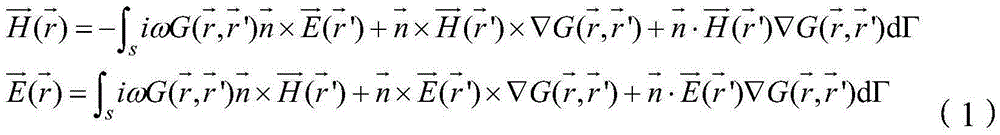A method for calculating the full vector of far-field light field
A full-vector computing, far-field technology, applied in optics, optical components, instruments, etc., can solve problems such as occupying a large amount of running memory, unable to give far-field results, and slow computing speed.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0018] Embodiments of the present invention will be further described in detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and examples. The following examples are used to illustrate the present invention, but should not be used to limit the scope of the present invention.
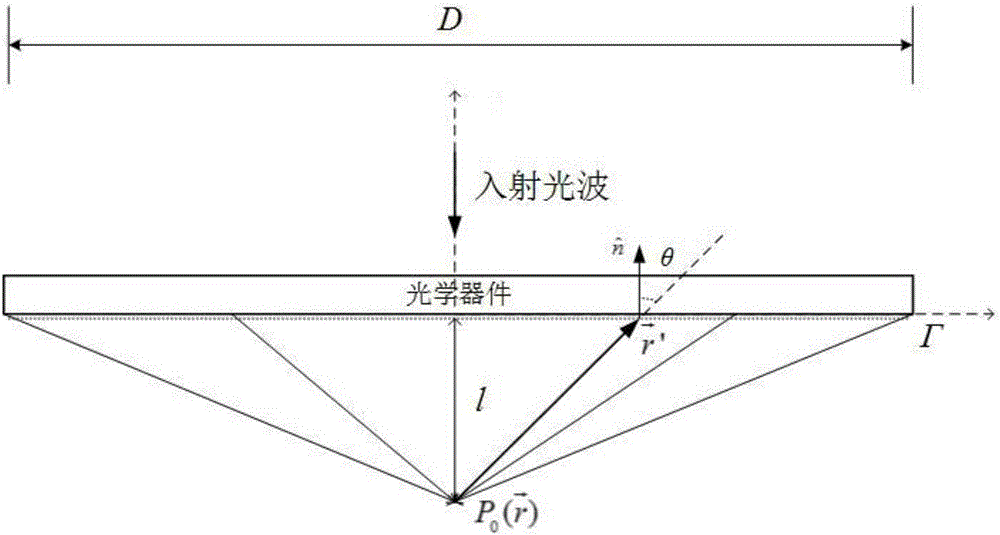
[0019] This embodiment provides a schematic diagram of a far-field light field full vector calculation method, as shown in figure 1 As shown, P 0 The point is a certain point in the far field, which is the required position of the light field. The width of the optic is D. This calculation method can be divided into two steps:
[0020] In the first step, the light field distribution of the light field passing through a certain near-field plane Γ of the optical device is obtained through the traditional full vector calculation method. The near-field light field distribution of the optical device can be obtained by using any full vector calculation method such as finite time domain difference or ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com