Method for improving anti-irradiation properties of low activation material by using ion pre-irradiation
A low-activation, pre-irradiation technology, applied in the field of structural steel materials, can solve the problems of complex and uneconomical processes, and achieve the effects of simple process, easy operation, stable size and structure
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0018] 1) The low activation steel model alloy (Fe-10wt%Cr) was mechanically thinned to 100 um, polished and cleaned with acetone.
[0019] 2) Load the sample on the ion accelerator target, close it, and pump the vacuum of the accelerator to 1×10 -6 Pa.
[0020] 3) The implanted ions are D ions, the energy is 58 keV, and the dose is 1×10 17 ions / cm 2 . The temperature was set at 500 °C. The irradiation time is about 10 hours.
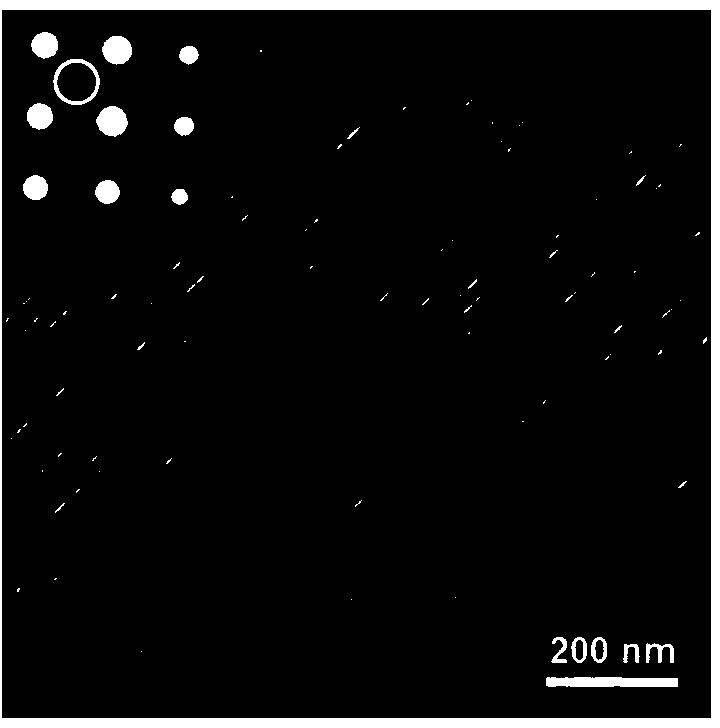
[0021] 4) After the pre-irradiation is completed, a large number of nanoscale precipitates are produced in the alloy, and the size distribution is between 30 and 200 nanometers, as shown in the electron microscope image above. The precipitates remained dimensional and structurally stable during subsequent irradiation.
[0022]
Embodiment 2
[0024] 1) Low activation steel (Fe-9Cr-2W-V-Ta-C-Mn) was mechanically thinned to 100 um, polished and cleaned with acetone.
[0025] 2) Load the sample on the ion accelerator target, close it, and pump the vacuum of the accelerator to 1×10 -6 Pa.
[0026] 3) The implanted ions are H ions, the energy is 100 keV, and the dose is 1.6×10 17 ions / cm 2 . The temperature was set at 500 °C. The irradiation time is about 16 hours (6-24 hours).
[0027] 4) After the pre-irradiation is completed, a large number of nanoscale precipitates are produced in the alloy, and the size distribution is between 30 and 200 nanometers. The precipitates remained dimensional and structurally stable during subsequent irradiation.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com