Tibet hazel agaricus bisporus strains and cultivation method of fruit bodies of Tibet hazel agaricus bisporus strains
A technology of Agaricus bisporus and fruiting bodies, applied in botany equipment and methods, horticulture, application, etc., can solve problems such as unfavorable cultivation and production of Agaricus bisporus, narrow genetic basis, and accelerated degradation of Agaricus bisporus species
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0060] Example 1, the acquisition and classification identification of Hazel Agaricus bisporus 2094 in Tibet
[0061] The strain of the present invention (referred to as 2094) is obtained from fresh specimens of wild mushroom Agaricus bisporus collected from Nyingchi, Tibet Autonomous Region, and obtained through tissue separation, cultivation and domestication. The strain was classified and identified by observing the morphological characteristics of its fruiting bodies and mycelium, combined with nuclear rDNA-ITS sequencing.
[0062] 1. Morphological characteristics
[0063] 1. Morphological characteristics of mycelium
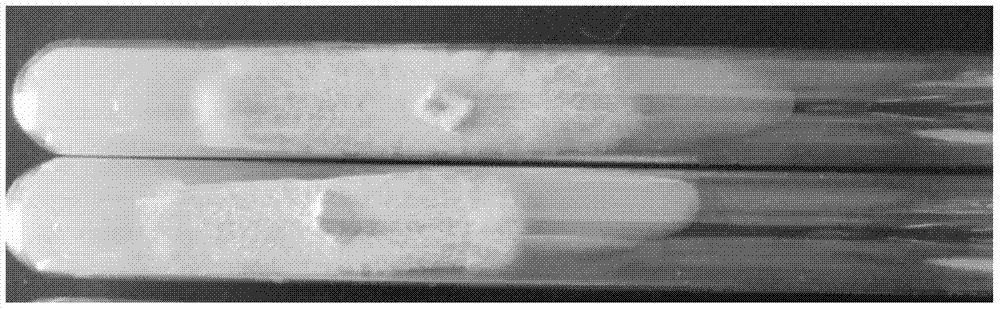
[0064] The hyphae of the bacterial strain 2094 of the present invention are dense and vigorous, white in the early stage, slightly light brown after a period of cultivation. Such as figure 1 , figure 2 shown.
[0065] 2. Morphological characteristics of fruiting bodies
[0066] The fruiting body morphology of bacterial strain 2094 of the present inven...
Embodiment 2
[0071]Example 2. Artificial cultivation of the fruiting bodies of Tibetan Hazel Agaricus bisporus 2094 (CGMCC No.8308)
[0072] 1. Cultivation process
[0073] The cultivation process of Tibetan Hazel Agaricus bisporus 2094 (CGMCC No.8308) is as follows: mother seed preparation → original seed preparation → cultivated seed preparation → inoculation and germination → soil covering → fruiting management → fruiting → harvesting.
[0074] (1) Preparation of the mother species: inoculate the sparse hyphae of Tibetan Hazel Agaricus bisporus 2094 (CGMCC No.8308) obtained from the tissue separation on the mother species medium, and the inoculation amount is 20 cm 2 Mycelium with an area size of 0.2cm×0.2cm is inserted into the surface area of the mother seed medium, cultured at a certain temperature in the dark, until the mycelium is covered with the medium, and the obtained mycelium is used as the mother seed.
[0075] (2) Preparation of original seed: transfer the mother seed obt...
Embodiment 3
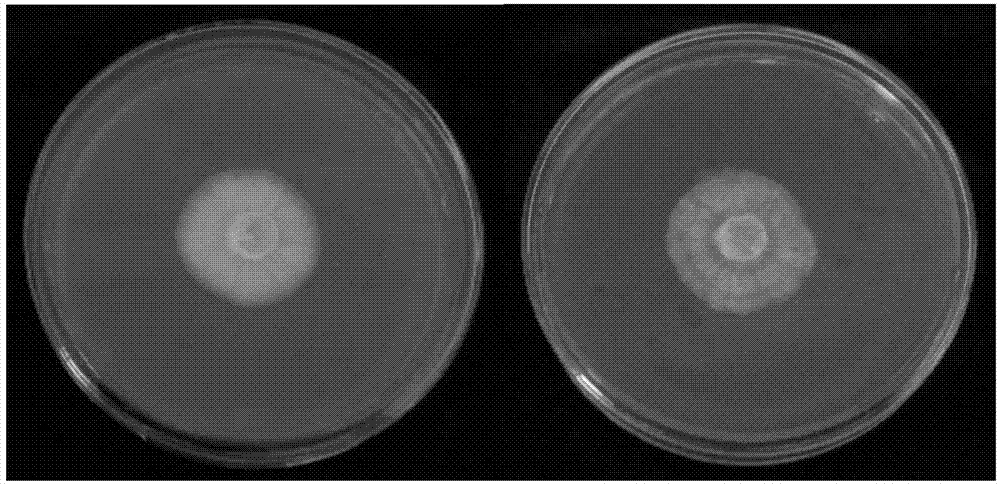
[0157] Example 3. Comparative analysis of Tibetan Hazel Agaricus bisporus 2094 (CGMCC No.8308) and existing As2796
[0158] In this example, from the three aspects of the basic traits of the strain, the nutritional components of the fruiting body, and the antioxidant capacity of the ethanol extract of the fruiting body, the Tibetan Hazel Agaricus bisporus 2094 (CGMCC No.8308) and the existing cultivars provided by the present invention are compared. Agaricus bisporus As2796 was comparatively analyzed.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com