Use of biomarker in preparation of heart failure diagnosis composition and diagnosis device
A diagnostic composition and biomarker technology, which can be used in disease diagnosis, biological testing, measurement devices, etc., to solve problems such as cardiac insufficiency and increased discomfort
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
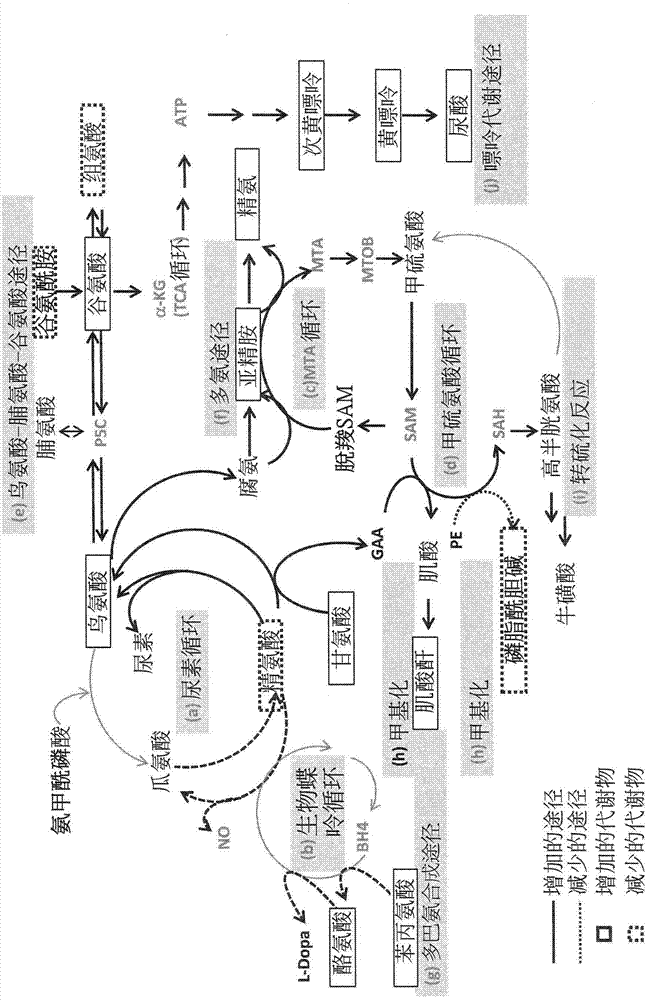
[0106] Example 1: Whole metabolomics analysis for diagnosing and judging the stage of heart failure
[0107] 1. Basic characteristics of each group of patients
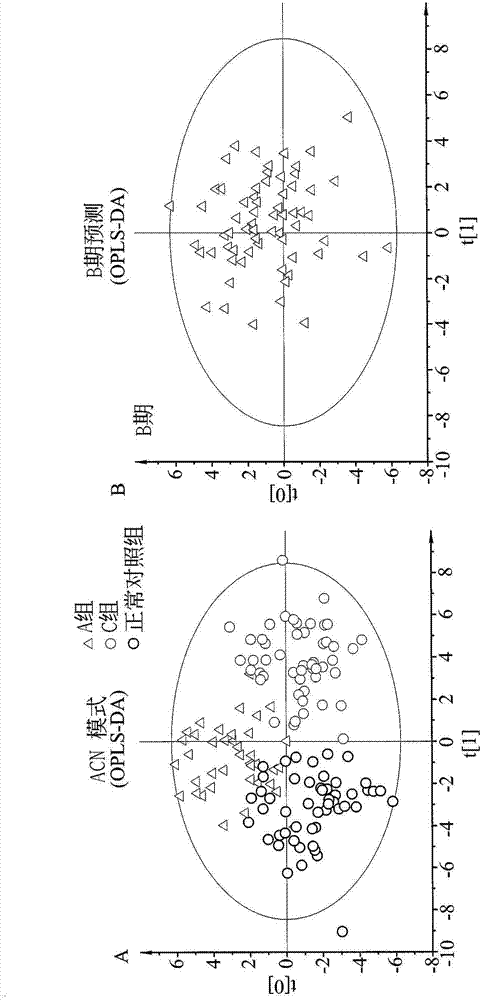
[0108] In this embodiment, a total of 234 individuals were recruited, including 51 normal individuals and 183 patients in stage A (n=43), stage B (n=67) and stage C (n=73). The room data are shown in Table 1. In most of the variables, a significant trend of change from normal controls to patients with stages A, B, and C can be noted. Compared with the normal control group, the BNP content of patients in stage C was significantly higher, and the QRS complex was wider, but the total cholesterol, low and high density lipoprotein cholesterol (low and high density lipoprotein cholesterol), sodium, hemoglobin , albumin (albumin) and estimated glomerular filtration rate (estimated glomerular filtration rate) are lower. In terms of age, although there was no significant difference among the patients in each group, they wer...
