Tunable laser using tunable fabry-perot filter
A Perot filter and tuning laser technology, applied in the field of optoelectronics, can solve the problems of difficulty in implementation, poor resistance to various mechanical vibrations, low tuning accuracy and output bandwidth, etc., to achieve easy installation and production, no mechanical movement. components, to meet the effect of reliable operation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0032] Embodiments of the present invention will be described in further detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings.
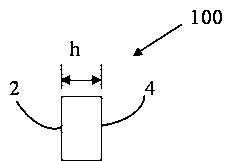
[0033] figure 1 A schematic diagram of a common Fabry-Perot optical etalon 100 is given. The material of the Fabry-Perot optical etalon 100 generally uses optical glass such as fused silica or BK7 in the near-infrared and visible light bands. Assuming that the refractive index of the material is n, the two light-transmitting surfaces 2 and 4 are coated with high The reflective film, whose reflectivity is R, has a thickness of h, and light is incident at an incident angle close to zero, can only pass through the etalon if it satisfies 2nh=mλ, where m is the order of the transmitted light. Free Spectral Range FSR of Optical Etalon 100 1 Can be expressed as: Δλ=λ 2 / (2nh), or in frequency: Δν=c / (2nh), where c is the speed of light. The peak frequency of transmitted light can be expressed as: ν=mc / (2nh), where m is the interference order, and t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com