Magnetic resonance imaging method and device
A magnetic resonance imaging and algorithm technology, which is applied in medical science, sensors, diagnostic recording/measurement, etc., can solve problems such as small data volume in overlapping sampling areas, reducing the accuracy and robustness of motion parameter estimation, and affecting the effect of motion artifact elimination. , to achieve the effect of eliminating motion artifacts
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
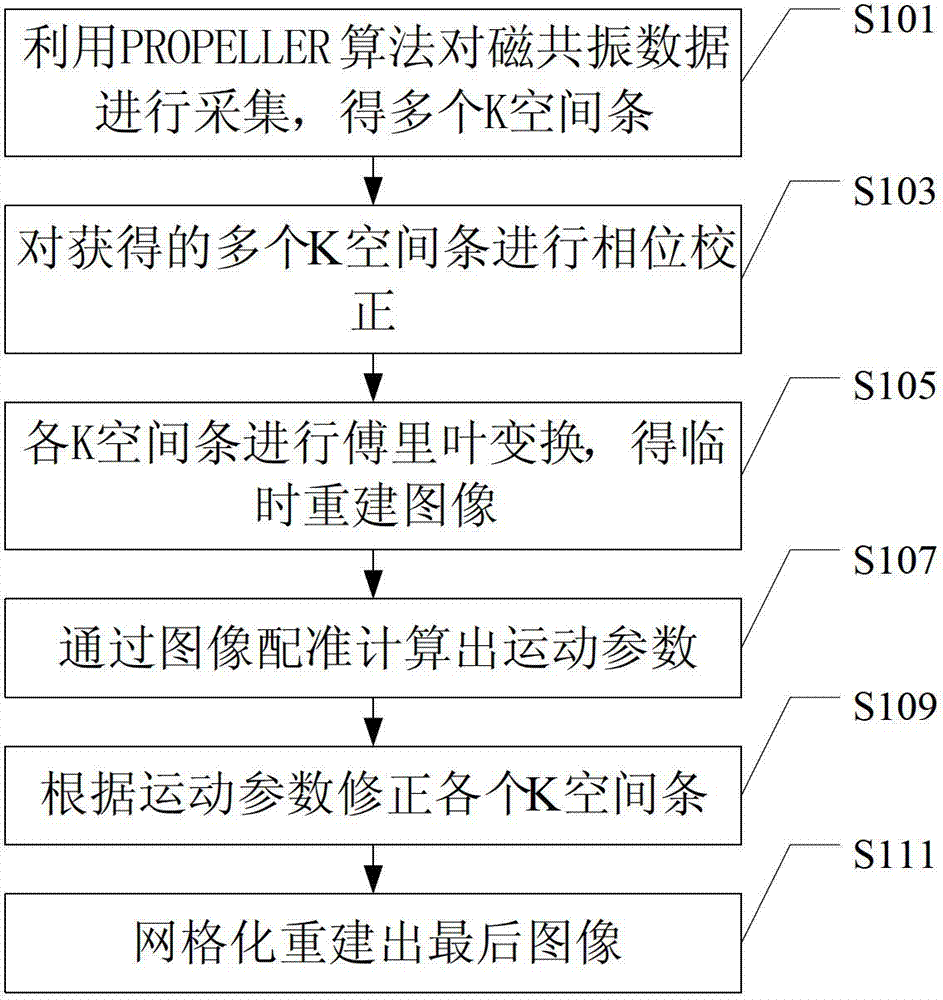
[0015] Such as figure 1 As shown, the magnetic resonance imaging method of this embodiment includes the following steps S101~S111:
[0016] Step S101, the data collection step, using the PROPELLER algorithm to collect magnetic resonance data to obtain multiple K-space strips;
[0017] K space refers to the frequency data space composed of magnetic resonance data collected after phase encoding and frequency encoding, that is, the frequency space composed of magnetic resonance sampling data, that is, the frequency domain space corresponding to the magnetic resonance image.
