Heat-resistant austenitic stainless steel having excellent cyclic oxidation resistance
An austenitic and cyclic oxidation technology, which is applied in the field of heat-resistant austenitic stainless steel, can solve the problems of unconfirmed cyclic oxidation resistance, low cyclic oxidation resistance, and increased manufacturing procedures, and achieves suppression of oxide scale scattering. , The effect of improving power generation efficiency and reducing maintenance costs
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
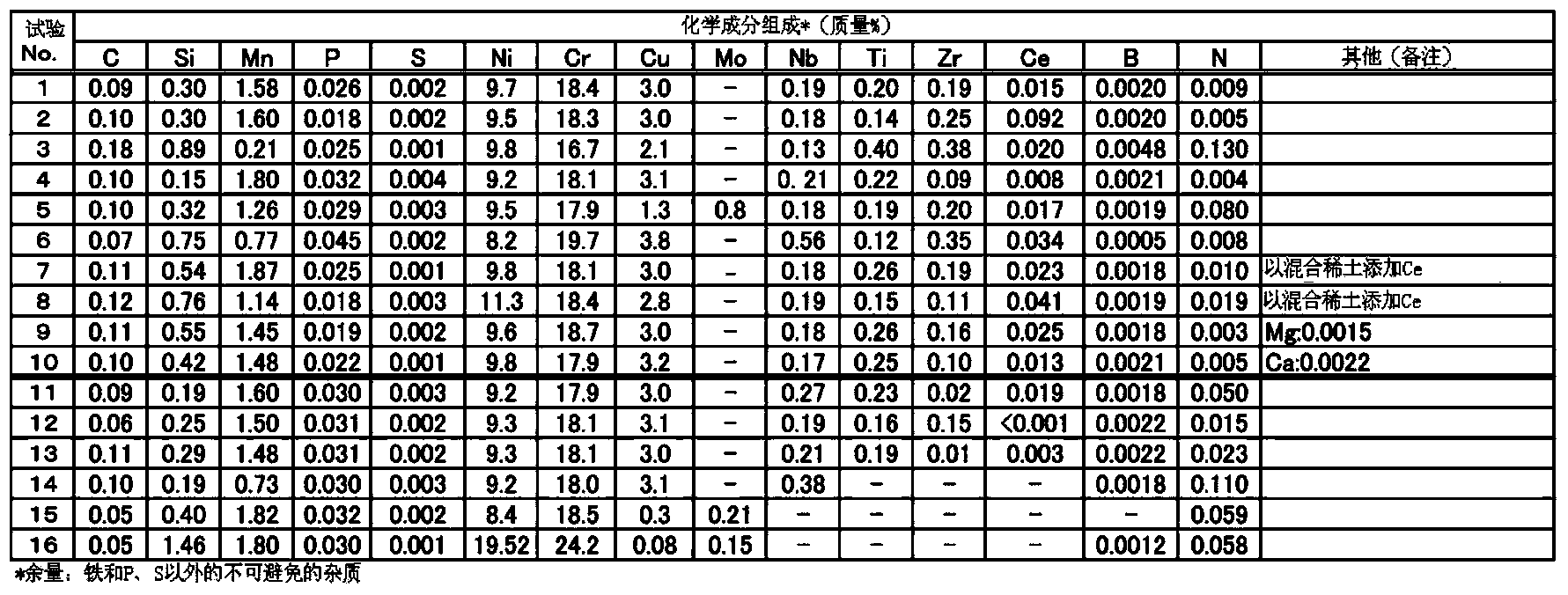
[0069] Melt various steel materials with the chemical composition shown in the following Table 1, and heat-forge a 20kg ingot melted in a vacuum melting furnace (VIF) into a size of width: 120mm×thickness: 20mm, after heat treatment at 1250°C , processed by cold rolling to thickness: 13mm. Thereafter, heat treatment was performed again at 1150° C. for 5 minutes, and this was used as a base material. A steel material of 20 mm x 30 mm x 2 mm was cut out from the base material by machining, and the surface of the steel material was smoothed / mirrored by grinding with sandpaper and buffing with diamond abrasive grains to prepare a test piece.
[0070] In addition, among the steel materials shown in the following Table 1, test Nos. 1 to 10 are steel materials (steels of the present invention) that satisfy the requirements specified in the present invention, and test Nos. 11 to 16 deviate from the requirements specified in the present invention. Among them, Test Nos. 14, 15, and 16 ...
