Dynamic V2V link delay predicting method in VANETs
A technology of dynamic prediction and link delay, which is applied in the traffic control system of road vehicles, traffic flow detection, instruments, etc., can solve the problem of inability to accurately predict link delay, link delay or link connectivity inappropriate, It is difficult for the driver to discover the general law of vehicle node speed changes and other issues
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
[0051] Specific implementation mode 1: A dynamic prediction method for V2V link delay in VANETs according to this implementation mode is specifically prepared according to the following steps:
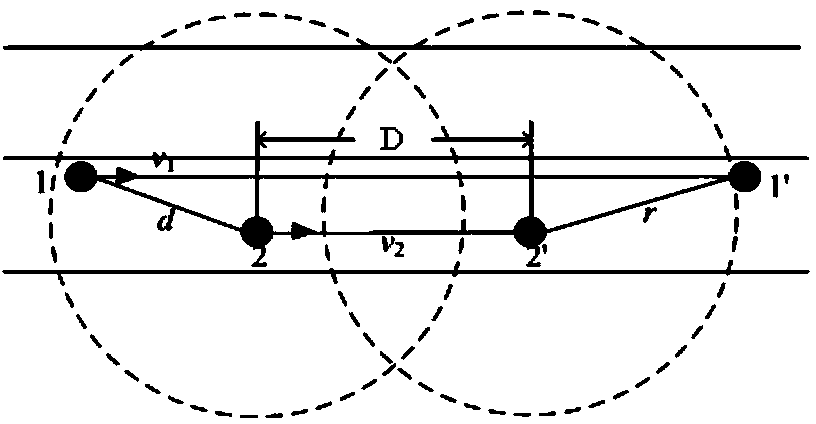
[0052] Step 1. Assume that the speed of the i-th vehicle is The speed of the jth vehicle is then the relative velocity for According to the relative speed Calculate the relative velocity value △v of any two vehicles;
[0053] Step 2. Calculate the relative displacement value ΔS of the fronts of the i-th vehicle and the j-th vehicle;
[0054] Step 3. According to the relative velocity value △v calculated in step 1, it is calculated that △v obeys the general normal distribution, that is, the Gaussian distribution The average speed difference u, the variance σ 2 , where V i is the random variable of the speed of car i subject to normal distribution, V j is a random variable that obeys the normal distribution of the speed of car j, v i is the speed value of the i-th vehicle,...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0063] Specific embodiment two: the difference between this embodiment and specific embodiment one is: in step one, it is assumed that the speed of the i-th vehicle is The speed of the jth vehicle is then the relative velocity for According to the relative speed Calculate the relative velocity value △v of any two vehicles as follows:
[0064] The present invention stipulates that the vehicle traveling from left to right and from bottom to top (on the street map, from west to east and from south to north) is forward travel; Vehicles; for convenience, all velocities in the invention are treated as scalar quantities;
[0065] △v is the relative velocity value of vehicle i and vehicle j, then
[0066] Δv = | | v → i | - ...
specific Embodiment approach 3
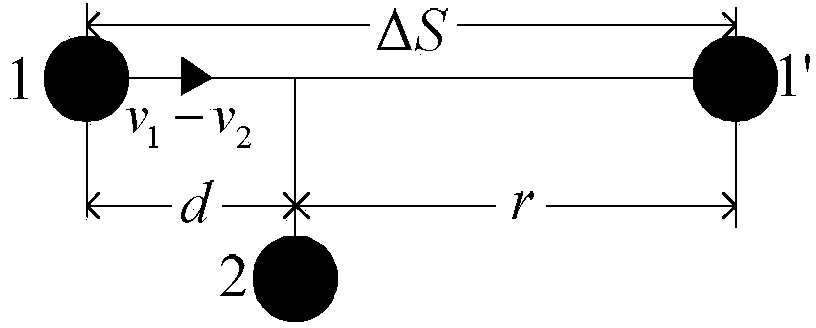
[0068] Specific embodiment 3: The difference between this embodiment and specific embodiment 1 or 2 is that in step 2, the relative displacement value ΔS of the fronts of the i-th vehicle and the j-th vehicle is calculated as:
[0069] ΔS = | | S → i | - | S → j | | diri = dirj | S → i | ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com