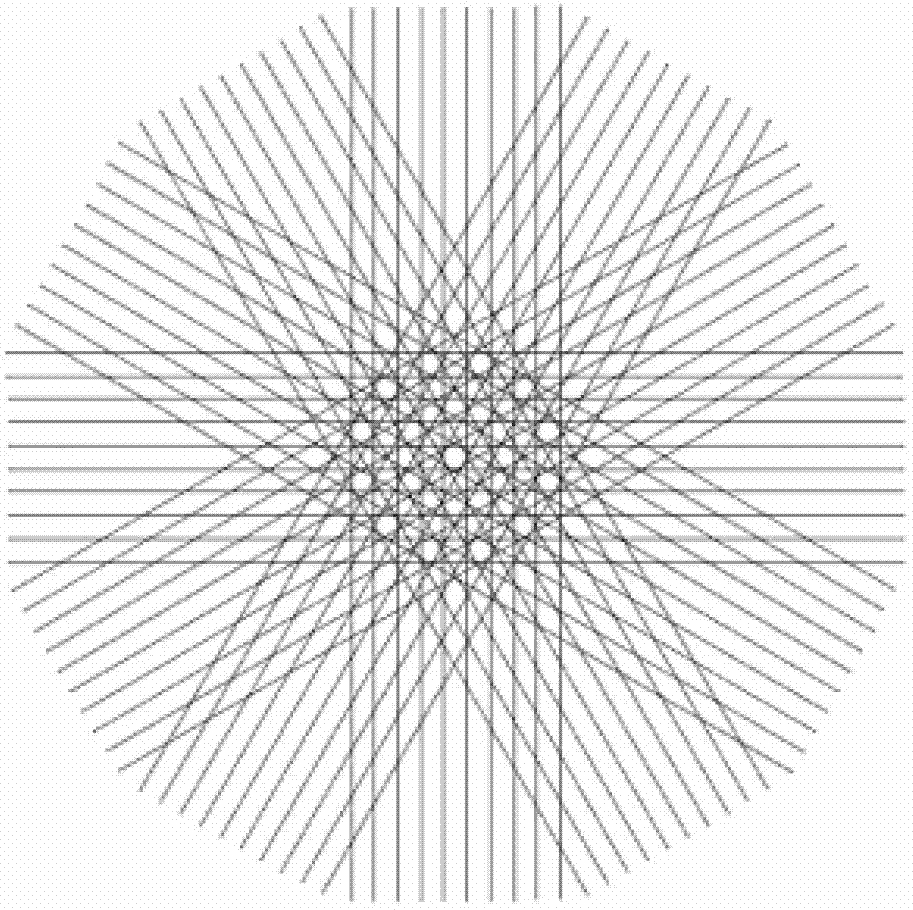
[0018] The magnetic resonance data can be sampled by the commonly used PROPELLER algorithm. For example, firstly, a group of K-space lines near the center of K-space is collected by conventional methods such as FSE (fast spin echo) sequence, single-shot echo-planar sequence, etc., assuming For L strips, a K-space strip is obtained, and then the data of the next K-space strip is collected in the same way eve...
Embodiment 2
[0060] Such as Figure 4 As shown, the magnetic resonance imaging method of this embodiment includes steps S401~S411, wherein steps S401, S403, S405, S407, S409, and S411 are similar to steps S101, S103, S105, S107, S109, and S111 of Embodiment 1, respectively, No longer. The difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 is that step S406 is added after step S405 and before step S407 to filter the temporarily reconstructed image.
[0061] Due to the lack of many high-frequency signals, the image reconstructed in step S405 is generally blurred, and because the phase encoding direction is truncated, the image has obvious Gibbs artifacts, so it is necessary to further filter the image (that is, step S406 ). In this embodiment, a two-dimensional Gaussian window function is used for filtering, and the formula is as follows:
[0062] G ( k x , k y ...
Embodiment 3
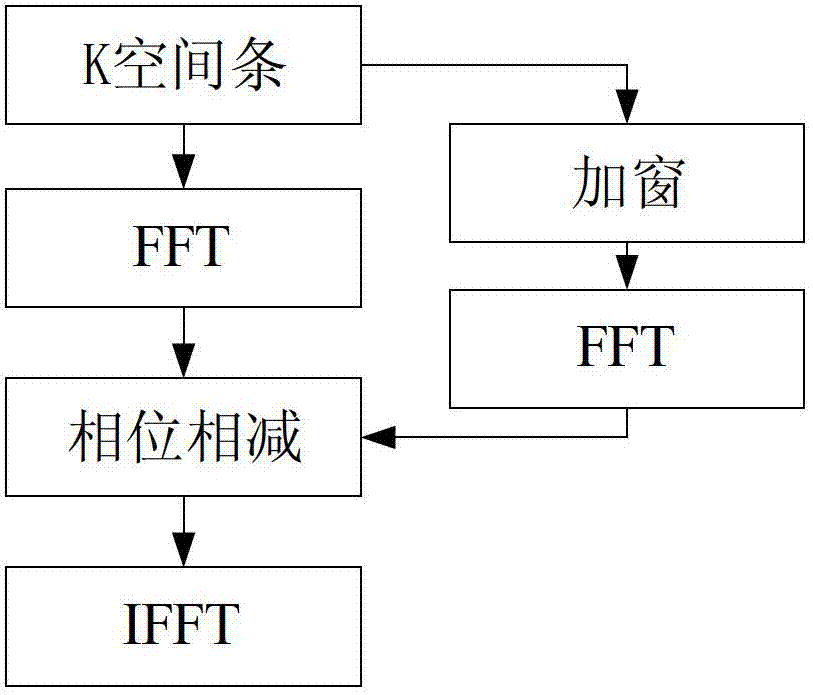
[0066] Such as image 3 As shown, this embodiment proposes a magnetic resonance imaging device corresponding to the magnetic resonance imaging method of embodiment 1 or embodiment 2, including:
[0067] The data collection module is used to collect the magnetic resonance data by using the PROPELLER algorithm to obtain a plurality of K-space bars;
[0068] A phase correction module, configured to perform phase correction on the obtained multiple K-space strips, so that the center position of each K-space strip coincides with the center of K-space;
[0069] The temporary reconstruction module is used to perform Fourier transform on the corrected K-space strips to obtain temporary reconstructed images respectively corresponding to each K-space strip; or, the temporary reconstruction module is used to perform Fourier transform to obtain temporary reconstructed images respectively corresponding to each K-space strip, and also to filter the temporary reconstructed image after obtai...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com