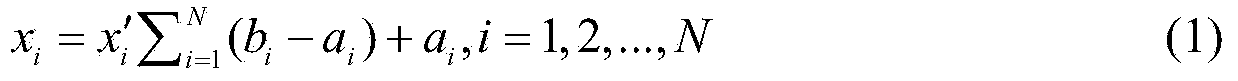Population global optimization method for regional dynamic subdivision based on local Lipschitz estimation
A global optimization and regional technology, applied in computing, special data processing applications, instruments, etc., can solve problems such as low reliability, high calculation cost evaluation times, and slow convergence speed
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0070] The present invention will be further described below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings.
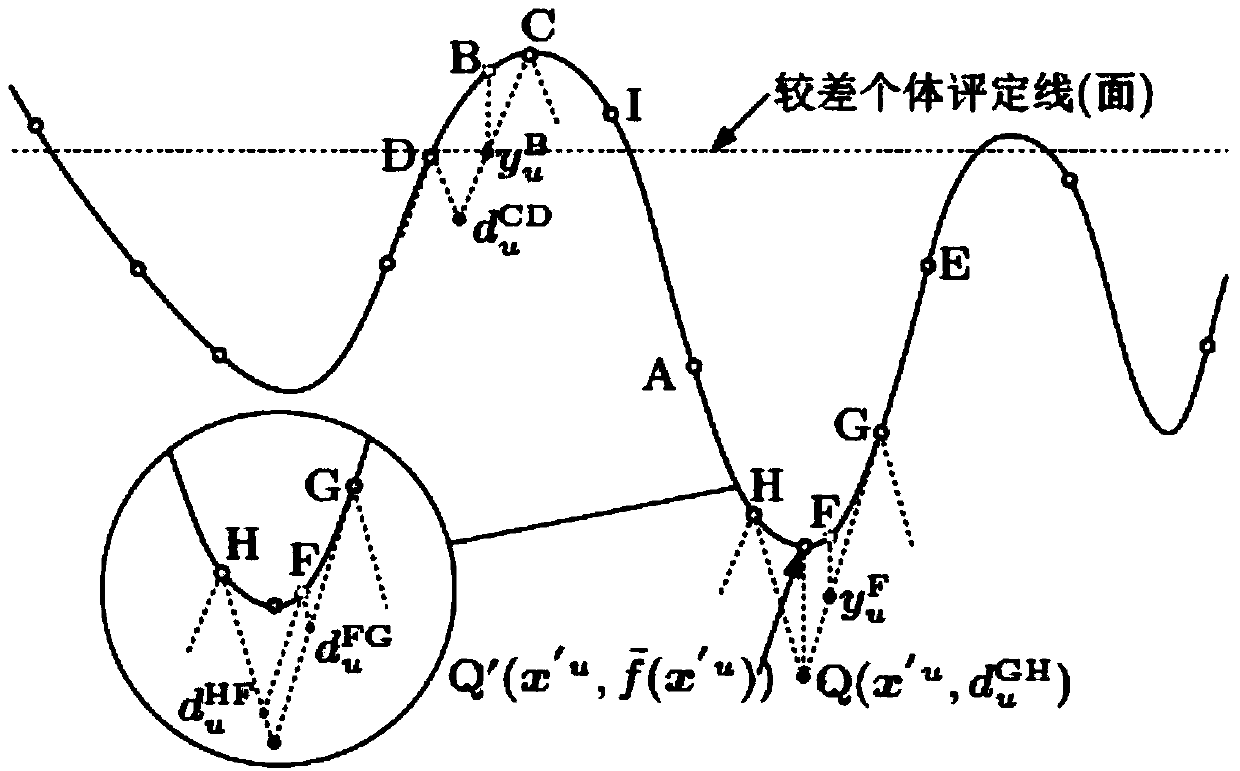
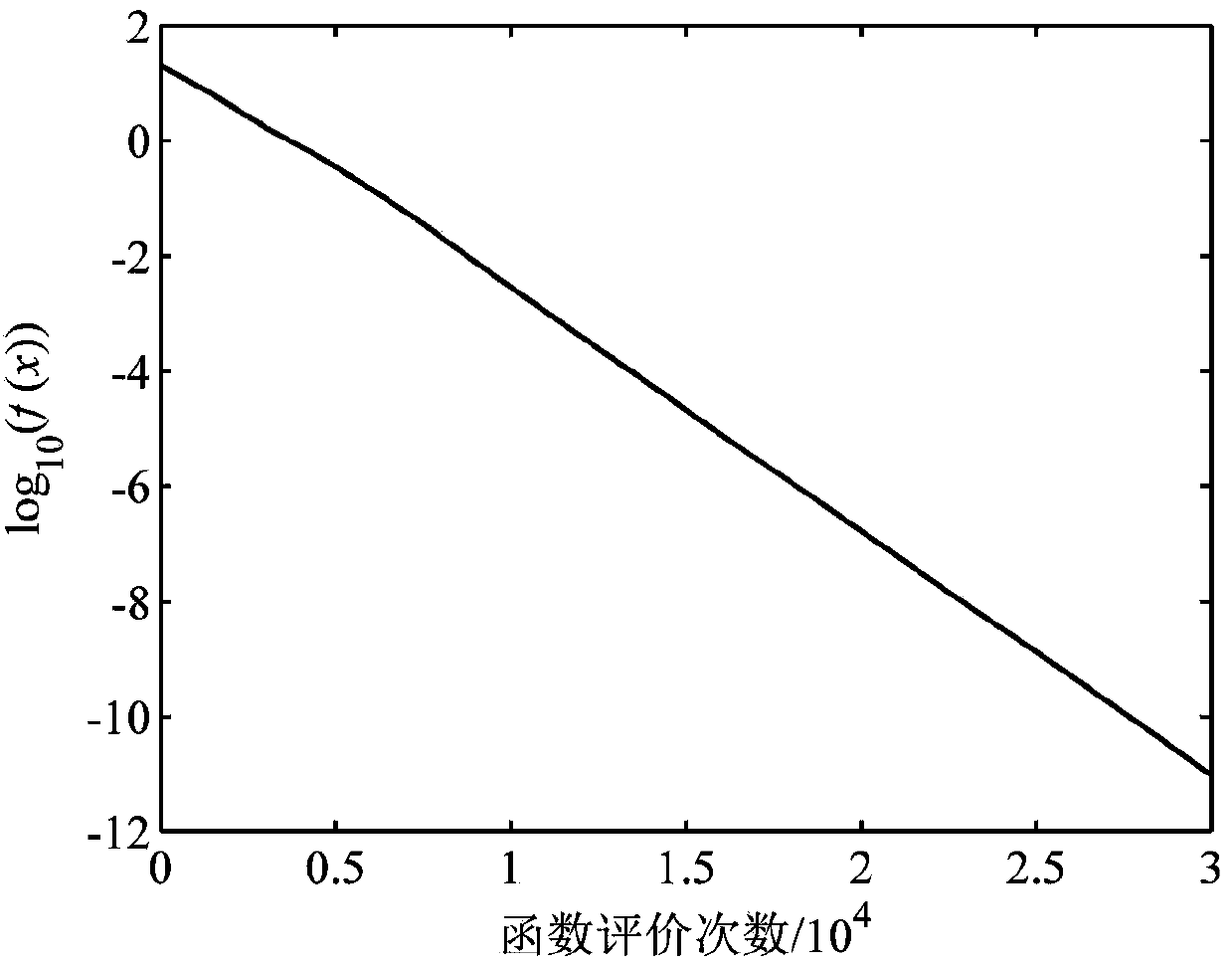
[0071] refer to figure 1 with figure 2 , a global optimization method for regional dynamic subdivision population based on local Lipschitz estimation, including the following steps:
[0072] 1) Initialization: set constant C, population size N P , the lower bound a of each variable i and upper bound b i , set the invalid region IR to empty, generation g=0, and the number of poor individuals is N j = 0, the number of re-initialization of poor individuals t = 0, the initial population is randomly generated within the domain of each variable
[0073] 2) Support matrix initialization:
[0074] 2.1) According to the formula (1) for the unit simplex area S Each vertex of is converted to get the point x 1 ,x 2 ,...,x N+1 ;
[0075] x i = x i ′ Σ ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com