Global land vegetation biomass change monitoring method
A vegetation biomass and change monitoring technology, which is applied in the field of global terrestrial vegetation biomass change monitoring, achieves the effects of simple operation, high precision on the surface, and improved change monitoring accuracy
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example
[0023] Step 1: Process and spatially interpolate the raw data, then use Equation 1 to calculate the spatial average for the GPP / NPP product of MODIS in the morning (10:30) on the Terra satellite
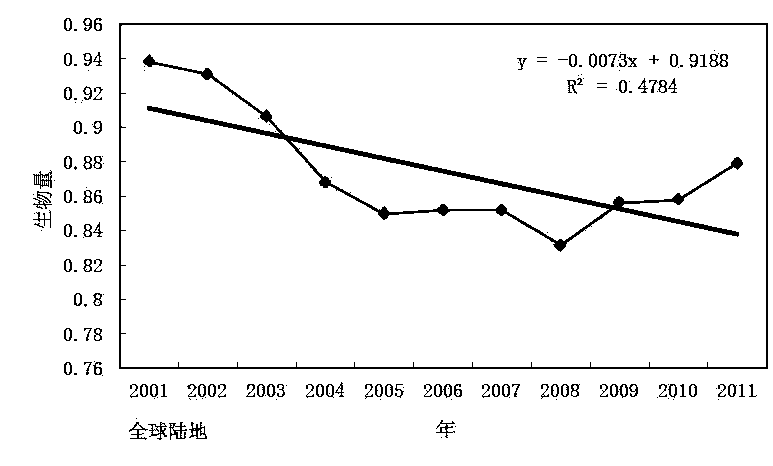
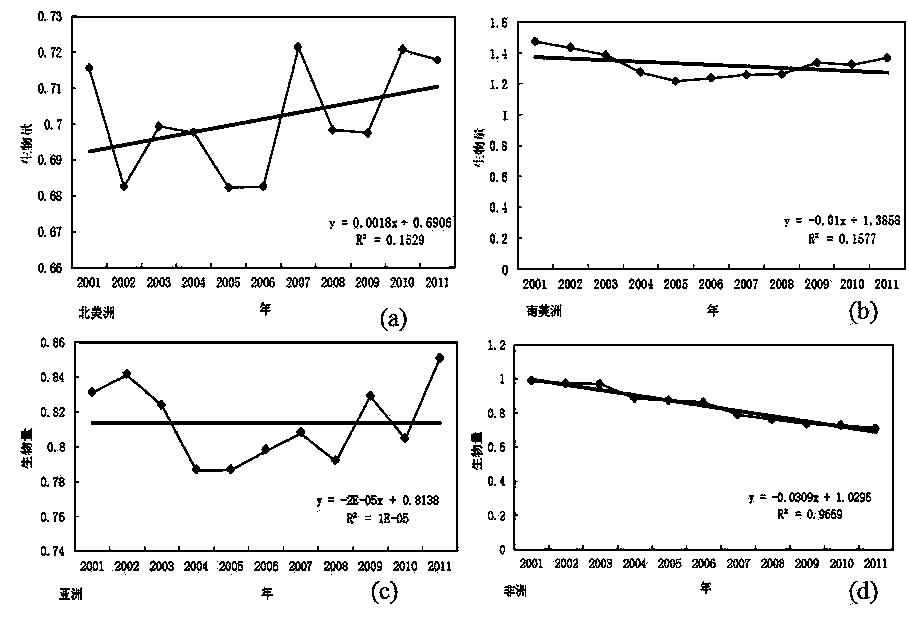
[0024] Step 2: Equation 2 calculates the global or regional average biomass status of vegetation biomass
[0025] The third step: use the average global or regional vegetation biomass calculated in the second step and Equation 3 to further calculate and analyze the global or regional vegetation biomass change trend, and analyze the temporal and spatial changes of global or regional biomass changes.
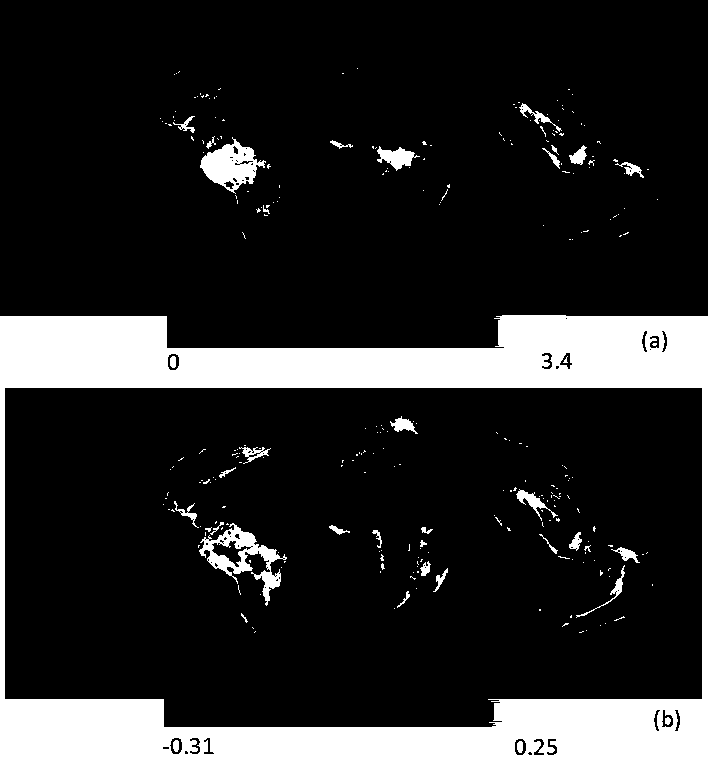
[0026] figure 1 From 2003 to 2010, (a) the average distribution map of global terrestrial vegetation, (b) the map of the change rate of global terrestrial vegetation biomass, from figure 1 a It can be seen that the area with the highest biomass in the world is distributed in the northern part of South America; from figure 1 b It can be seen that the most obvious increase in biology ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com