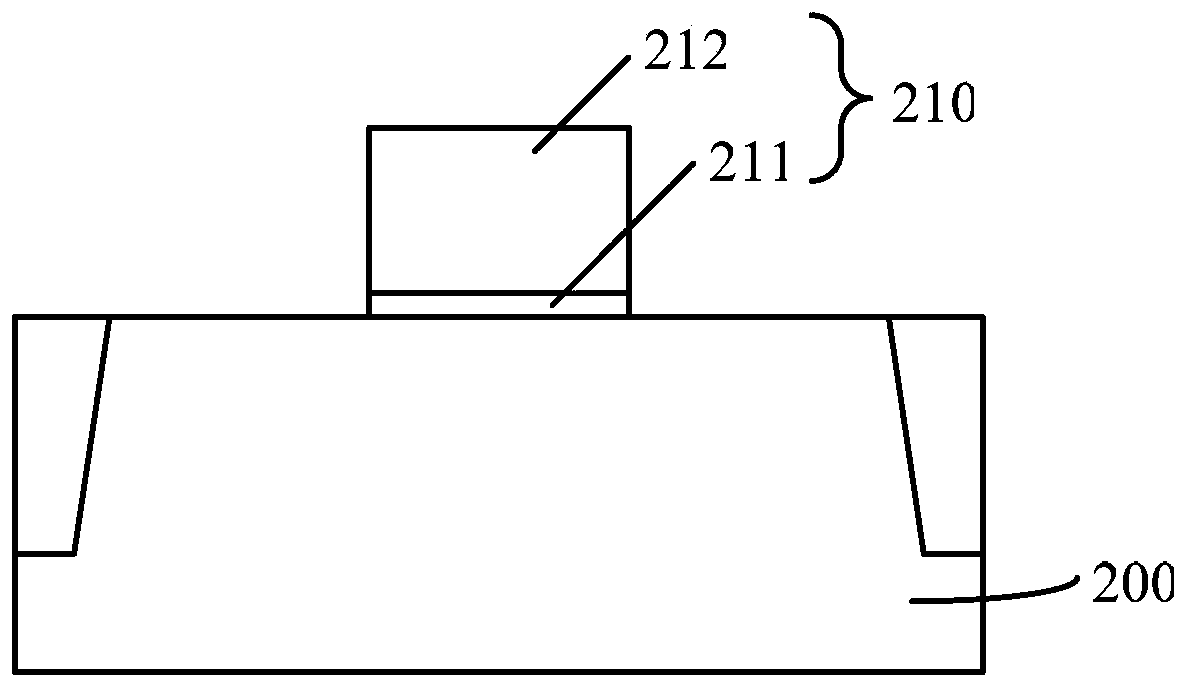
[0039] In order to improve the read margin, when the stru...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com