Variable-step LMS adaptive filtering method
A technology of adaptive filtering and variable step size, which is applied in the direction of adaptive network, impedance network, electrical components, etc., can solve the problem of not getting the effect, achieve the effect of optimal steady-state error and maintain the convergence speed
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0034] The present invention will be further described below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings. The following examples are only used to illustrate the technical solution of the present invention more clearly, but not to limit the protection scope of the present invention.
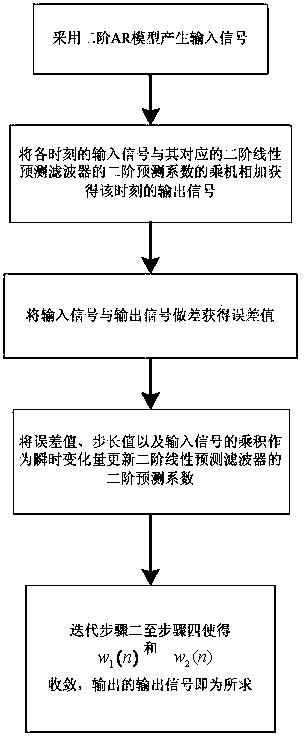
[0035] like figure 1 As shown, a variable step size LMS adaptive filtering method includes the following steps:
[0036] Step 1, using a second-order AR model to generate an input signal.
[0037] The input signal formula is,
[0038] x(n)+a 1 x(n-1)+a 2 x(n-2)=v(n)
[0039] Where x(n) is the input signal at time n, x(n-1) is the input signal at time n-1, x(n-2) is the input signal at time n-2, a 1 =-0.195, a 2 =0.95, v(n) is a normal distribution noise with a mean of zero and a variance of 0.0965.
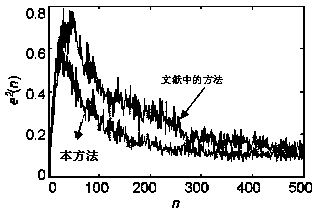
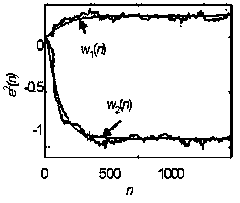
[0040] Step 2, adding the product of the input signal at each moment and the second-order prediction coefficient of the corresponding second-order linear prediction filter to obtain the outp...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com