SLNR (signal-to-leakage-and-noise ratio) beam forming based user need considered power distribution method
A beamforming method and beamforming technology, applied in power management, wireless communication, electrical components, etc., can solve the problem of low fairness satisfaction
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
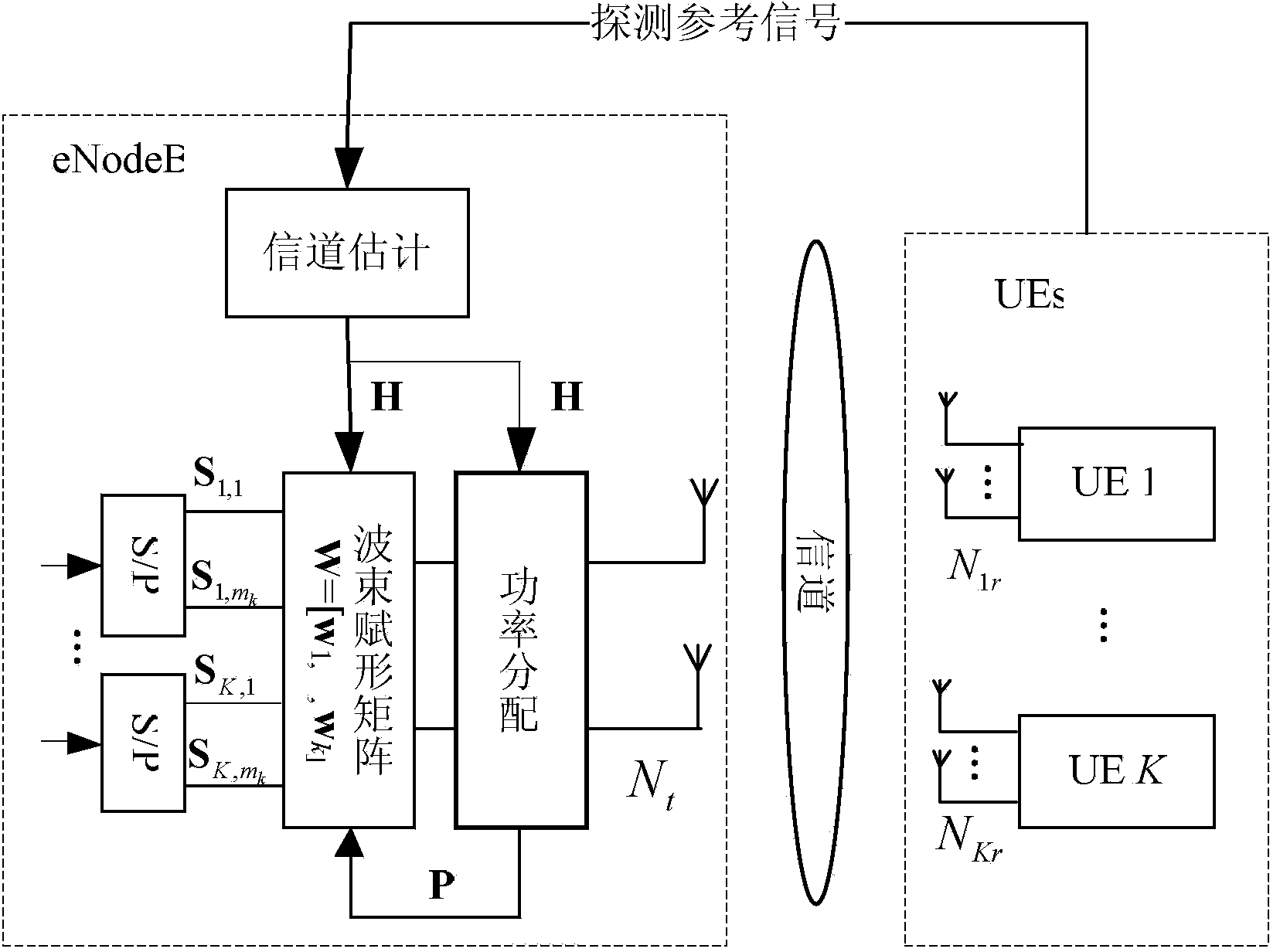
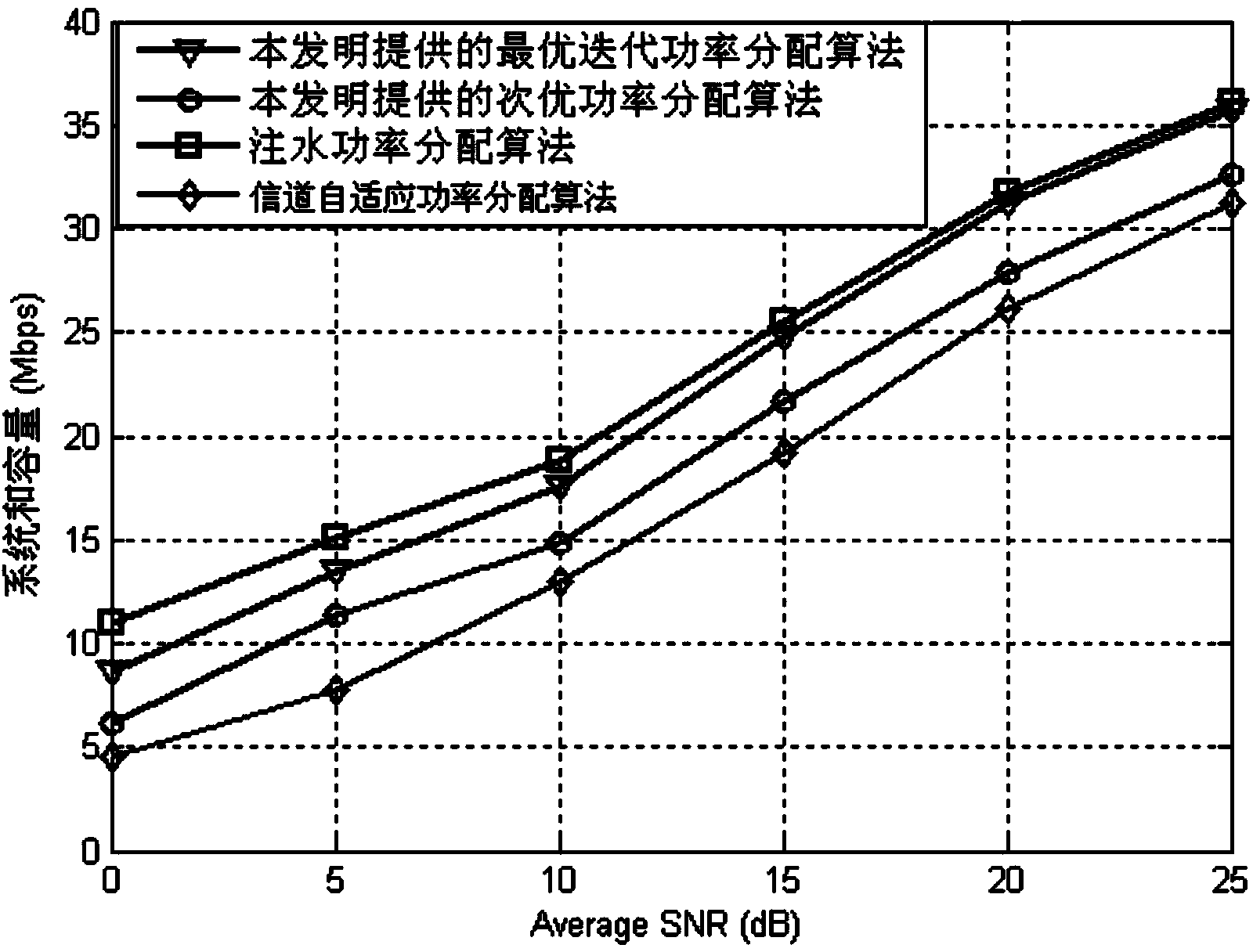
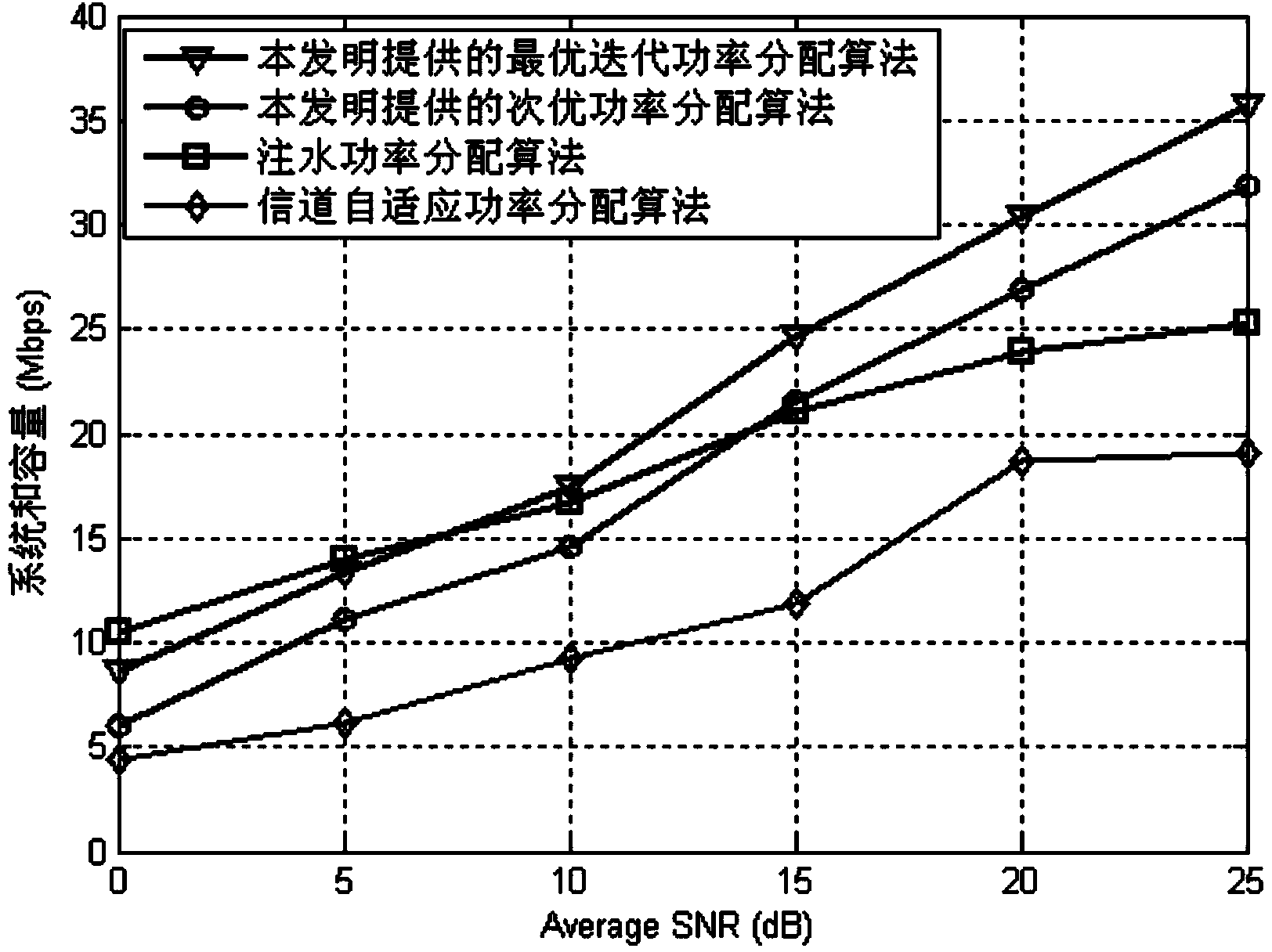
[0077] Specific implementation mode one: combine figure 1 Describe this embodiment, the power allocation method based on SLNR beamforming in this embodiment that considers user needs, wherein the optimal iterative power allocation method includes the following steps:
[0078] Step 1: Under the condition of equal power allocation, the corresponding beamforming matrix is obtained by using the SLNR beamforming method combined with user power;
