Detecting method for routing loop and device thereof
A routing and looping technology, applied in the field of communication, can solve problems such as occupying a large memory, and achieve the effect of ensuring normal operation and avoiding waste of resources
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
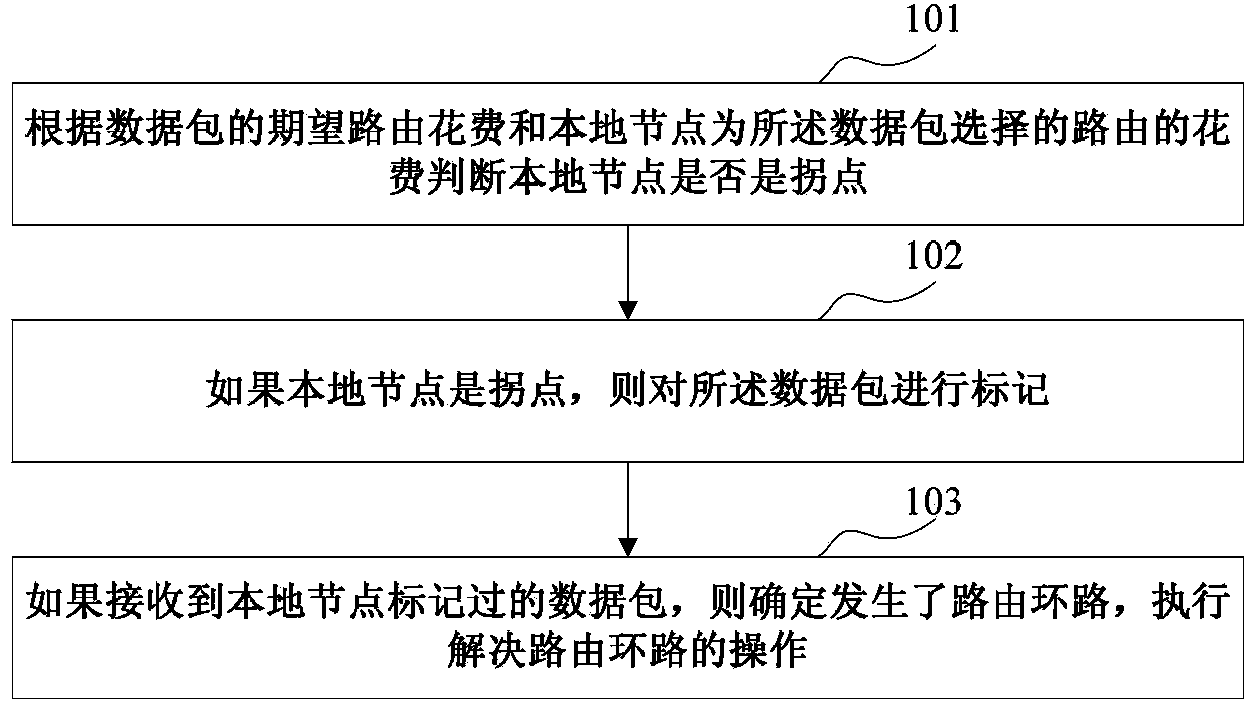
[0038] An embodiment of the present invention provides a method for detecting a routing loop. figure 1 is the flowchart of the method, please refer to figure 1 , the method includes:
[0039] Step 101: judging whether the local node is an inflection point according to the expected route cost of the received data packet and the cost of the route selected by the local node for the data packet;
[0040] Wherein, the local node may select a route with the least routing cost for the data packet by querying the routing table, and determine whether the local node is an inflection point by comparing the expected routing cost of the data packet with the cost of the selected route.
[0041] Among them, if the cost of the selected route is greater than or equal to the expected route cost, the local node is considered to be an inflection point. Works as normal; if the cost of the chosen route is less than the expected route cost, the local node is considered not to be an inflection poin...
example 1
[0080] In this example, the method of the embodiment of the present invention is described by taking the method of marking the data packet by putting the address of the inflection point into the data packet as an example, wherein the frame structure of the data packet is shown in Table 2 as an example, and the structure of the inflection point list Take Table 3 as an example.
