Detection method of erosion depth of free so42- ions on concrete surface
A technology of concrete surface and erosion depth, which is applied in the direction of material analysis by observing the influence of chemical indicators, and analysis by chemical reaction of materials, etc., can solve problems such as difficulty in accurately observing and judging erosion depth, and achieve convenient judgment. Accurate, color rendering effect is obvious, the effect of accelerating the reaction
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
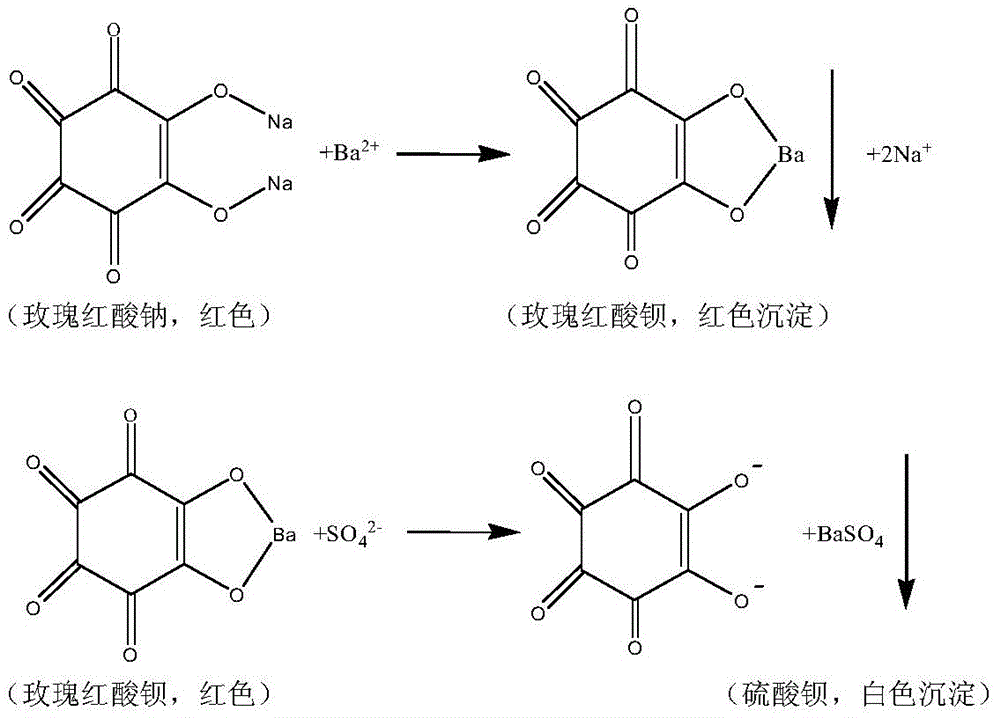
[0017] PO42.5 ordinary Portland cement 450g; standard sand 1350g; water 225g. The water-cement ratio is 0.5. After mixing cement and standard sand evenly, add water and stir, pour into a mold of 40mm×40mm×160mm, and standardize for 28 days. Then the mass fraction is transferred to 5%Na 2 SO 4 After soaking in the solution, the mortar test block was taken out after 28 days, and the concrete test block was split mechanically to obtain a fresh flat section (100mm×100mm). Immerse the fresh section of concrete into the fresh suspension solution of barium roseate, and keep it in an incubator at 60°C for 1 hour. Use a straightedge to measure the distance between the boundary line of the concrete section color (dark red and white) and the edge of the test block to be 3.0mm.
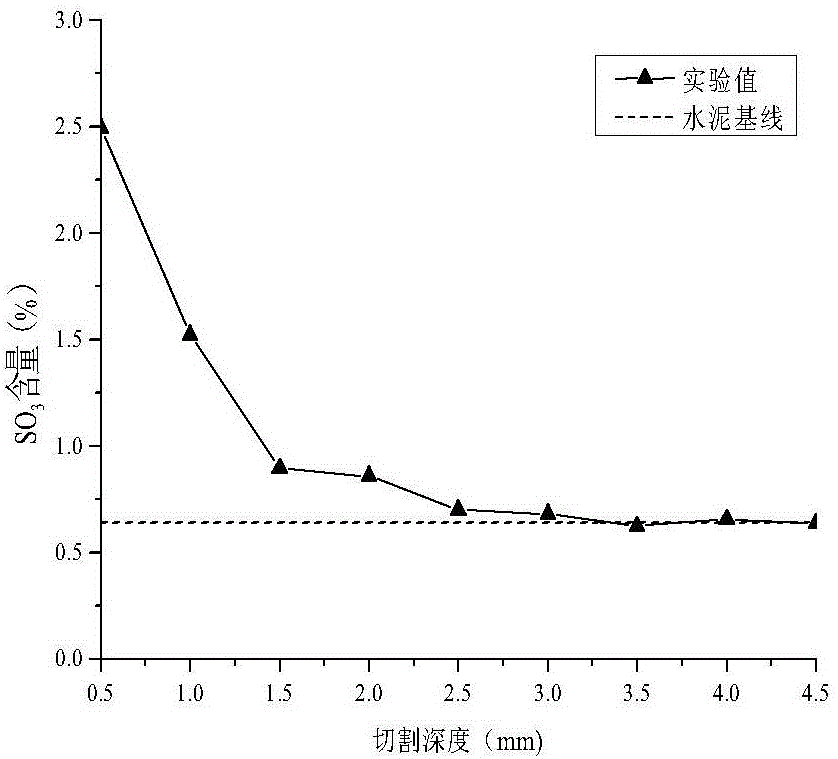
[0018] The cement mortar with the above mix ratio was soaked for 28 days and then tested for SO by conventional methods. 4 2- Penetration depth, grind and cut the cement mortar from the eroded surface to th...
Embodiment 2
[0020] PO42.5 ordinary portland cement 2.19kg; sand 2.84kg; gravel 5.76kg; water 0.96kg. The water-cement ratio is 0.44. Mix cement: sand: gravel evenly, add water and stir, pour into a mold of 100mm×100mm×400mm, after standard curing for 28 days, then add 5% Na 2 SO 4 Soak in the solution. Take it out after 90 days, and mechanically split the concrete to produce a fresh flat section (100mm×100mm). Immerse the fresh section of concrete into the fresh suspension solution of barium roseate, and keep it warm in an incubator at 55°C for 1.5h. Use a ruler to measure the distance between the boundary line of the concrete section color (dark red and white) and the edge of the test block to be 11.3mm, which is the SO value of the sample to be tested. 4 2- The ion penetration depth is 11.3mm.
Embodiment 3
[0022] PO42.5 ordinary portland cement 2.19kg; sand 2.84kg; gravel 5.76kg; water 0.96kg. The water-cement ratio is 0.44. Mix cement: sand: gravel evenly, add water and stir, cast in a mold of 100mm×100mm×400mm, and put in 5% Na 2 SO 4 Soak in the solution, take it out after 180 days, and mechanically split the concrete to produce a fresh flat section (100mm×100mm). Immerse the fresh section of concrete into the fresh barium roseate suspension solution, and keep it warm in an incubator at 50°C for 2 hours. Use a straightedge to measure the distance between the boundary line of the concrete section color (dark red and white) and the edge of the test block, and free SO in the concrete can be detected 4 2- Erosion depth, its depth detection is 21.0mm.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com