Shortwave infrared telescope lens
A telescopic lens and short-wave infrared technology, which is applied in the field of infrared telescopic lens, can solve the problems of large size of the first lens group, heavy system weight, and non-compliance with miniaturization, and achieve improved imaging performance, high resolution, and excellent imaging performance. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
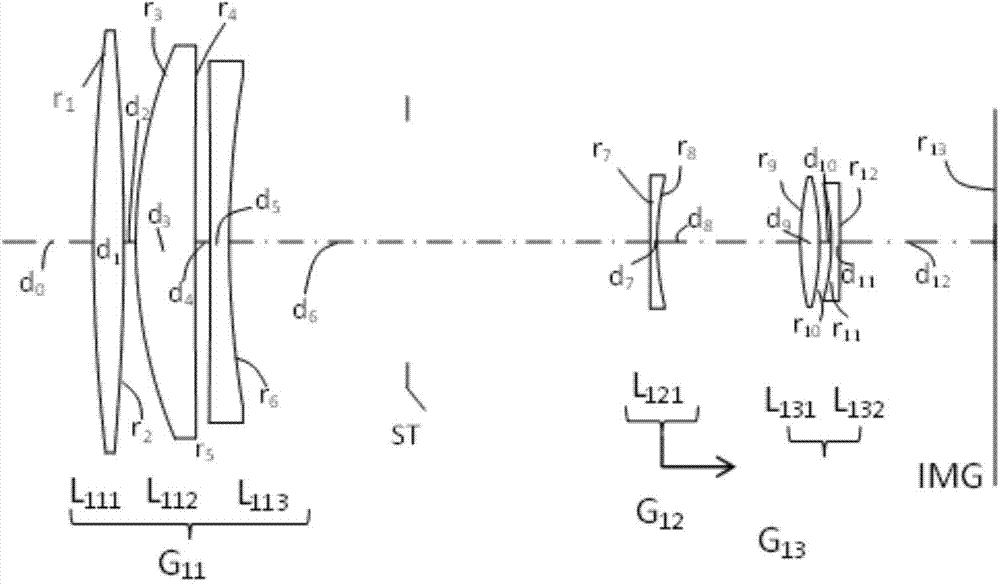
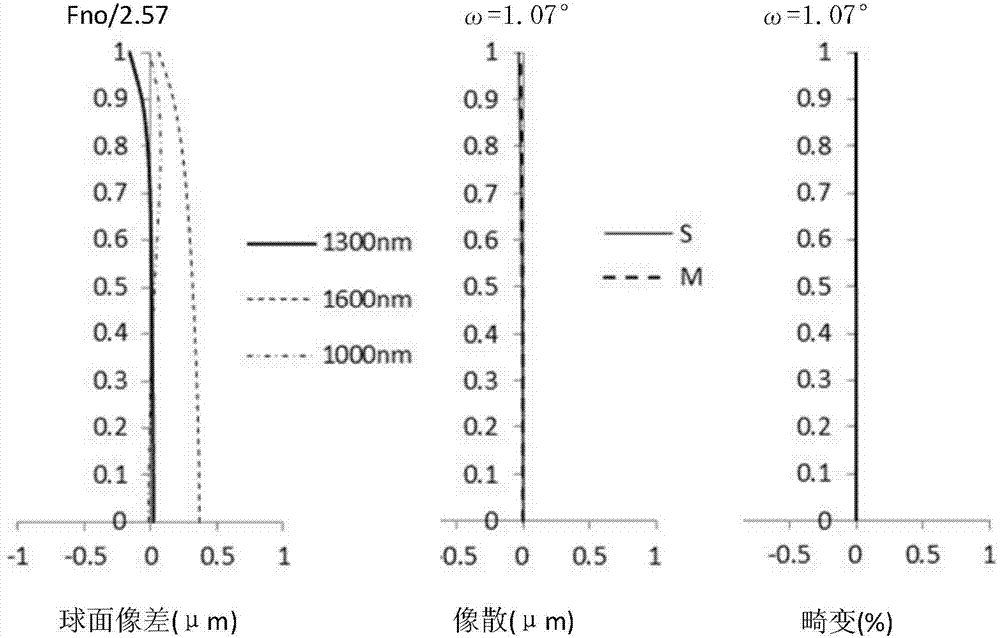
[0069] figure 1 It is a cross-sectional view along the optical axis showing the structure of the fixed-focus lens of Example 1. The fixed-focus lens is composed of the following lens groups arranged in order from the object side in the figure: the first lens group G11 with positive refractive power; the second lens group G12 with negative refractive power; The third lens group G13. In addition, an aperture stop ST defining a predetermined aperture is arranged between the first lens group G11 and the second lens group G12.