Embodiment 2
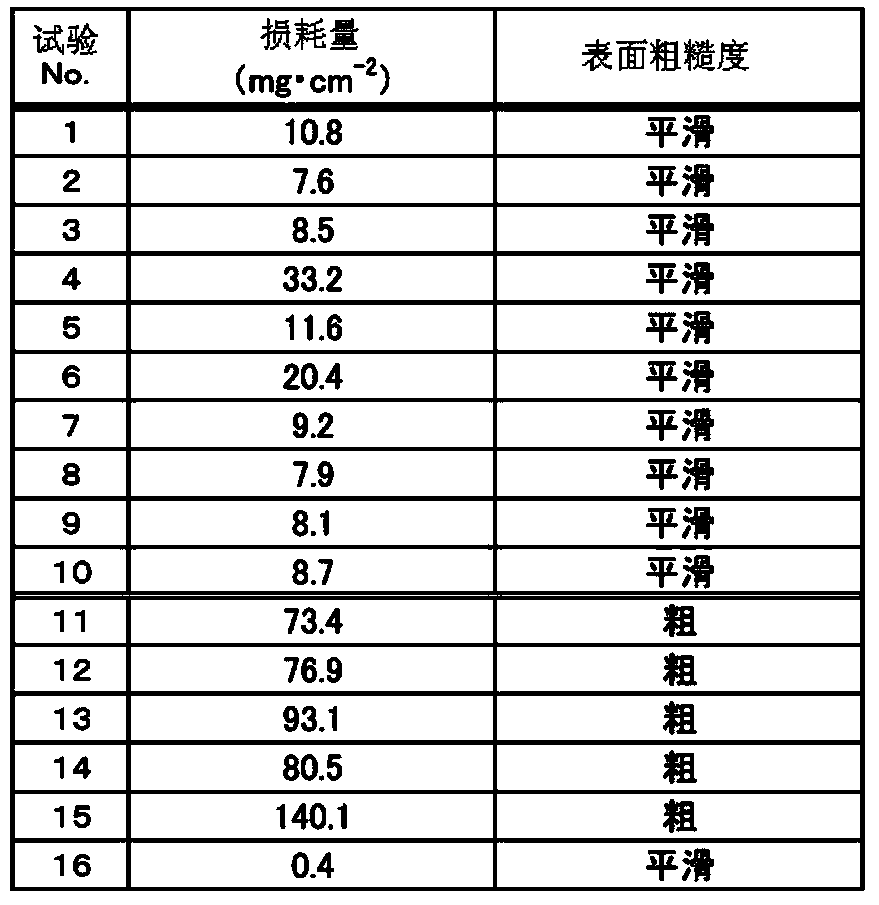
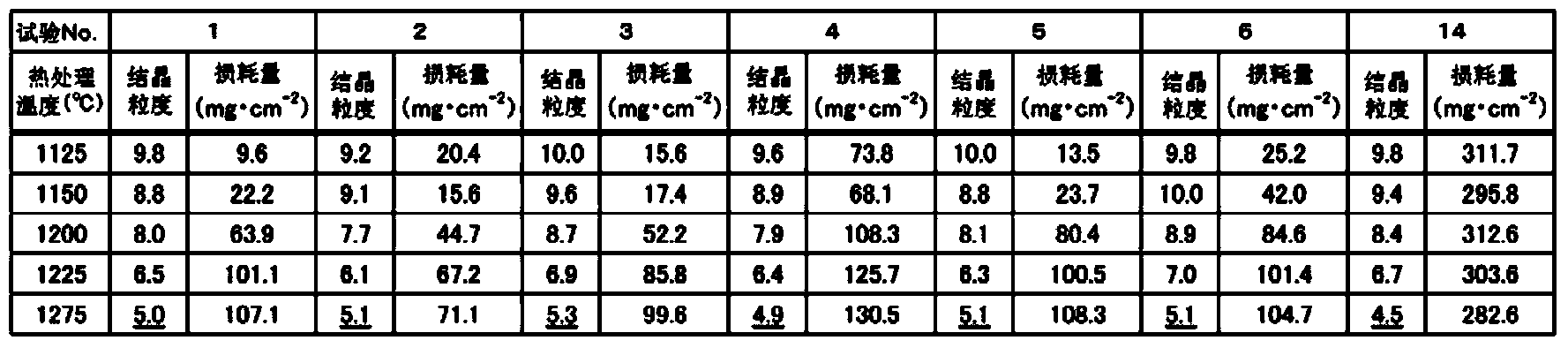
[0081] For the invention steels of Test Nos. 1 to 6 shown in Tables 1 and 2, and the comparative steel of Test No. 14, the heat treatment temperature was changed in the temperature range of 1125 to 1275°C after cold working with a reduction in area of 35%. Samples with crystal grain sizes ranging from 4.5 to 10.0 were prepared from various steel materials. The cyclic oxidation test is to heat in the furnace for 25 minutes and let the air cool for 5 minutes. The sample is put in and out of the atmospheric furnace at 1100 ℃, and the mass of the test piece after 40 cycles is compared with the mass of the test piece in the initial state. Compare and obtain the mass reduction (loss: mg / cm -2 ).
[0082] Regarding the number of cycles, part of the steel to which Zr and Ce were added showed a significant improvement in loss, and the loss after 20 cycles had a degree of error depending on the particle size, so heating and cooling were repeated up to 40 cycles. In the calculation o...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com