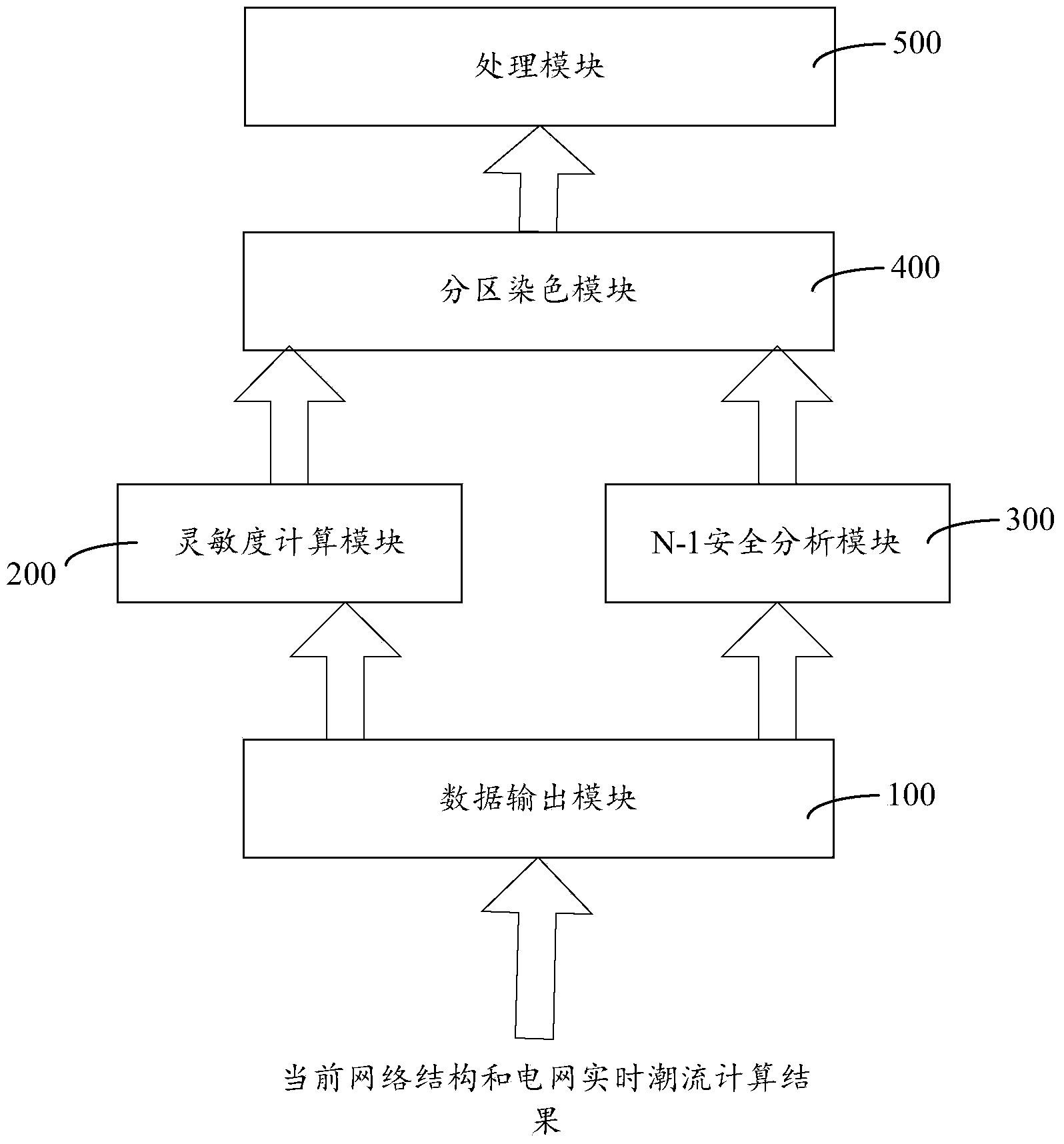
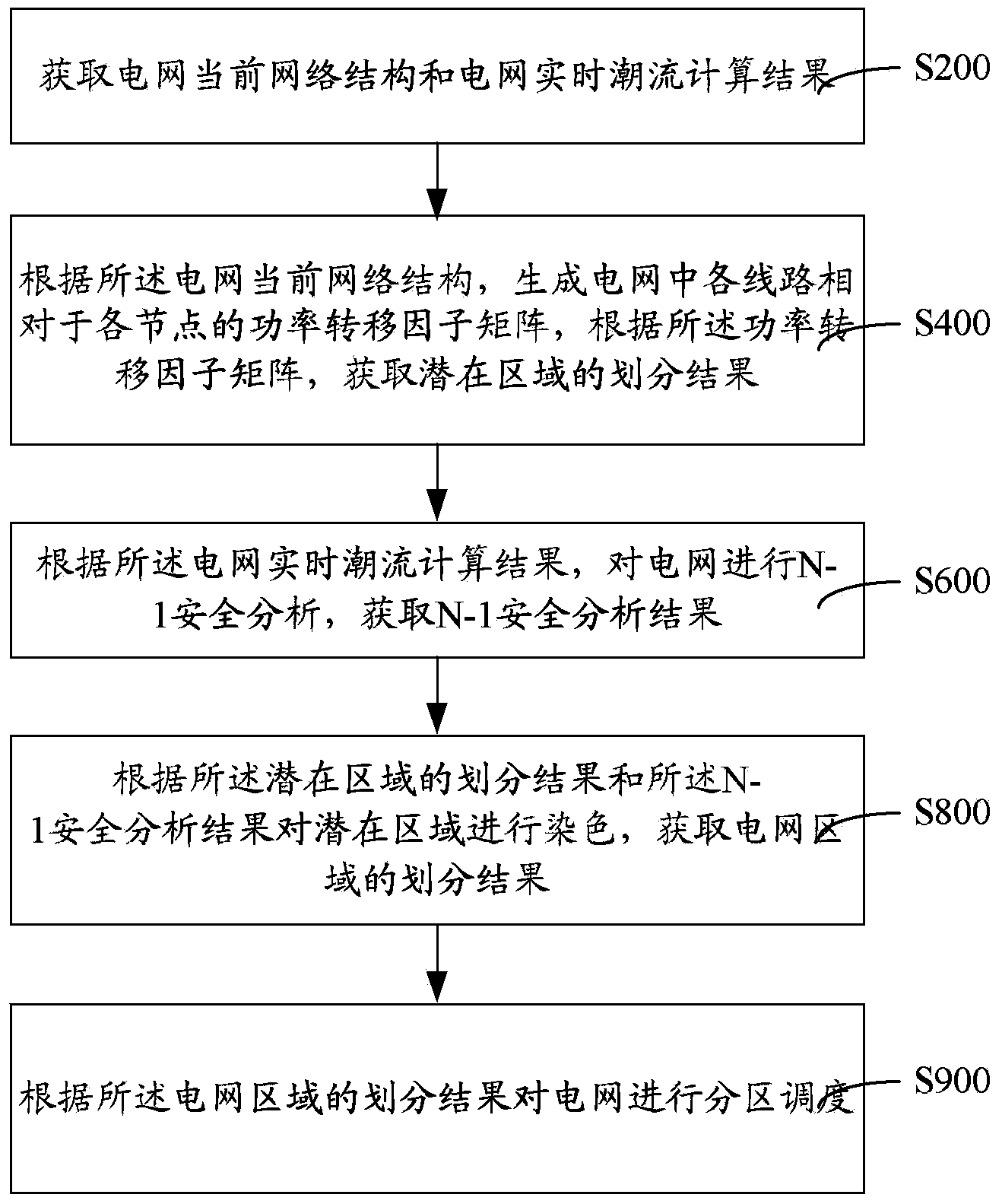
Power grid partition scheduling device and partitioning method and system thereof
A technology of power grid partitioning and scheduling method, which is applied in the field of power grid to achieve strong adaptability and good overall effect.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0088] like Image 6 As shown, the power grid system to be evaluated is divided into 39 potential zones after sensitivity calculation and analysis. When the power grid is in a growing state, the topology structure does not change and there is no N-1 problem, the power grid is not zoned, and each potential zone does not need to be stained and Boundaries are shown in dashed lines.
[0089] like Figure 7 As shown, when a tripping fault occurs in one of the double-circuit tie lines between 500kV substation A and 500kV substation B, the grid topology changes, and the data transmission module transmits the grid topology and real-time power flow calculation results to N. -1 Security Analysis Module. The N-1 safety analysis results show that there is an N-1 problem in the power grid at this time: if another tie line between AB also trips at this time, the tie line between potential area 26 and potential area 39 will have an overload problem. After being dyed by the partition dyein...
Embodiment 2
[0091] like Figure 8 As shown, when an important tie line in the power grid system to be evaluated fails (one of the double-circuit tie lines between 500kV substation E and 500kV substation F trips), the data transmission module will compare the grid topology and real-time power flow at this time. The calculation results are communicated