Method for computing maloperation rate of nuclear power station system
A calculation method and nuclear power plant technology, applied in the field of nuclear power plant system misoperation rate calculation, can solve problems such as huge workload, huge number of units, complex structure, etc., and achieve the effect of saving remodeling time
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
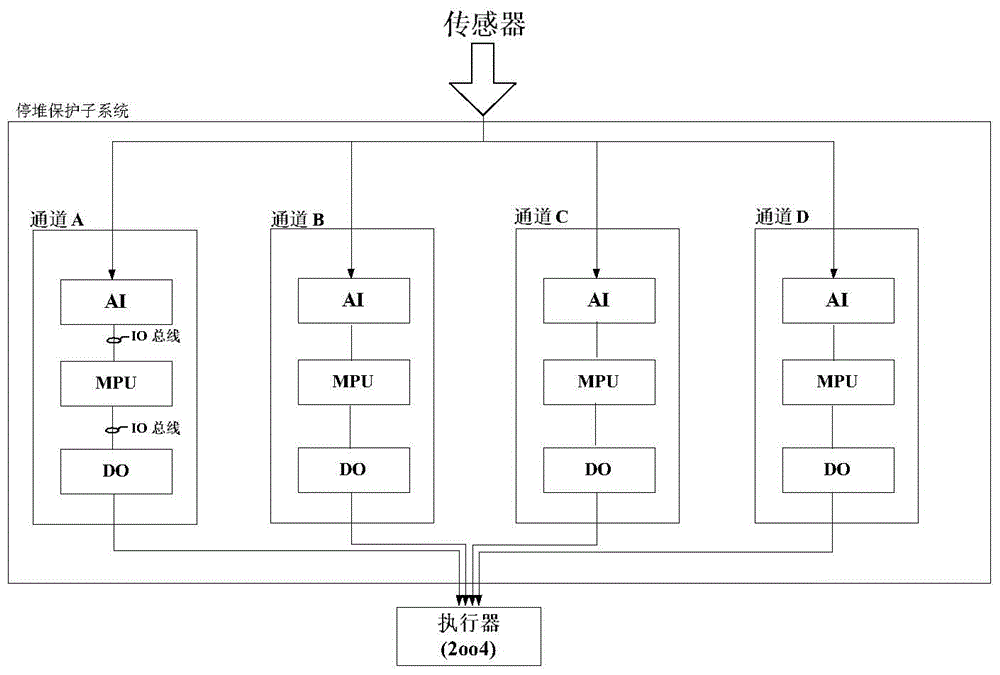
[0054] Based on the Markov theory, the present invention establishes a calculation method for the misoperation rate of the MooN repairable system, which mainly includes workflow and engineering calculation examples. The following content of the invention will describe the workflow and application calculation examples in detail.
[0055] 1. Workflow
[0056] Workflow of the present invention follows general scientific research workflow, comprises following three steps:
[0057] a) Proof of applicability: first determine the applicability of the inventive method, and judge whether the actual application meets the constraints of the invention;
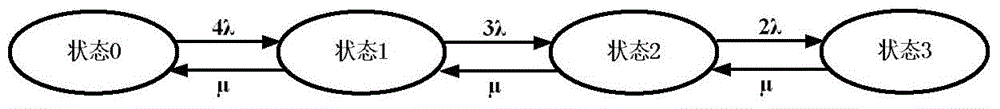
[0058] b) Establish a state space diagram (Markov chain): on the premise of satisfying a), apply Markov theory, and establish a system state space diagram according to the system malfunction and failure logic;
[0059] c) Deriving the expression of system misoperation rate (solving characteristic quantities): according to the state space...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com