[0079] Step 2: Under the beamforming matrix obtained in Step 1, obtain a feasible initial power value through the initial point selection algorithm;
[0080] Step 3: Under the initial power value obtained in Step 2, solve the approximate convex optimization problem of the established power optimization problem, and obtain the user's power allocation value;
[0081] Step 4: Use the power distribution result obtained in step 3 as the initial value of step 3, repeat step 3, and judge whether the difference between the two power distributio...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0083] Specific embodiment 2: This embodiment is a further limitation of the power allocation method based on SLNR beamforming that considers user needs described in specific embodiment 1. The SLNR beamforming method combined with user power used in step 1 The method to obtain the corresponding beamforming matrix is:
[0084] The SLNR of user k is expressed as:
[0085] SLNR k = | | P k H k w k | | F 2 N ...
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0089] Specific embodiment 3: This embodiment is a further limitation of the optimal iterative power allocation method based on SLNR beamforming in consideration of user needs described in specific embodiments 1 or 2,
[0090] The steps of the initial point selection method in step 2 are:
[0091] Step 1: Set the equal power distribution value as the initial value P m , m=0, the i-th constraint of the optimization problem is set to c i (P).
[0092] Step 2: Calculate the non-valid set J, set J={j:c j (P k )>0}, if At the end of the algorithm, a reasonable power initial value vector is obtained. Otherwise, proceed to step three;
[0093] Step 3: Take j ∈ J, with P m As the initial value, use the interior point method to solve the following problems:
[0094] min c j (P) j∈J
[0095] s.t.c i (P)≤0
[0096] Step 4: If the optimal solution P of this subproblem m+1 meet c j (P m+1 )≤0, then m=m+1, go to step 2.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com