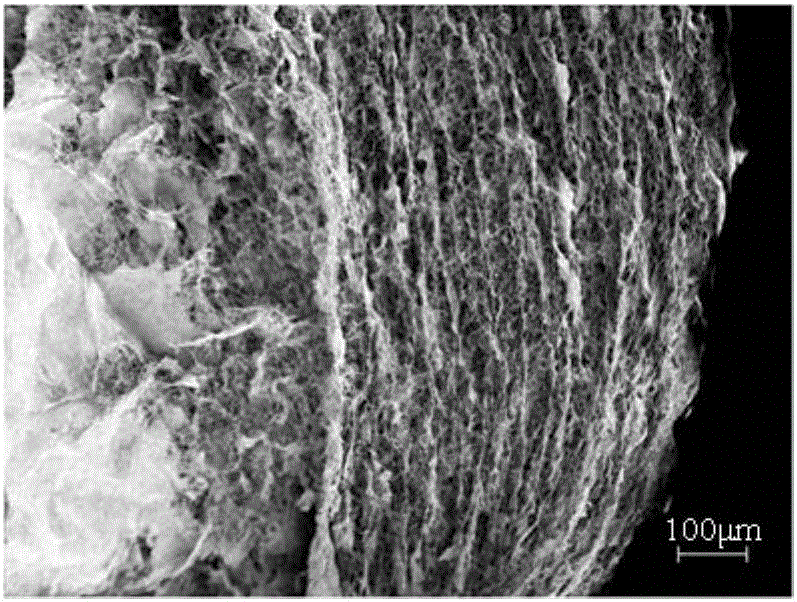
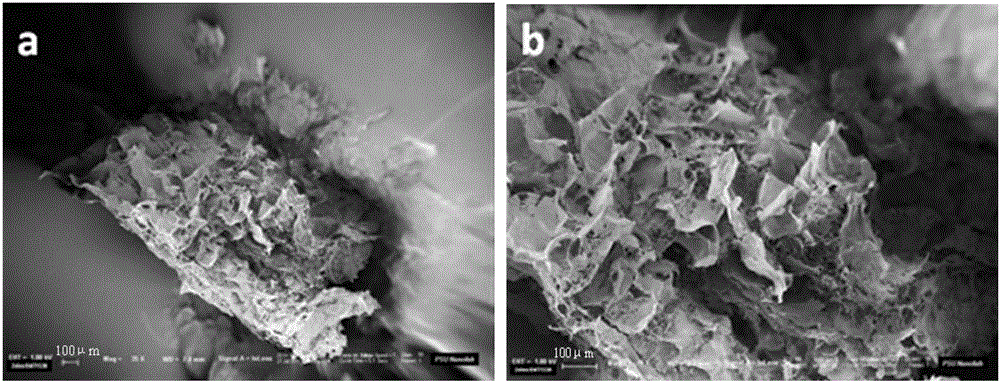
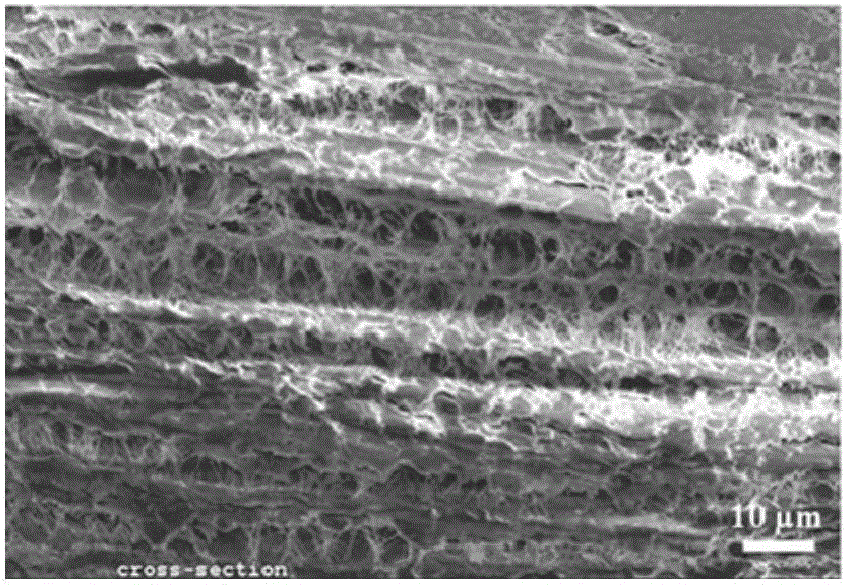
A method for reducing the crystallinity of bacterial cellulose during fermentation
A technology for bacterial cellulose and fermentation process, applied in microorganism-based methods, fermentation, biochemical equipment and methods, etc., can solve problems such as cost increase, impact on cellulose mechanical properties, cellulose molecular weight loss, etc. Good control effect, simple and fast effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0039] A method for reducing the crystallinity of bacterial cellulose in a fermentation process, comprising the following steps:
[0040] (1) Prepare the culture medium, the composition of the culture medium is: 0.2g / mL glucose, 0.02g / mL peptone, 0.02g / mL yeast powder, 0.005g / mL disodium hydrogen phosphate, 0.001g / mL magnesium sulfate, 0.01g / mL ammonium sulfate, 0.005mL / mL corn syrup extract;
[0041] (2) Inoculate 1 mL of Acetobacter xylinum with the preservation number ATCC700178 into 100 mL of the above-mentioned culture solution; filter and sterilize the fluorescent whitening agent through a 25 μm filter membrane, and then add 0.01 mL of fluorescent whitening agent to the culture solution The agent Fluka18909 (purchased from Simga) was rotated and fermented at 125rpm for 120h. After the fermentation, the culture solution was poured out and the generated cellulose was rinsed with deionized water until no residue of the culture solution remained. After steam sterilization, t...
Embodiment 2
[0043]A method for reducing the crystallinity of bacterial cellulose in a fermentation process, comprising the following steps:
