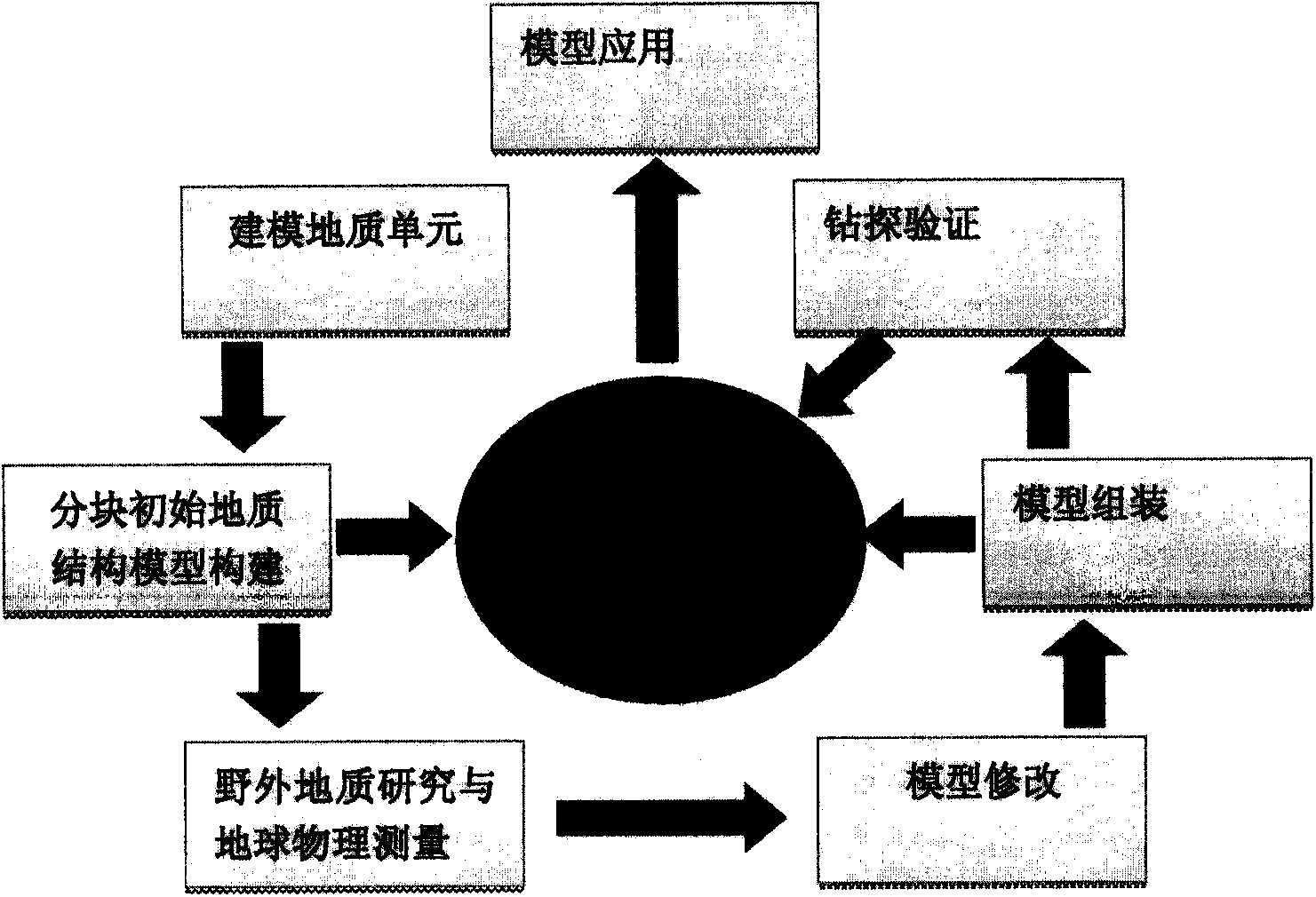
[0004] The block-by-unit three-dimensional geological survey method is characterized in that: it includes the following steps: step (1): modeling geological units, taking faults, rock
mass boundaries and
unconformity boundaries as boundaries, and dividing the stratum distribution area in the study area into one A series of geological units, taking faults and rock masses as separate geological objects, conducting comprehensive geological and geophysical research on these geological units and geological objects, compiling
geological section maps, revealing deep geological structures, and constructing three-dimensional
geological structure models. Modeling geological units are The fault and the rock
mass boundary are used as the boundary of the building block. A building block is a closed area enclosed by the fault and the rock
mass boundary. As long as there is a closed area enclosed by the fault and the rock mass boundary, it is divided into a building block. According to The overall trend of each building block stratum is designed to
cut the direction of the graph
cut section. The graph
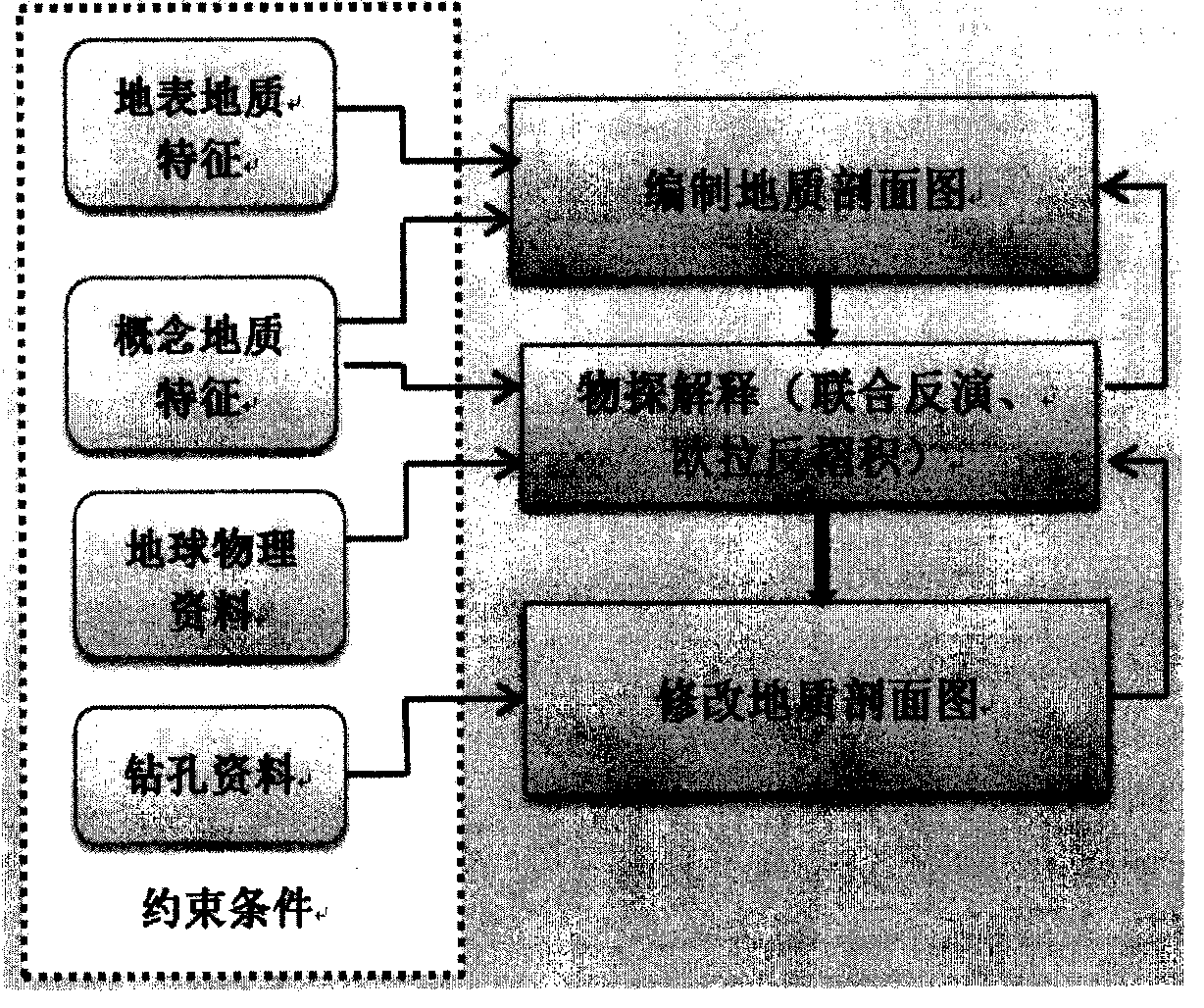
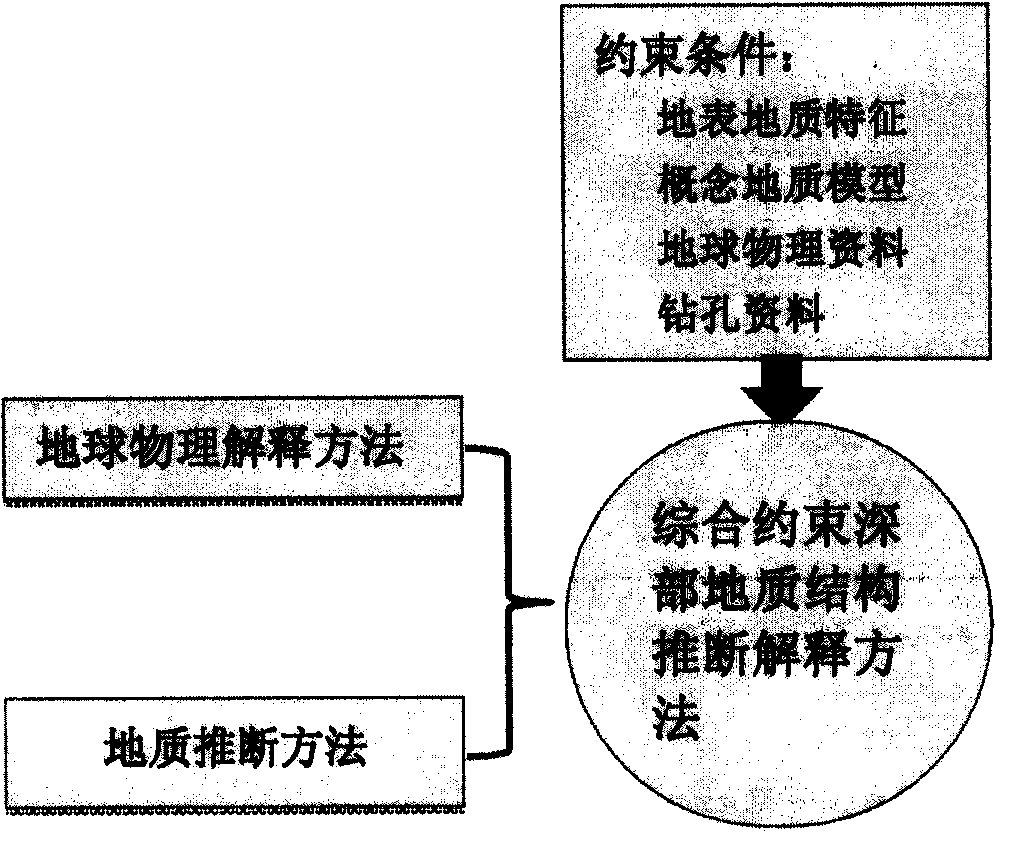
cut section is designed as a series of parallel sections or sections that change with the stratum trend. The sections cannot intersect. The distance between sections depends on the geological complexity. The distance between sections in areas with complex boundary changes should be reduced, and the distance between sections should be increased in areas with low geological complexity. The first section and the last section of a building block control the scope of the building block. Geological sections can be divided into main sections , connecting section and constrained section, the main section is a section perpendicular to the structural line, used to build a 3D geological model, the connecting section is a section parallel to the structural line, used to establish the relationship between the main sections, and the constrained section refers to the section that needs to be carried out The
geophysical inversion section is used to constrain the
geological section in the building block. In one building block, select several sections in the main part of the structure for
geophysical inversion, and constrain the
subsurface geology inferred from the regional geological data. According to the
geophysical inversion results, the cut section of the map is appropriately modified; step (2): the block initial geological structure model is constructed, and on the basis of fully collecting the regional geological, drilling, and geophysical data of the building blocks, combined with Based on the regional geological data and related research results, on the basis of the graph-cut section, the initial geological model of the block is constructed using the block-by-block three-dimensional geological modeling method, and the uncertain factors in the modeling process are found out; step (3): field Geological research and geophysical measurement, aiming at the key geological problems and target geological bodies in the study area, as well as the uncertain parameters existing in the process of building the initial geological structure model of the building module, arrange the whole area or local geological and geophysical sections, for constrained three-dimensional The geological model provides new data. According to the situation that the stratum occurrence cannot be determined during the initial
model building process, the
occurrence data is supplemented in the field geological work.
Surface structure research is the basis for deep geological
inference. If the initial model construction process cannot To determine the
structural deformation characteristics of the building block, it is necessary to carry out geological observation of the
route or measure the necessary geological sections, lay the foundation for deep geological
inference, conduct geophysical exploration of important deep geological structures, and comprehensively determine the deep geological structure with geological and geophysical data; steps (4):
Model modification. On the basis of the obtained geological and geophysical data and under the constraints of various data, carry out in-depth comprehensive geological and geophysical research, modify and improve the initial geological model; step (5): model Assemble, assemble and integrate the completed building blocks or geological object models according to a unified three-dimensional space coordinate
system, edit and modify the spatial intersection relationship between geological objects, and form a three-dimensional geological structure model of the research area; step (6): Drilling
verification, laying out boreholes, verifying the reliability of the model, and providing data for the further improvement of the model; step (7):
model application research, on the basis of the constructed 3D geological model of the research area, put forward the key geological model of the research area. Views and understanding of the problem, and summarize the three-dimensional
spatial distribution of mineral resources in the study area
 Login to View More
Login to View More  Login to View More
Login to View More