WSN (wireless sensor network) node positioning method based on RSS (Received Signal Strength) and distance measurement unbiased estimation
A technology of node positioning and bias estimation, applied in wireless communication, electrical components, etc., can solve the problems of inability to essentially eliminate ranging bias and insufficient analysis.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
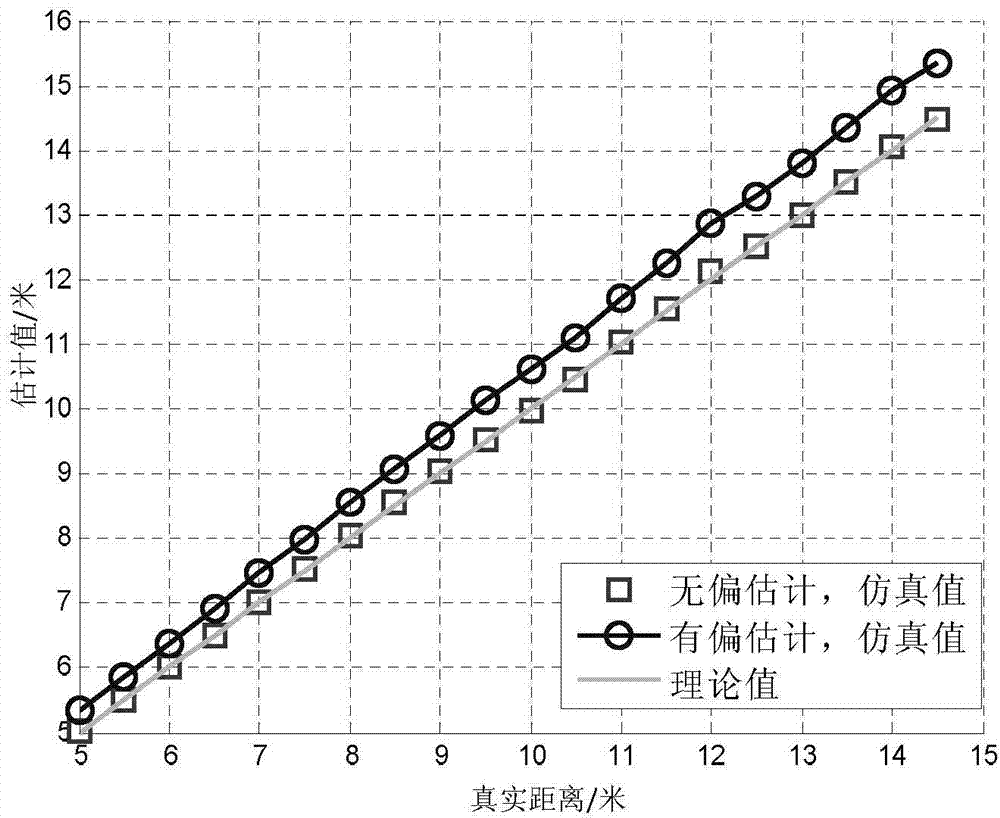
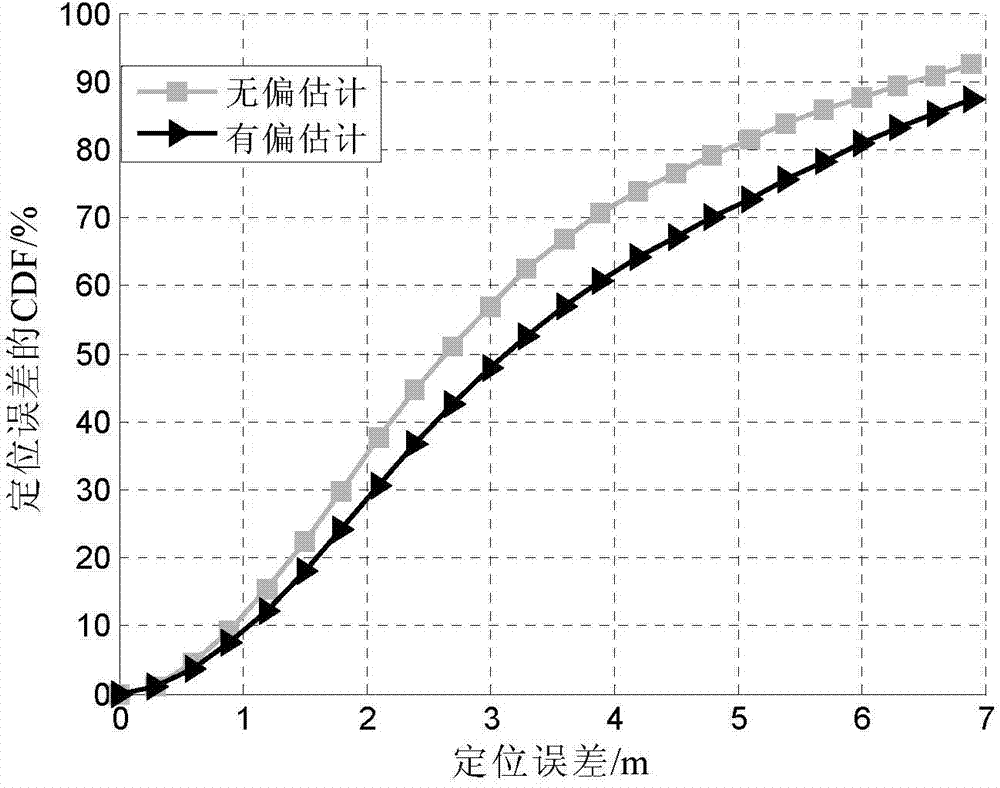
[0031] Specific embodiment one: a kind of WSN node localization method based on RSS and ranging unbiased estimation of this embodiment, specifically is prepared according to the following steps:
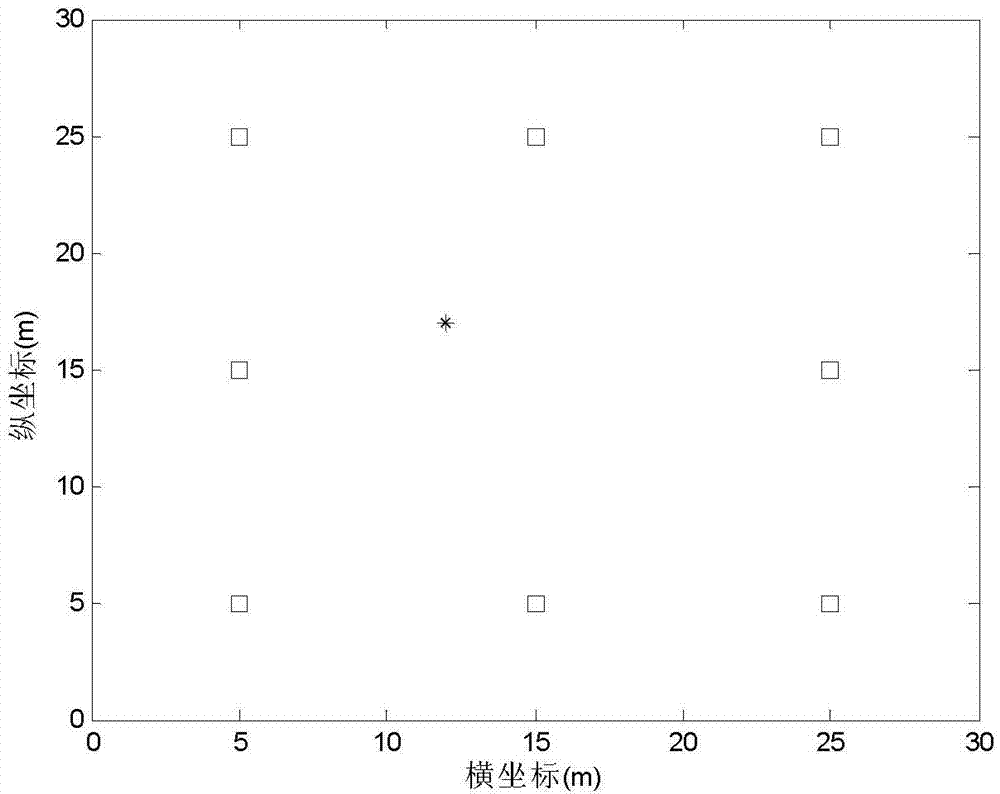
[0032] Step 1. Pre-deploy M beacon nodes in the working environment of the sensor network; assume any unknown node U in the working environment of the sensor network = (x, y), and let U receive information from the beacon node B i The coordinates of the signal are x i ,y i , namely B i It is visible to the unknown node U, i=1, 2,..., N, N≤M; wherein, N represents the number of beacon nodes visible to the unknown node U;
[0033] Step 2. According to the general signal propagation model, calculate the distance between the unknown node and the beacon node B under the influence of Gaussian noise n i distance Among them, at the distance from the beacon node d 0 Set the reference node at , and the reference node receives the beacon node B i The signal power is P i (d 0 ); unknown...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0052] Specific embodiment 2: The difference between this embodiment and specific embodiment 1 is that in step 2, according to the general signal propagation model, under the influence of noise n, the unknown node and the beacon node B i distance v i = 10 P i ( d 0 ) - P i ( d i ) - n 10 · α The specific process is:
[0053] P(d)=P(d 0 )-10αlg(d / d 0 ) (7)
[0054] Among them, d 0 is the distance f...
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0060] Specific implementation mode three: the difference between this implementation mode and specific implementation mode one or two is: in step three, v in step two i Perform an expectation analysis to get The specific process is:
[0061] Obtained according to formula (8),
[0062] lg v i = P i ( d 0 ) - P i ( d i ) - n 10 · α - - - ( 10 )
[0063] definition C = ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com