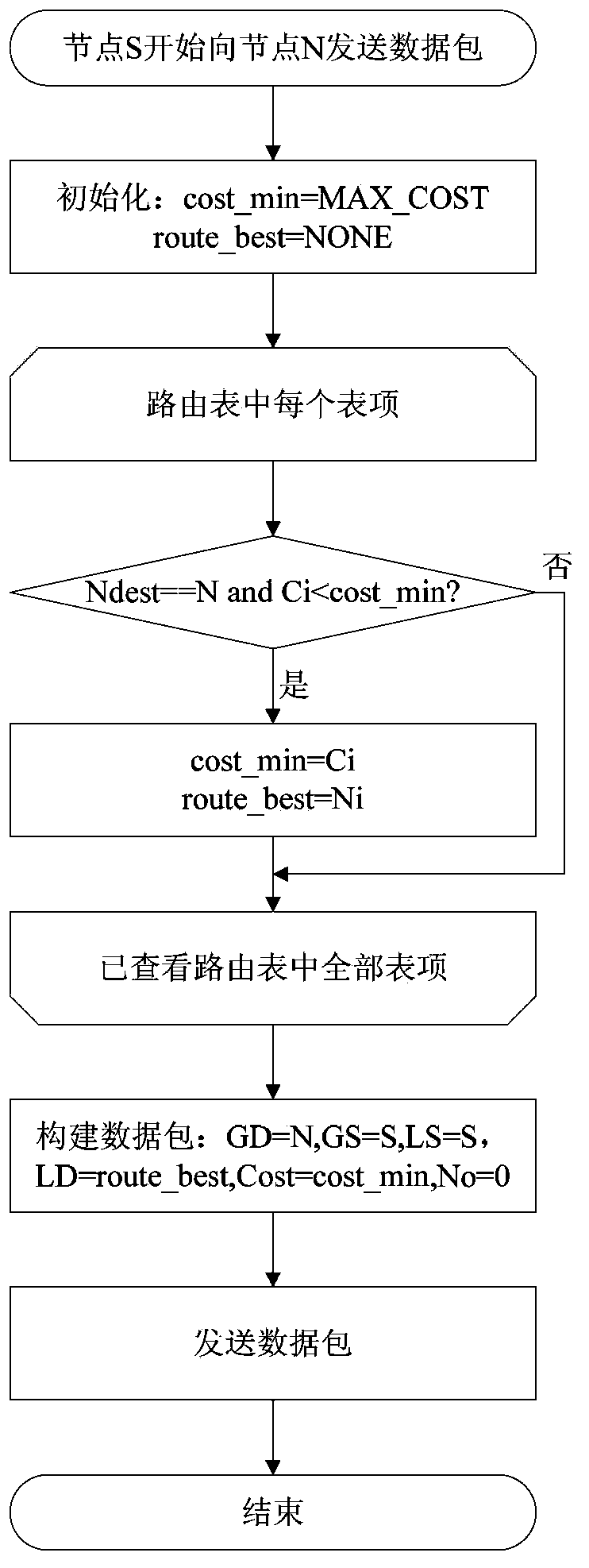
[0081] Figure 2a It is an operation flowchart of the source node sending information in an implementation manner of this example.
[0082] Please refer to Figure 2a, when node S needs to send data to node N, it first searches the routing table for the routing node whose target node address is N and the routing cost is the smallest, and the node address is recorded as route_best, and the routing cost is recorded as cost_min; then construct the data packet, let GD= N, GS=S, LD=route_best, LS=S, Cost=cost_min, No=0; finally, send the data packet.
[0083] Figure 2b It is an operation flowchart of th...
example 2
[0094] In this example, the method of the embodiment of the present invention is described by taking the method of storing the information of the data packet into the historical information table of the inflection point to mark the data packet as an example, wherein the frame structure of the data packet is shown in Table 4 as an example, Take Table 5 as an example for the structure of the historical information table of the inflection point.
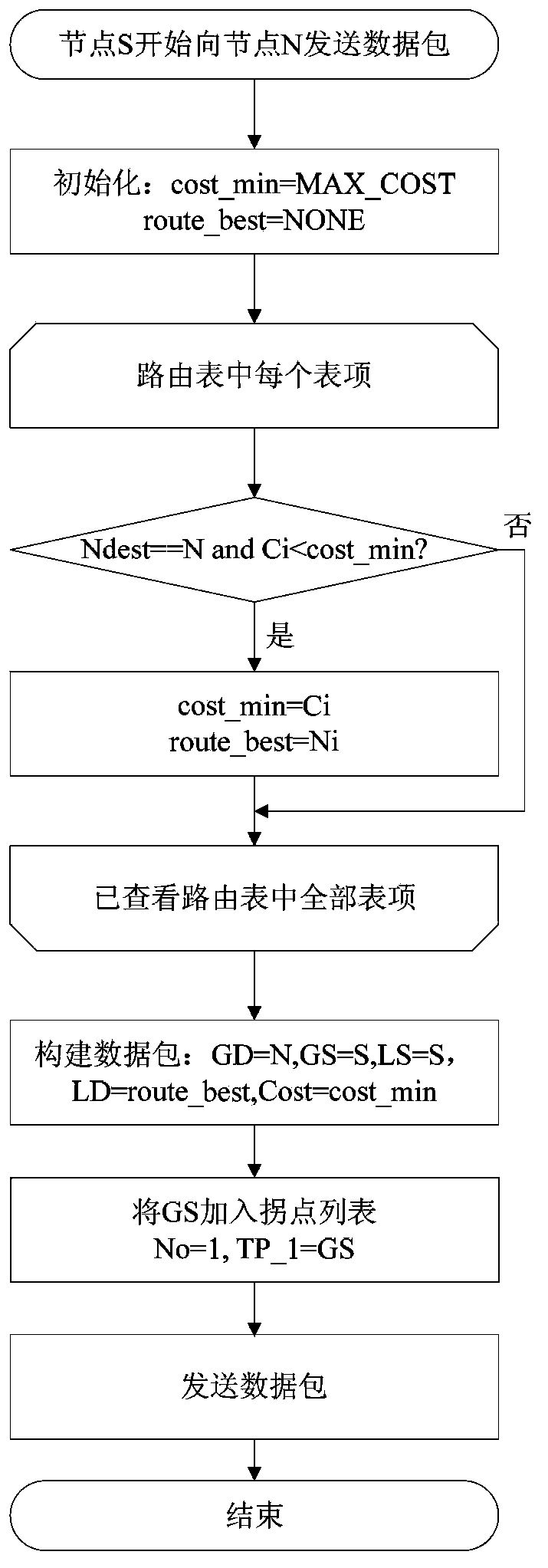
[0095] Figure 4a It is an operation flowchart of the source node sending information in an implementation manner of the second example.
[0096] Please refer to Figure 4a , when node S needs to send data to node N, it first searches the routing table for the routing node whose target node address is N and the routing cost is the smallest, and the node address is recorded as route_best, and the routing cost is recorded as cost_min; then construct the data packet, let GD= N, GS=S, LD=route_best, LS=S, Cost=cost_min; finally, send the ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com