to the N-1 Safety Analysis Module. The N-1 safety analysis results show that there will be serious N-1 problems in the power grid at this time: except for the fault area, although some lines are not geographically connected to the fault area, they are electrically close together, such as potential area 21 and potential area 22. The power flow of the tie line between them increases greatly due to the failure; if another tie line between the substations EF trips at the same time, a large-scale chain accident will occur in the power grid. The partition dyeing module divides the power grid into two areas, I and II, after calculation. The dispatc...
Embodiment 3
[0093] like Figure 9 As shown, one of the two 500kV busbars in the 500kV substation G in the potential division 7 of the power grid system to be evaluated is in the maintenance state, and the station is wired in a 3 / 2 manner. One of the series of tie breakers tripped, causing the 500kV substation to split into 2 500kV nodes. The data transmission module transmits the grid topology structure and real-time power flow calculation results to the N-1 safety analysis module. The N-1 safety analysis results show that when a busbar split occurs in a 500kV substation, the power flow of the tie line between potential area 7 and adjacent potential areas 6 and 8 is very likely to exceed the limit. There is also a high possibility that the flow of the tie line between areas 6 and 11 will exceed the limit. The partition dyeing module divides the power grid into three areas: I, II, and III after calculation. The dispatcher needs to closely monitor and control the flow of key sections betw...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com