Method for discovering small stations based on graph coloring in ultra-dense wireless network
A wireless network and discovery method technology, applied in the field of cell search, can solve problems such as the inapplicability of ultra-dense wireless networks and the complex interference relationship of small stations, and achieve the effects of increasing the probability of small stations, increasing the number of small stations, and reducing interference
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
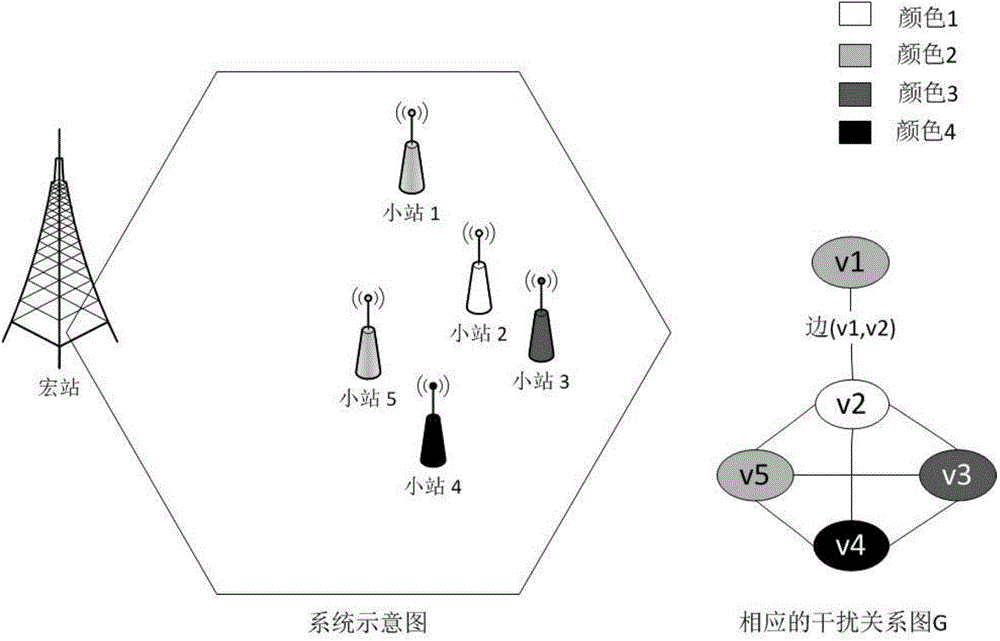
[0045] Below in conjunction with accompanying drawing, the embodiment of the present invention in LTE ultra-dense wireless network is further introduced:
[0046] 1 Construction of Interference Relationship Diagram
[0047] The interference relation graph is an undirected graph C=(V,E). Among them, V is the set of all vertices in the graph, and each vertex represents a small station; E is the set of all edges in the graph, and each edge represents the interference between two small stations.
[0048] Since the UE does not have information such as SINR (Signal to Interference and Noise Ratio) and RSRP of the small cell in the initial search phase, it uses the geographic location information of the small cell, that is, the location of the small cell, to construct an interference relationship graph. The closer the distance between the small stations, the stronger the interference between the small stations is considered.
[0049] Assume that the distance between small stations is...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com