Real-time camera tracking method for dynamically-changed scene
A dynamic change, camera technology, applied in image analysis, image communication, image data processing, etc., can solve the problems of camera tracking, loss of invariant features of SIFT feature points, inability to accurately estimate camera parameters, etc. The effect of accuracy
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
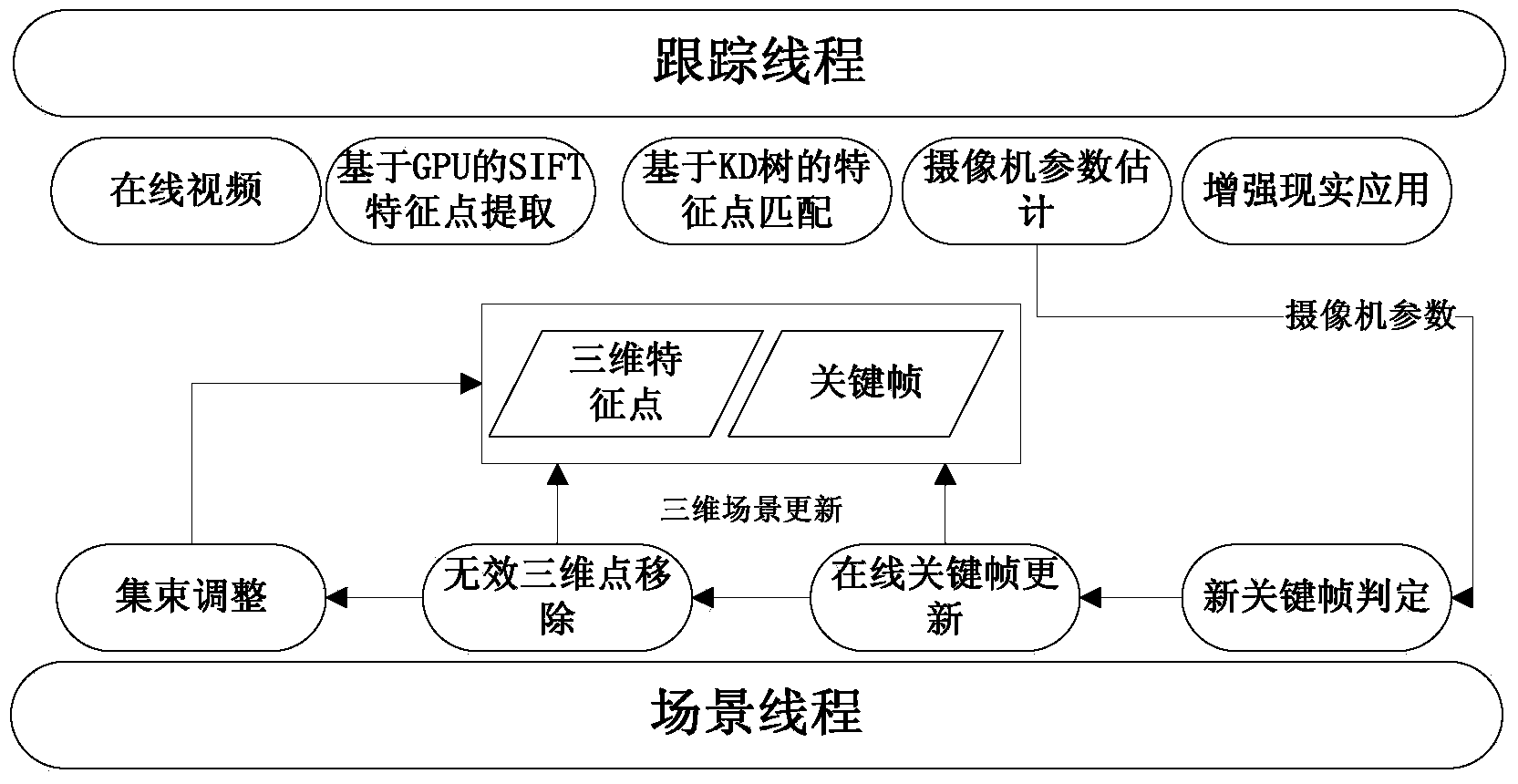
[0057] For a set of continuously changing video sequences (such as figure 2 (a), figure 2 (a), Figure 4 (a), Figure 5 (a)), the arrangement and position of the objects on the table in the scene in the video sequence have changed significantly, and the method proposed in this patent is used to estimate the camera parameters.
[0058] Such as figure 1 As shown, the implementation steps are as follows:
[0059] 1. Feature point matching and camera parameter estimation. Use SIFT feature description to express scene features, each scene point corresponds to a feature description, use KD tree to organize all scene features, use GPU to extract SIFT feature points for each frame of image and search for feature matching in KD tree, and then perform camera parameters The estimation of , including the following steps:
[0060] 1.1. Use SIFT feature description (David G.Lowe: Distinctive Image Features from Scale-Invariant Keypoints. International Journal of Computer Vision60 (2...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com