Solution polymerization method of polyvinylidene fluoride copolymer
A polyvinylidene fluoride and polymerization method technology, applied in the polymer field, can solve the problems of affecting the thermal stability of the polymer, increasing the complexity of the process, and being expensive, and achieving low production cost, good processing performance, and less environmental pollution. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
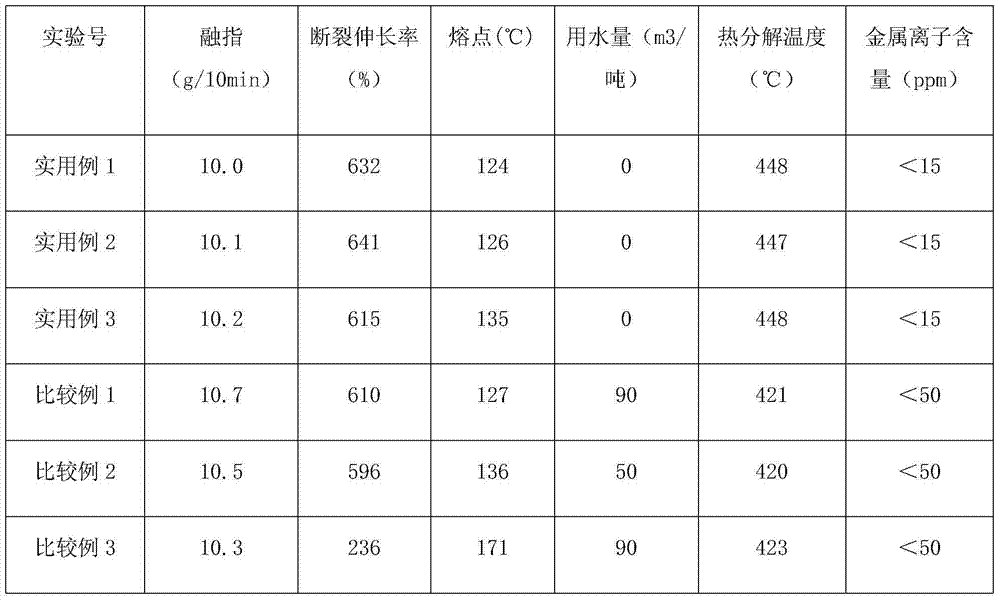
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0024] Taking a 5L polymerization kettle as an example, after evacuating and removing oxygen, after the oxygen content is qualified, the reactor is cooled to 0°C, and 15kg of initial monomer mixture is added. The initial monomer mixture is hexafluoropropylene and vinylidene fluoride with a molar ratio of 1:5 mixing, heat the reactor to 50°C, at this time the pressure is 0.9±0.1MPa, add 300g of 1.0wt% peroxydicarbonate bis(3-methoxybutyl) initiator and 5g of acetone. Reaction starts, add to reactor and add monomer mixture, keep pressure constant, when adding 250g to add monomer mixture, add 5g molecular weight regulator acetone again, stop the heating of reactor when adding 500g to add monomer mixture, Stop adding the monomer mixture, stop stirring, cool the reaction material to 10°C, collect the unreacted monomer into the recovery tank for subsequent copolymerization, and add the monomer mixture of hexafluoropropylene and vinylidene fluoride to massage The mixing ratio is 1:6....
Embodiment 2
[0026] Taking a 5L polymerization kettle as an example, after evacuating and removing oxygen, after the oxygen content is qualified, the reactor is cooled to 10°C, and 15kg of initial monomer mixture is added. The initial monomer mixture is hexafluoropropylene and vinylidene fluoride with a molar ratio of 1:3 mixing, heat the reactor to 55°C, at this time the pressure is 1.0±0.1Mpa, add 300g of 1.0wt% bis(3-methoxybutyl) peroxydicarbonate initiator and 5g of ethyl propionate ester. Reaction starts, add additional monomer mixture to the reactor, keep the pressure constant, when adding 250g additional monomer mixture, add 5g molecular weight modifier ethyl propionate again, after adding 500g additional monomer mixture, stop the reaction Heating of the reactor, stop adding the monomer mixture, stop stirring, cool the reaction material to 30°C, collect the unreacted monomer into the recovery tank for subsequent copolymerization, and add the monomer mixture as hexafluoropropylene a...
Embodiment 3
[0028] Take a 5L polymerization kettle as an example. After evacuating and removing oxygen, after the oxygen content is qualified, the reactor is cooled to 5°C, and 15kg of initial monomer mixture is added. The initial monomer mixture is hexafluoropropylene and vinylidene fluoride. The molar ratio is 1:1.5 mixing, heat the reactor to 60°C, at this time the pressure is 1.1±0.1Mpa, add 300g of 1.0wt% azobisisobutyronitrile initiator and 5g of acetone. Reaction starts, add to reactor and add monomer mixture, keep pressure constant, when adding 250g to add monomer mixture, add 5g molecular weight regulator acetone again, stop the heating of reactor when adding 500g to add monomer mixture, Stop adding the monomer mixture, stop stirring, cool the reaction material to 20°C, collect the unreacted monomer into the recovery tank for subsequent copolymerization, and add the monomer mixture of hexafluoropropylene and vinylidene fluoride to massage The mixing ratio is 1:15. Vent, unload t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com