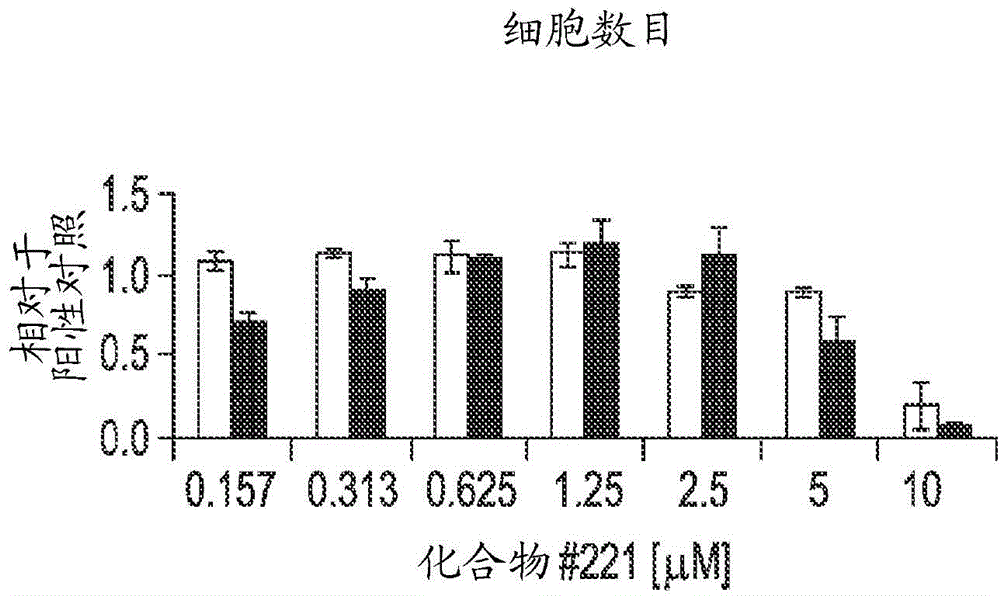
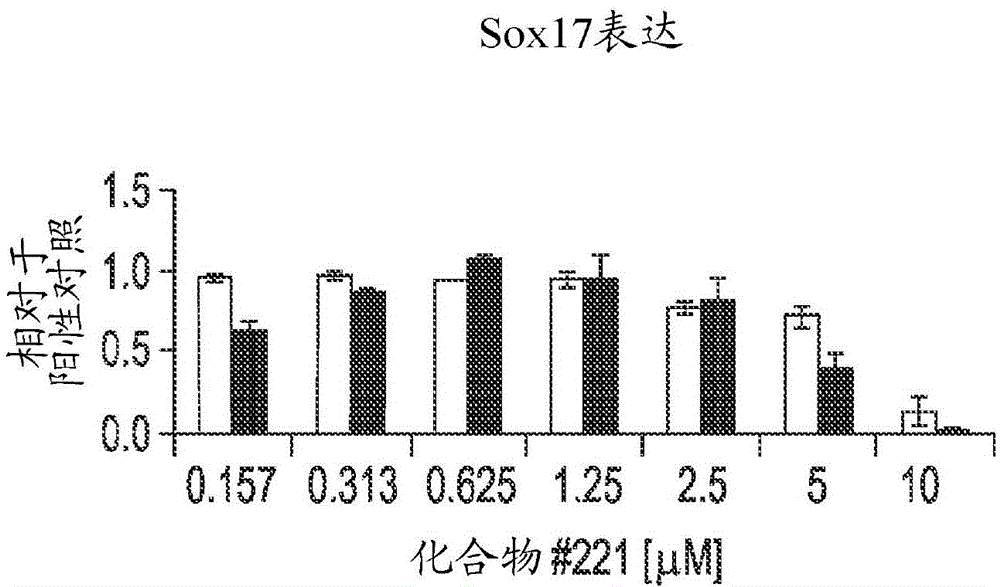
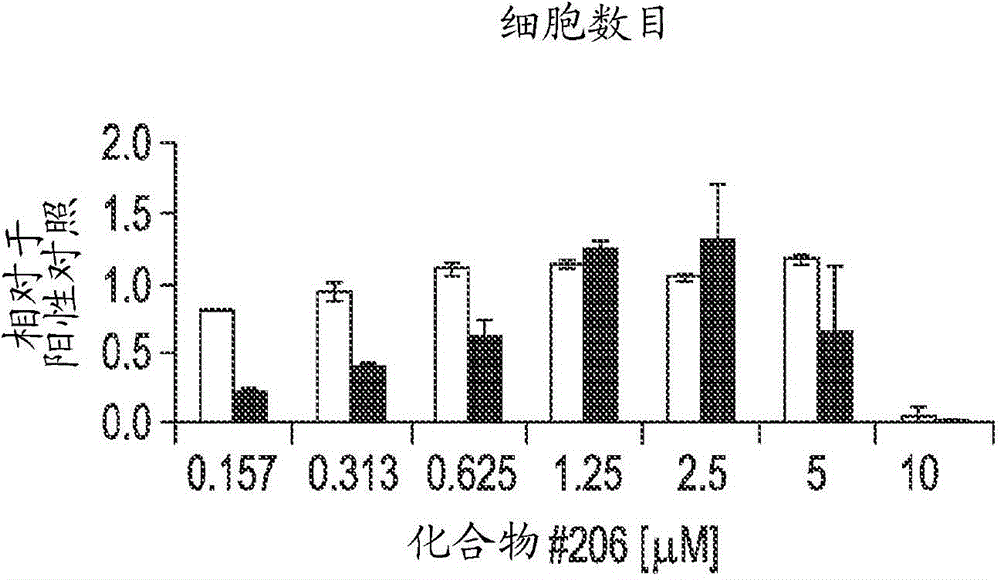
Differentiation of human embryonic stem cells into pancreatic endocrine cells
A technology of embryonic stem cells and cells, applied in the field of processing pluripotent cells, can solve problems such as complex methods and reduced cell expansion
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0270] human embryonic stem cell cultures
[0271] Stem cells are undifferentiated cells defined by their ability at the single-cell level to both self-renew and differentiate to produce progeny cells, including self-renewing progenitors, non-renewing progenitors, and terminally differentiated cells. Stem cells are also characterized in that they have functional cells differentiated from various germ layers (endoderm, mesoderm, and ectoderm) into various cell lineages in vitro, as well as tissues that generate various germ layers after transplantation and are substantially The ability to contribute to the formation of most, if not all, organizations.
[0272] Human embryonic stem cell lines H1, H7 and H9 were obtained from WiCell Research Institute, Inc., (Madison, WI) and cultured according to the instructions provided by the source company. Briefly, cells were grown on mouse embryonic fibroblast (MEF) feeder layers in ES cell medium consisting of 20% Knockout serum replac...
example 2
[0275] Derivation and culture of cells expressing pluripotency markers derived from human embryonic stem cells
[0276] Cells from multiple passages (passages 30-54) of human embryonic stem cell lines H1 and H9 were grown under hypoxic conditions (approximately 3% O 2 ) for at least three generations. Cells were cultured in MEF-CM supplemented with 8 ng / mL bFGF and seeded on MATRIGEL-coated plates according to Example 1.