[0070] The first lens group G11 is configured such that a positive lens L111, a positive lens L112, and a negative lens L113 are arranged in this order from the object side. Also, the first lens group G11 is fixed and does not move during focusing.
[0071] As for the second lens group G12, it is composed of a negative lens L121. By moving the second lens group G12 along the optical axis from the object side to the imaging surface IMG side, focusing is ...
Embodiment 2
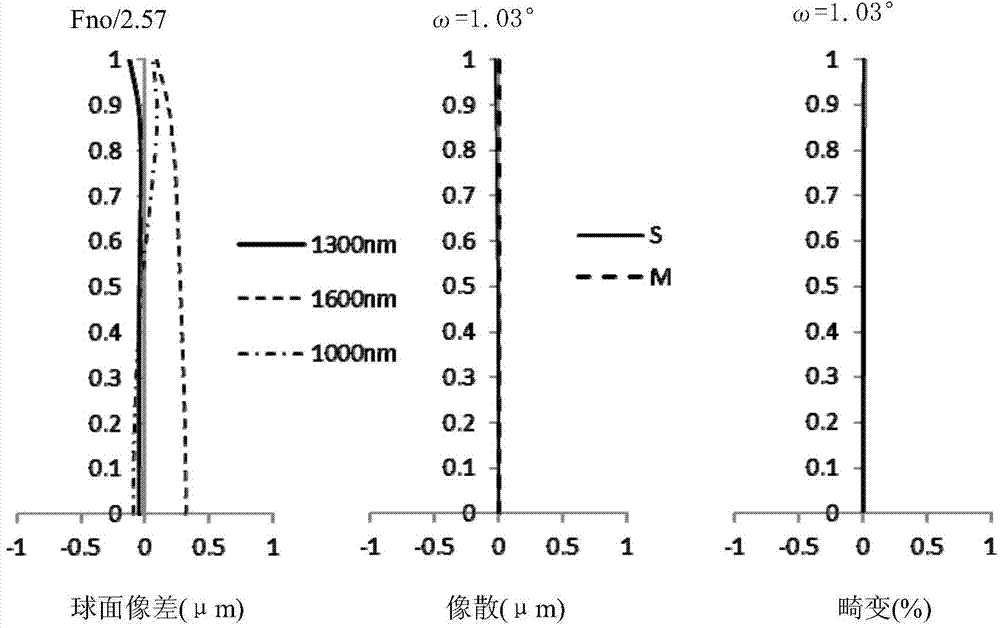
[0079] Figure 5 It is a cross-sectional view along the optical axis showing the structure of the fixed-focus lens of Example 2. The fixed-focus lens is composed of the following lens groups arranged in order from the object side in the figure: the first lens group G21 with positive refractive power; the second lens group G22 with negative refractive power; The third lens group G23. In addition, an aperture stop ST defining a predetermined aperture is arranged between the first lens group G21 and the second lens group G22.
[0080] The first lens group G21 is configured such that a positive lens L211, a positive lens L212, and a negative lens L213 are arranged in this order from the object side. Also, the first lens group G21 is fixed and does not move during focusing.
[0081] As for the second lens group G22, it is composed of a negative lens L221. By moving the second lens group G22 along the optical axis from the object side to the imaging surface IMG side, focusing is...
Embodiment 3
[0087] Figure 9 It is a cross-sectional view along the optical axis showing the structure of the fixed-focus lens of Example 3. The fixed-focus lens is composed of the following lens groups arranged in order from the object side in the figure: the first lens group G31 with positive refractive power; the second lens group G32 with negative refractive power; The third lens group G33. In addition, an aperture stop ST defining a predetermined aperture is disposed between the first lens group G31 and the second lens group G32.
[0088] The first lens group G31 is configured such that a positive lens L311, a positive lens L312, and a negative lens L313 are arranged in this order from the object side. Also, the first lens group G31 is fixed and does not move during focusing.
[0089] The second lens group G32 is composed of a negative lens L321. By moving the second lens group G32 along the optical axis from the object side to the imaging surface IMG side, focusing is performed ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com