Embodiment 2
[0158] Example 2: Targeted Metabolomics Analysis for Diagnosis and Judgment of Heart Failure Stage
[0159] 1. Patient
[0160] A total of 145 individuals were enrolled in this embodiment, including 62 normal individuals and 83 patients in stage C.
[0161] 2. Target metabolomic analysis in HF and normal control group
[0162] In order to quantify the concentration of metabolites, this example uses the Biocrates kit to perform plasma metabolomics analysis according to the target metabolomics workflow, and uses the OPLS-DA mode to perform bioinformatics data set analysis. To test whether target metabolite profiles could distinguish stage C HF patients from normal controls, a total of 201 variables were used in this analysis. Metabolites sufficient to distinguish between the two groups are listed in Table 9 (these metabolites had a VIP score >1.0).
[0163]
[0164]
[0165]
[0166]
[0167]
[0168] 3. Distinguish stage C patients from normal controls
[016...
Embodiment 3
[0173] Example 3: Targeted Metabolomics Analysis for Assessing Heart Failure Prognosis
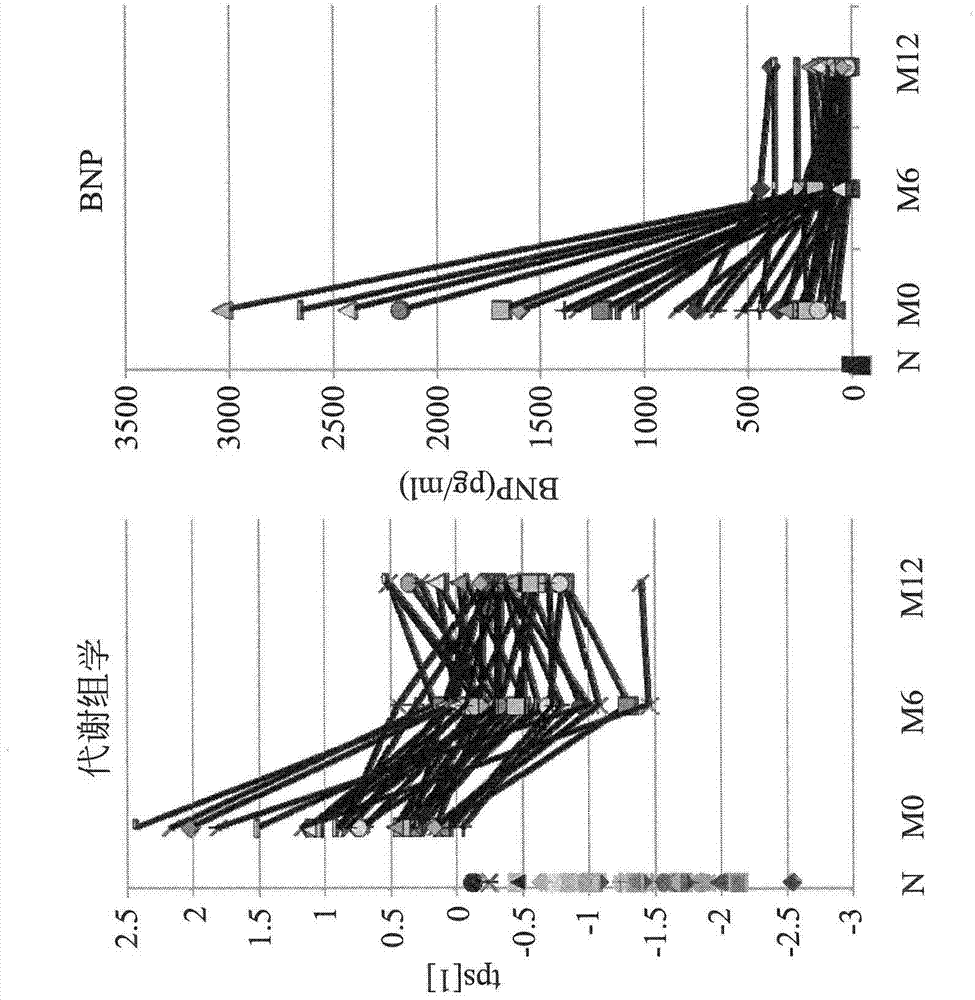
[0174] 1. Prognostic value of metabolomic signatures
[0175] To assess the prognostic value of metabolomics and BNP, the following assays were performed for stage B and C patients. In order to search for predictive metabolites (predictors) in the composite event of all-cause mortality and HF-related readmission rate, extensive analysis in the target metabolite data set showed that four metabolites (dimethylarginine / Arginine ratio, spermidine, butyrylcarnitine, and total essential amino acids) combined to produce ideal prognostic value significantly better than BNP. The resulting parameter by combining these four metabolites is called tPS [3]. The AUCs of the ROC curves for tPS[3], tPS[2] (derived from all target metabolite data sets) and BNP content were 0.853, 0.792 and 0.744 ( Figure 5 A). Table 11 shows the AUC data (by ROC curve) and log rank (by Kaplan-Meire analysis) of these ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com