A friction stir lap welding method for reducing the size of interface defects
A friction stir and interface defect technology, applied in welding equipment, non-electric welding equipment, metal processing equipment, etc., can solve the problems of reducing the mechanical properties of joints, reducing the effective bearing thickness and effective lap width of joints, and increasing the effective lap width. The effect of reducing the joint area, reducing the cold lap defect, and reducing the bending deformation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
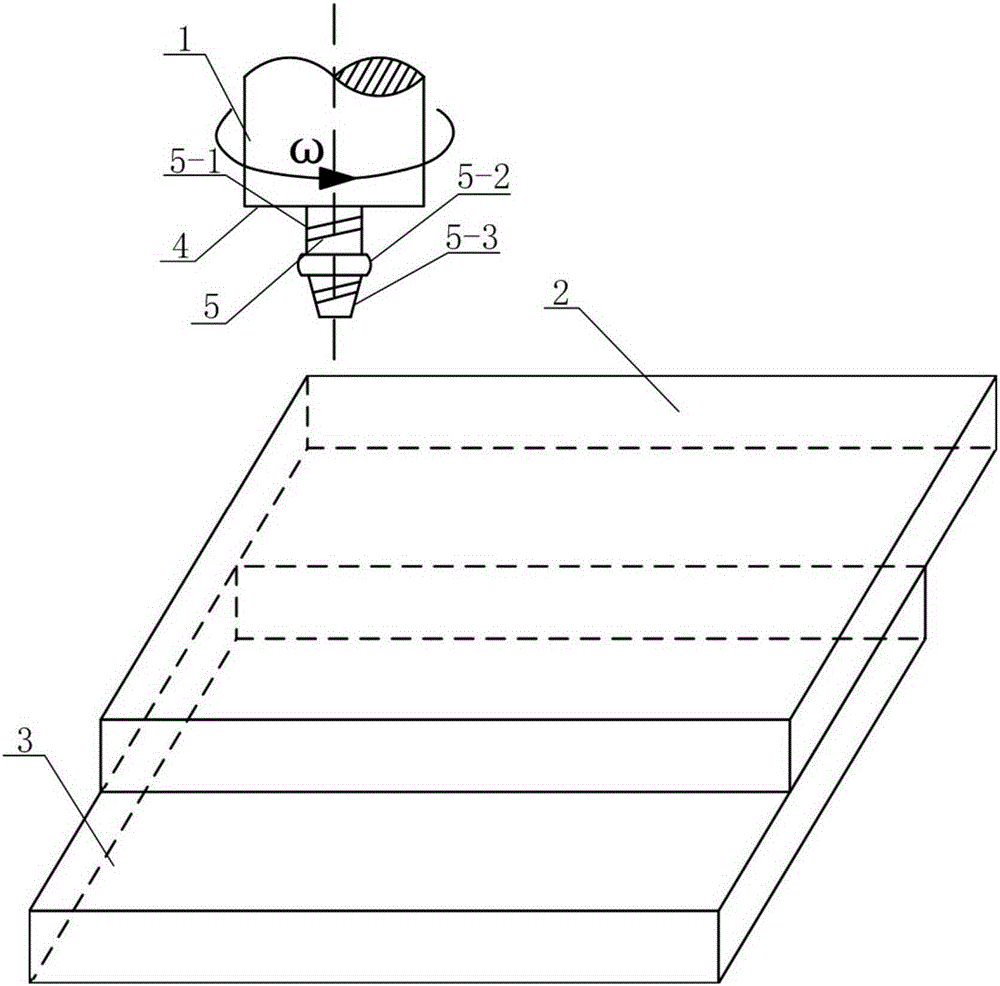
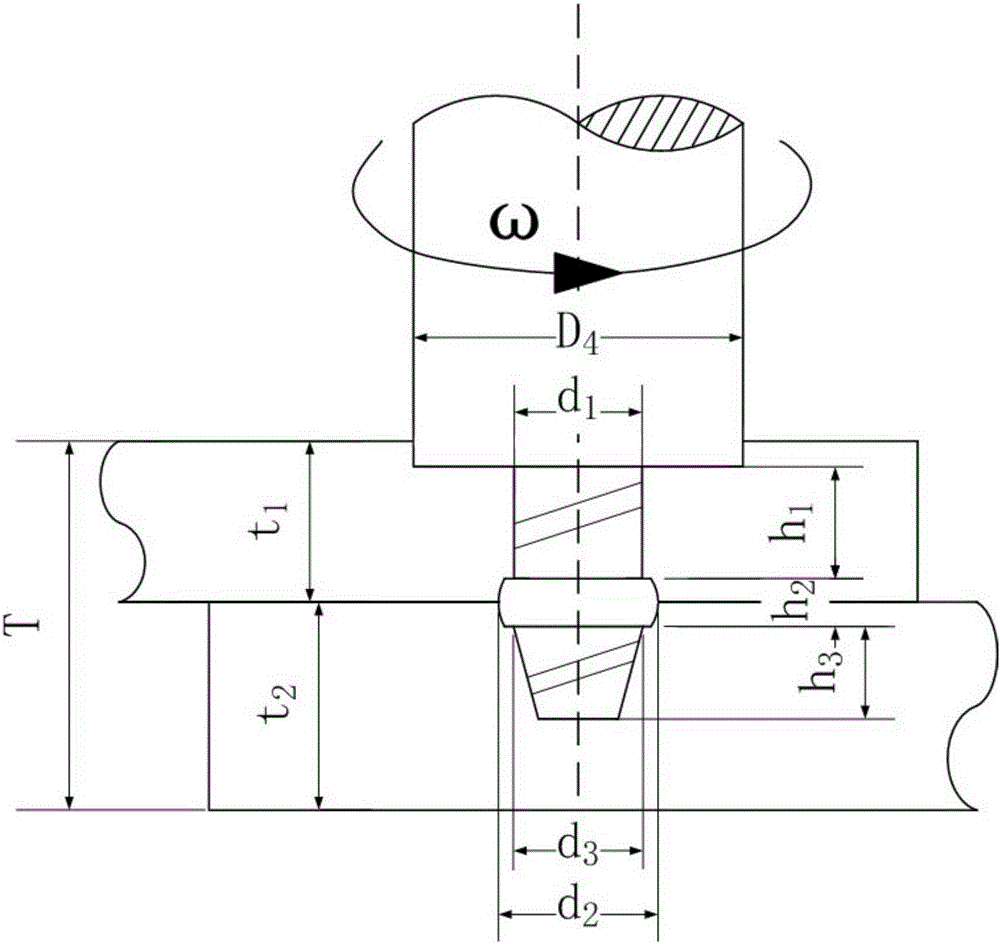
[0018] Specific Embodiment 1: In this embodiment, the stirring head 1 for friction stir lap welding that reduces the size of the interface defect is composed of a shaft shoulder 4 and a stirring pin 5. The cylinder 5-1, the middle convex circle 5-2 and the lower round platform 5-3 are composed, one end of the upper cylinder 5-1 is fixed on the lower end surface of the shoulder 4, the other end of the upper cylinder 5-1 is connected with the middle convex circle 5 -2 connection, the lower end surface of the middle convex circle 5-2 is connected to the bottom surface of the lower round platform 5-3, and the diameter d of the upper cylinder 5-1 1 and the bottom surface diameter d of the lower round platform 5-3 3 equal, the diameter d of the upper cylinder 5-1 1 Smaller than the diameter d of the central convex circle 5-2 2 , and there are right-hand threads on the outer surfaces of the upper cylinder 5-1 and the lower round table 5-3.
