Method and apparatus for printing two-dimensional code by use of 9-pin printer in embedded system
An embedded system and needle printer technology, which is applied in the field of two-dimensional code printing, can solve the problems of low printing resolution, large area of two-dimensional code, and unable to save the printed content for a long time, and achieve the effect of high reading rate
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
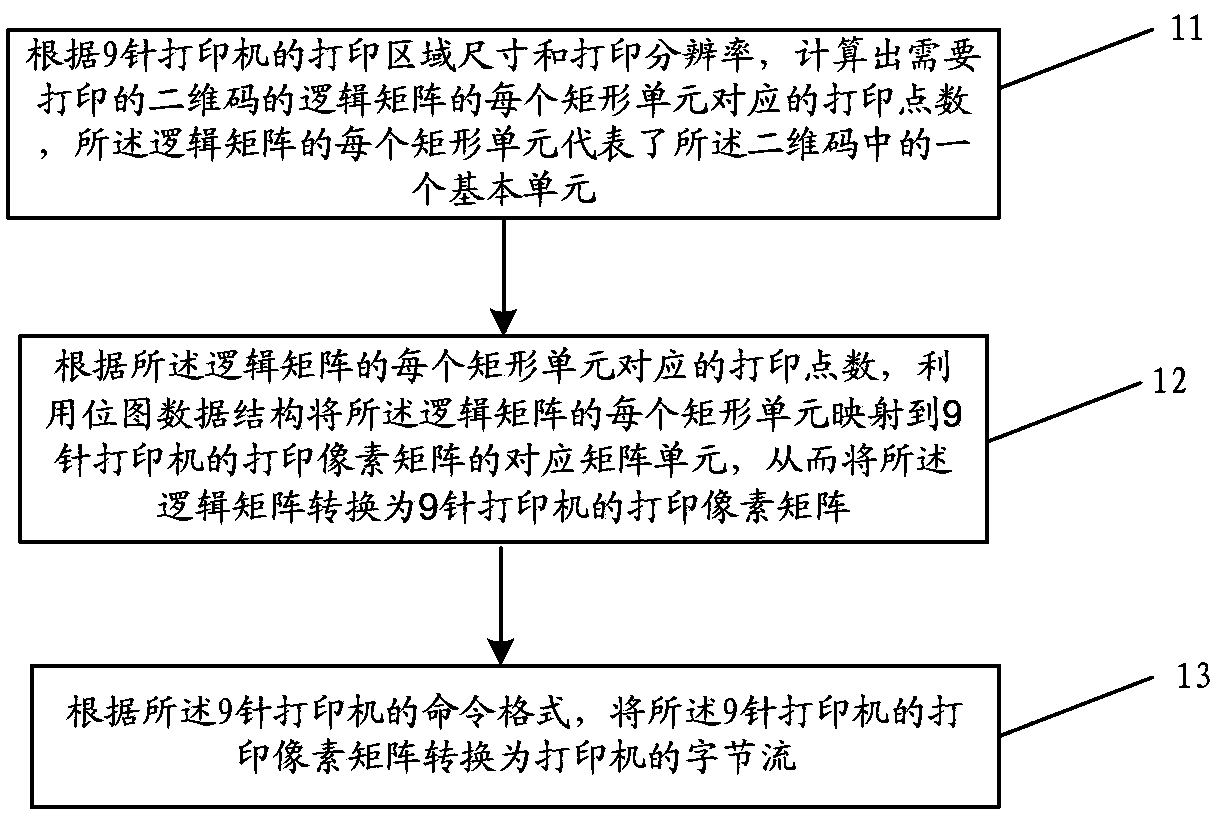
[0020] A schematic diagram of the processing flow of a method for printing a two-dimensional code using a 9-pin printer in an embedded system provided by this embodiment is as follows figure 1 As shown, the following processing steps are included:
[0021] Step 11, according to the printing area size and printing resolution of the 9-pin printer, calculate the number of printing points corresponding to each rectangular unit of the logical matrix of the two-dimensional code to be printed, and each rectangular unit of the logical matrix represents the A basic unit in a QR code.
