A Phantom Grounding Identification Method of Distribution Network Based on the Distance Between Adjacent Points on the Plane Constructed by Zero-sequence Voltage Adjacent Sub-differences
A technology of zero-sequence voltage and phantom grounding, which is applied in the direction of measuring electricity, measuring electrical variables, measuring devices, etc., can solve the problems of long time window, unfavorable discovery, etc., and achieve the effect of easy realization and simple calculation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
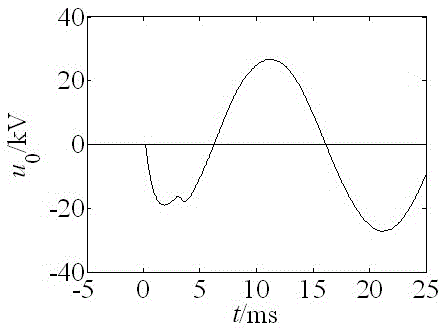
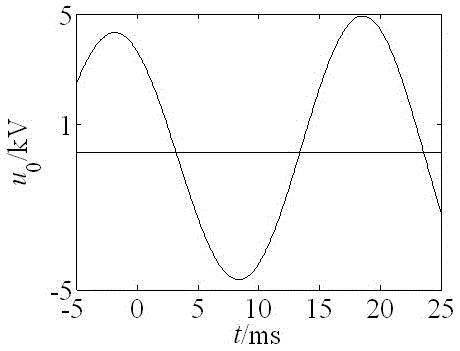
[0043] Embodiment 1: A distribution network phantom grounding identification method based on the distance between adjacent points on the plane formed by the adjacent sub-differences of the zero-sequence voltage. Calculate the first-order difference and second-order difference of the zero-sequence voltage data of the distribution network bus in the short time window after the phantom grounding, use the first-order difference and second-order difference to construct a plane, and calculate the adjacent points on the plane The sum of squares of the distances is used to distinguish phantom grounding and single-phase grounding faults according to the sum of squares of distances between adjacent points.
[0044] The specific steps of the method are as follows:
[0045] (1) After a single-phase ground fault or phantom ground occurs in the distribution network line, the line selection device starts immediately and records the wave, and records the zero-sequence voltage of the bus;
[...
Embodiment 2
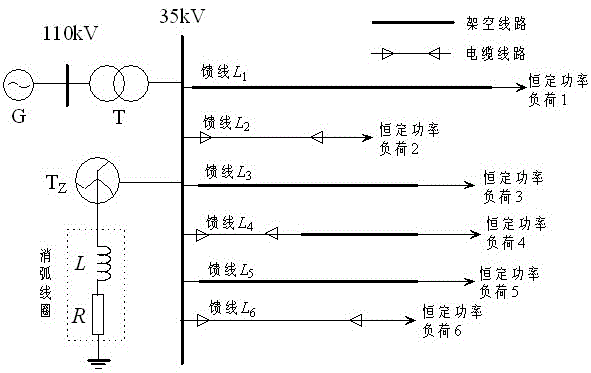
[0058] Embodiment 2: as figure 1 The shown 110kV / 35kV neutral point is grounded through the arc suppressing coil single-phase ground fault simulation model of the distribution network system. It has 6 feeders, and the neutral point of the Z-shaped transformer is grounded through the arc suppressing coil in series with resistance. Overhead feeder L 1 =15km,L 3 =18km, L 5 = 30km, wire-cable hybrid feeder L 4 =17km, the overhead feeder is 12km, the cable is 5km, and the cable feeder is L 2 = 6km, L 6 = 8km. Among them, the overhead feeder is JS1 rod type, LGJ-70 type conductor, the span is 80m, and the cable feeder is YJV23-35 / 95 type cable. G in the power grid is an infinite power source; T is the main transformer, the transformation ratio is 110kV / 35kV, and the connection group is Y N / d11;T Z Is a zigzag transformer; L is the arc suppression coil; R is the damping resistance of the arc suppression coil. The feeder adopts three types of lines: overhead line, overhead l...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com