Trans-impedance amplification circuit capable of realizing automatic gain control
A technology of automatic gain control and transimpedance amplification, applied in gain control, DC-coupled DC amplifier, amplification control, etc., can solve the problems of stability margin drop, signal processing ringing, insufficient loop stability margin, etc. Achieve the effect of loop gain reduction and large stability margin
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
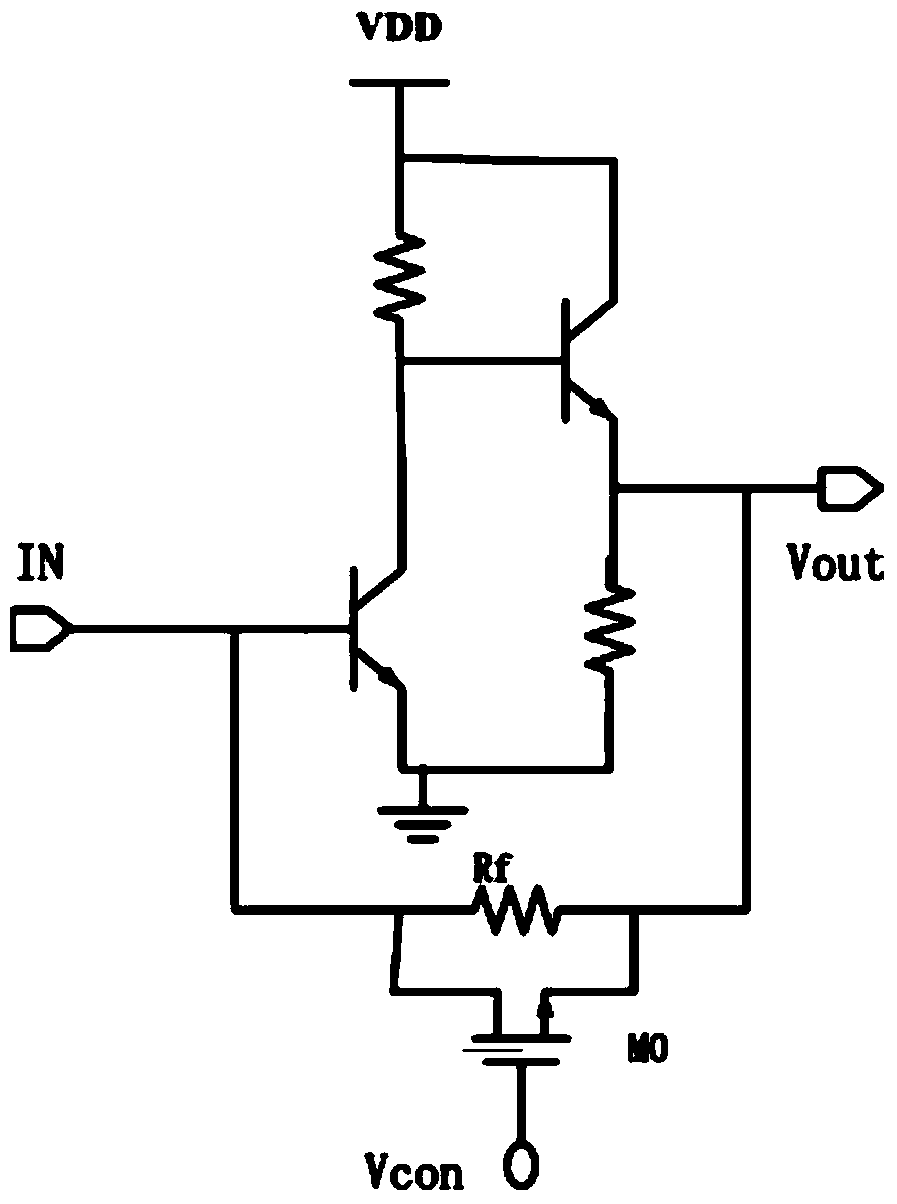
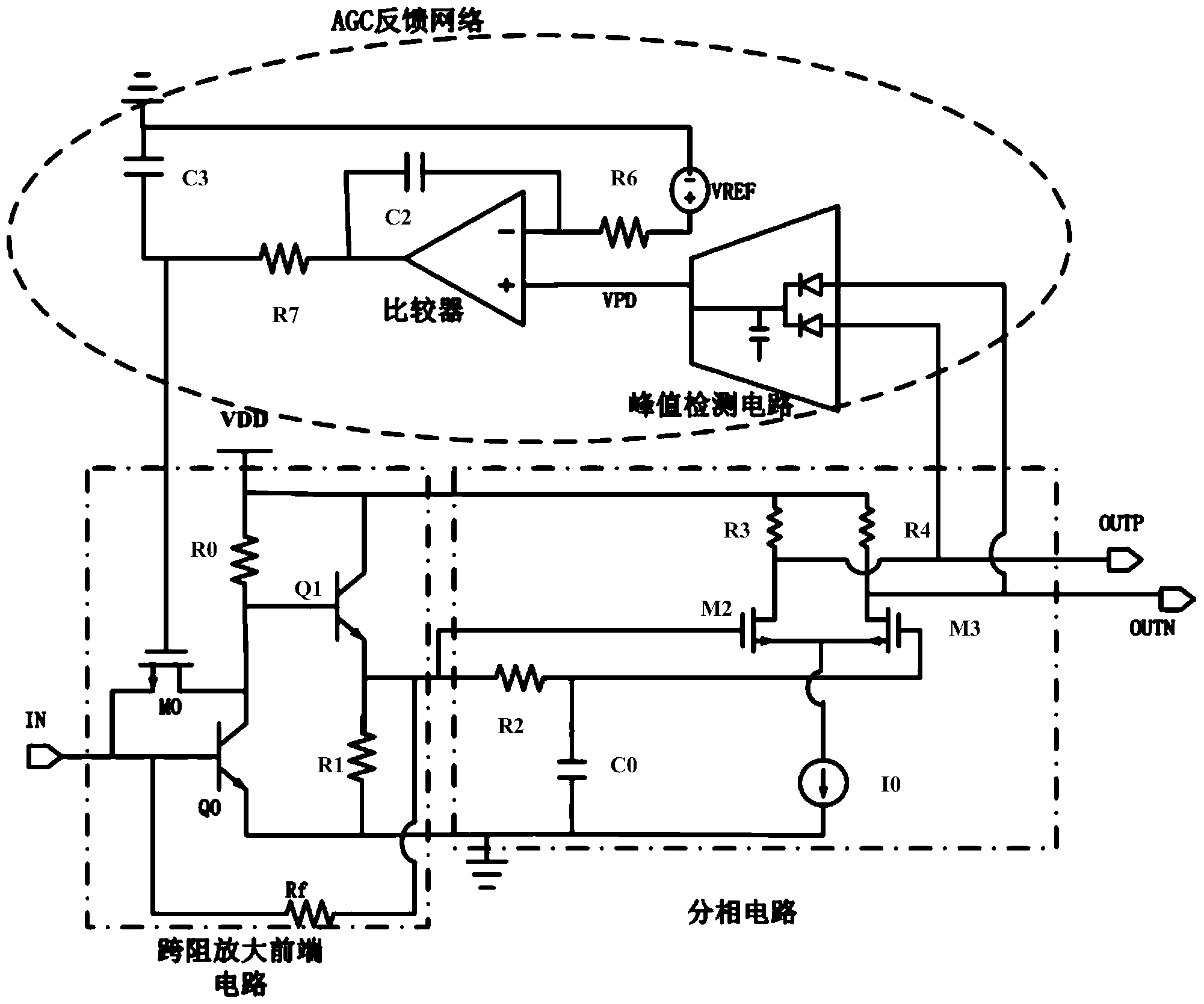
[0039] refer to image 3 , a transimpedance amplifier circuit capable of automatic gain control, comprising:
[0040] Transimpedance amplification front-end circuit, the transimpedance amplification front-end circuit converts the input current signal into a voltage signal, including the first switch tube Q0, the second switch tube Q1 and the first MOS tube M0, the first switch tube in this embodiment Q0 and the second switching tube Q1 are preferably triodes; the collector of the first switching tube Q0 is connected to the base of the second switching tube Q1; the base of the first switching tube Q0 is connected to the second switching tube through the transimpedance Rf The emitter of the transistor Q1 is connected; the source of the first MOS transistor M0 is connected to the base of the first switching transistor Q0, and the drain of the first MOS transistor M0 is connected to the collector of the first switching transistor Q0 Electrode connection; the first MOS transistor ...