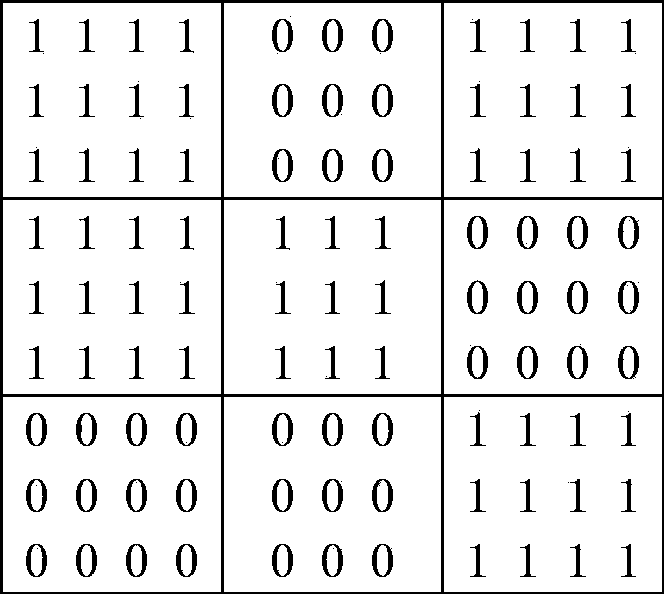
[0022] For a rectangular two-dimensional code, the generation algorithm provides an M*N logic matrix, each element in the logic matrix represents a basic unit in the two-dimensional code, which appears as black or white on the image. When the two-dimensional code stipulates that each basic unit is a rectangular square of equal area (this is the case for most mainstream two-dimensional codes), each eleme...
Embodiment 2
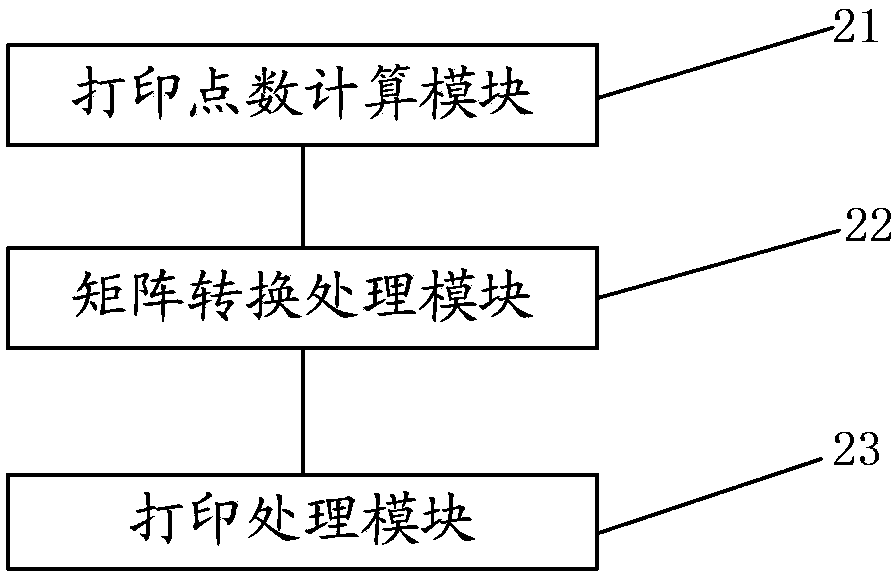
[0049] The specific structure of a device for printing a two-dimensional code using a 9-pin printer in an embedded system provided by this embodiment is as follows: figure 2 shown, including:
[0050] The number of print points calculation module 21 is used to calculate the number of print points corresponding to each rectangular unit of the logic matrix of the two-dimensional code that needs to be printed according to the print area size and print resolution of the 9-pin printer, and each rectangle of the logic matrix A unit represents a basic unit in the two-dimensional code;
[0051] The matrix conversion processing module 22 is used to map each rectangular unit of the logical matrix to the corresponding matrix of the printing pixel matrix of the 9-pin printer according to the number of printing dots corresponding to each rectangular unit of the logical matrix using a bitmap data structure unit, thereby converting the logic matrix into a printing pixel matrix of a 9-pin p...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com