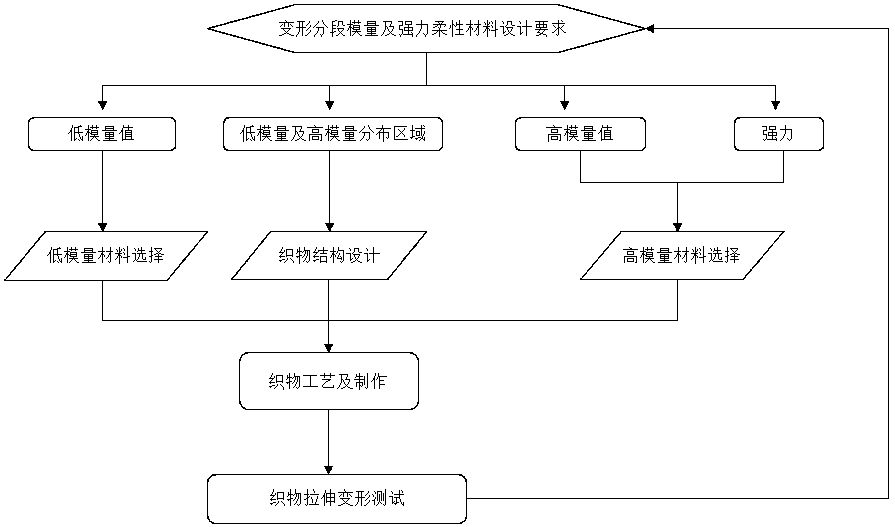
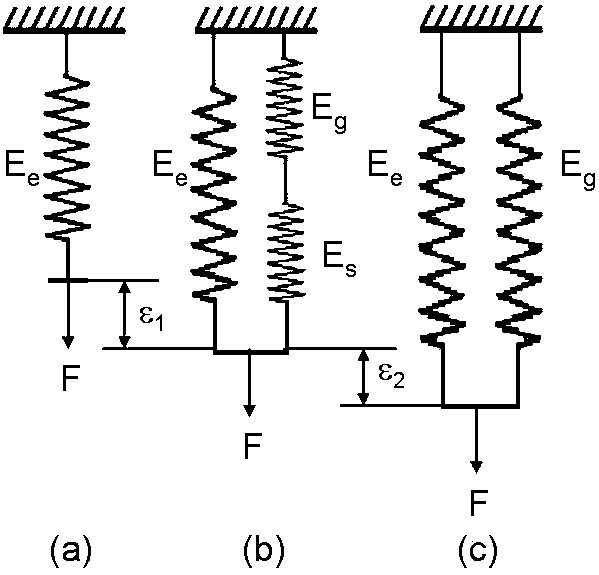
Design principle and manufacturing method of flexible material with segmental deformation modulus and strength
A flexible material and deformation modulus technology, applied in the field of flexible materials, can solve problems such as physical movement injury problems, and achieve the effect of maintaining freedom of movement, low deformation, and preventing injury
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0023] The fabric in this embodiment is woven by knitting double-face weft knitting technology. The low modulus deformation range is set at 70%.
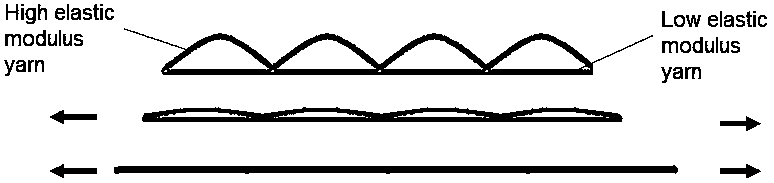
[0024] The fabric structure is a 3-way weaving cycle, and its weaving diagram is as follows Figure 4 shown. First pass: Low modulus yarn is knit in a loop on the upper cylinder needles and in a tuck loop on the lower cylinder knitting needles. Second pass: High modulus yarns are knitted in loops only on the lower cylinder needles. Third way: Low modulus yarn is knitted in loops on the upper dial needles only. The relationship between the external force and the deformation required for its deformation The tension / load curve is as follows Figure 7 shown. From Figure 7 We can get the low modulus area of the fabric in the 0%-50% stretch area, the 50%-70% stretch area is the structural conversion area, and the stretch area above 70% is the high modulus area. The tensile force required for tensile deformation increases very sl...
example 2
[0026] In order to further demonstrate that the deformation range of the low modulus area can be controlled, the same high and low modulus materials as in Example 1 are used, and the fabric in this example is woven by knitting double-sided weft knitting technology to form Example 2.
[0027] The fabric structure is a 7-way weaving cycle, and its weaving diagram is as follows Figure five . First pass: Low modulus yarn is knit in a loop on the upper cylinder needles and in a tuck loop on the lower cylinder knitting needles. Second pass: High modulus yarns are knitted in loops only on the lower cylinder needles. Third way: Low modulus yarn is knitted in loops on the upper dial needles only. The fourth way: the high modulus yarn weaving method is the same as the second way. The fifth way: the low modulus yarn is knit in a circle on the upper needle disc, and in a tuck on the lower cylinder knitting needle. Sixth way: High modulus yarns are knitted in loops only on the lower c...
example 3
[0030] Continue to design a larger range of low modulus variation, using the same high and low modulus materials as in Example 1, the fabric in this embodiment is woven by knitting double-sided weft knitting technology
[0031] The fabric structure is a 4-way weaving cycle, and its weaving diagram is as follows image 3 . First pass: Low modulus yarn is knit in a loop on the upper cylinder needles and in a tuck loop on the lower cylinder knitting needles. Second pass: High modulus yarns are knitted in loops only on the lower cylinder needles. Third way: Low modulus yarn is knitted in loops on the upper dial needles only. The fourth way: the high modulus yarn weaving method is the same as the second way. Tensile force changes are measured as Figure 9 The low modulus area shown is increased to 150%.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com