Embodiment 2
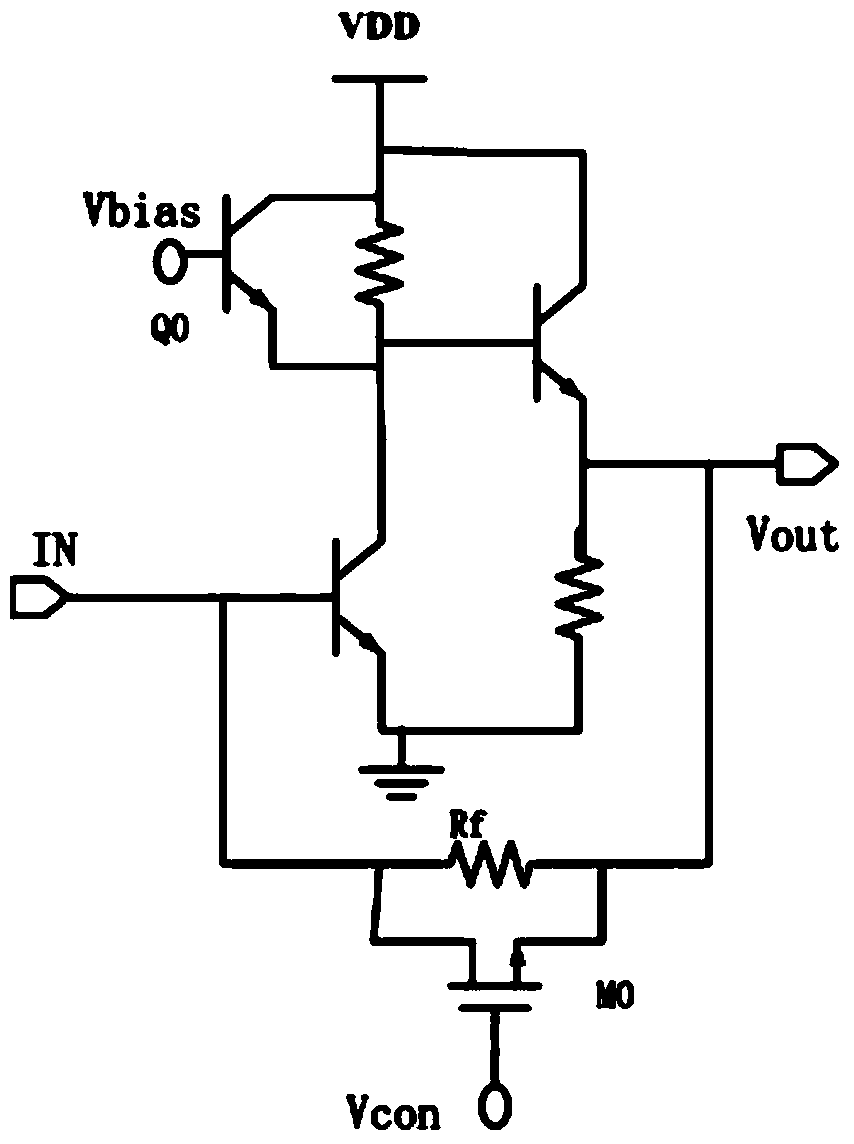
[0061] refer to Figure 5 , the difference from Example 1 is:
[0062] The transimpedance amplification front-end circuit further includes a third switching tube Q2, the emitter of the third switching tube Q2 is connected to the collector of the first switching tube Q0; the collector of the third switching tube Q2 is connected to the first switching tube Q2 The bases of the two switch tubes Q1 are connected. The third switching transistor Q2 is a cascode stage or a cascode stage, which can increase circuit bandwidth. The remaining parts are the same as those in Embodiment 1, so they will not be repeated here.
[0063] In this embodiment, the first switching tube Q0 , the second switching tube Q1 and the third switching tube Q2 are triodes, and can also be replaced with MOS tubes as required.
Embodiment 3
[0065] refer to Figure 6 , the difference from Example 2 is:
[0066] The second MOS transistor M1 is connected in parallel on both sides of the transimpedance Rf, the second MOS transistor M1 controls the transimpedance Rf, and the first MOS transistor M0 controls the loop gain, which further ensures the stability of the circuit. The rest of this embodiment is the same as the second embodiment, so it will not be repeated.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com