[0277]Cells were then treated with DMEM / F12 medium supplemented with 0.5% FBS, 20 ng / mL WNT-3a (Cat. No. 1324-WN-002, R&D Systems, MN) and 100 ng / mL Activin-A (R&D Systems, MN) For two days, they were then treated with DMEM / F12 medium supplemented with 2% FBS and 100 ng / mL Activin-A (AA) for an additional 3 to 4 days. This protocol resulted in significant upregulation of definitive endoderm markers.
[0278] Cells were then treated with TrypLE TM Express solution (Invitrogen, CA) was treated for 5 minutes. The detached cells were resuspended in DMEM-...
example 3A
[0281] Derivation of cells expressing pluripotency markers from single cell suspensions of human embryonic stem cells
[0282] Cells from human embryonic stem cell lines H1 passage 33 and H9 passage 45 were incubated under hypoxic conditions (approximately 3% O 2 ) for at least three generations. Cells were grown in MEF-CM supplemented with 8 ng / ml of bFGF and plated on MATRIGEL-coated plates according to Example 1. At approximately 60% confluence, the cultures were exposed to TrypLE TM Express solution (Invitrogen, CA) for 5 minutes. The detached cells were resuspended in DMEM-F12+2% FBS medium, recovered by centrifugation, and counted with a hemocytometer. Detach the detached cells at 1000 to 10,000 cells / cm 2 Inoculated on tissue culture polystyrene (TCPS) treated flasks and in a standard tissue culture incubator at 37°C under hypoxic conditions (approximately 3% O 2 ) in DM-F12+2% FBS+100ng / mL Activin-A+20ng / mL WNT-3A+50ng / mL IGF-I+0.1mM mercaptoethanol (Invitrogen...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com