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0019] Specific embodiment two: In this embodiment, the friction stir lap welding method for reducing the size of the interface defect is implemented according to the following steps:
[0020] 1. Determine the size of the stirring head: according to the thickness t of the first workpiece 2 to be welded 1 and the thickness t of the second workpiece 3 to be welded 2 And the total thickness T obtained by adding the thicknesses of the first workpiece 2 and the second workpiece 3 to be welded determines the diameter D of the shoulder 4 4 , the diameter d of the upper cylinder 5-1 of the stirring needle 1 , The diameter d of the bottom surface of the lower round table 5-3 3 , the diameter d of the convex circle 5-2 in the middle 2 , the diameter D of the shoulder 4 4 3 to 5 times the total thickness T, the diameter d of the upper cylinder 5-1 of the stirring needle 1 and the bottom surface diameter d of the lower round platform 5-3 3 1 to 2 times the total thickness T, the dia...
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0026] Specific embodiment three: the difference between this embodiment and specific embodiment two is the diameter D of the shoulder 4 in step one 4 4 times the total thickness T, the diameter d of the upper cylinder 5-1 of the stirring needle 1 and the bottom surface diameter d of the lower round platform 5-3 3 1.5 times the total thickness T, the diameter d of the convex circle 5-2 in the middle 2 For the upper cylinder 5-1 diameter d 1 1.4 times. Other steps and parameters are the same as in the second embodiment.
[0027] The dimensions of the stirring head in this embodiment can ensure the stability of the weld seam formation.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com