[0044] (1) Prepare the culture medium, the composition of the culture medium is: 0.2g / mL glucose, 0.02g / mL peptone, 0.02g / mL yeast powder, 0.005g / mL disodium hydrogen phosphate, 0.001g / mL magnesium sulfate, 0.01g / mL ammonium sulfate, 0.005mL / mL corn syrup extract;
[0045] (2) Inoculate 1mL of Acetobacter xylinum with preservation number ATCC700178 into 100mL of the above-mentioned culture solution; filter and sterilize the fluorescent whitening agent through a 25μm filter membrane, and then add 1mL of fluorescent whitening agent to the culture solution Fluka18909 (purchased from Simga), rotated and fermented at 125rpm for 120h. After the fermentation, pour out the culture solution and rinse the generated cellulose with deionized water until no residual solution of the culture solution remained. After steam sterilization, bacterial fibers were obtai...
Embodiment 3
[0050] A method for reducing the crystallinity of bacterial cellulose in a fermentation process, comprising the following steps:
[0051] (1) Prepare the culture medium, the composition of the culture medium is: 0.2g / mL glucose, 0.02g / mL peptone, 0.02g / mL yeast powder, 0.005g / mL disodium hydrogen phosphate, 0.001g / mL magnesium sulfate, 0.01g / mL ammonium sulfate, 0.005mL / mL corn syrup extract;
[0052] (2) Inoculate 1mL of Acetobacter xylinum solution with preservation number ATCC700178 into 100mL of the above culture solution; filter and sterilize the fluorescent whitening agent through a 25μm filter membrane, and then add 1mL of fluorescent whitening agent Fluka18909 to the culture solution (purchased from Simga), cultured and fermented statically at 28°C for 120 hours. After the fermentation, pour out the culture solution and rinse the generated cellulose with deionized water until no residual solution of the culture solution remained. After steam sterilization, bacteria wer...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com