Method for rapidly decomposing time gap conflicts in distributed type TDMA protocol
A distributed and time-slotted technology, applied in the field of communication, can solve problems such as lack of information interaction, resource waste, and information duplication, and achieve the effects of improving transmission performance, good portability, and guaranteed utilization
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0031] The content of the present invention will be described in detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings.
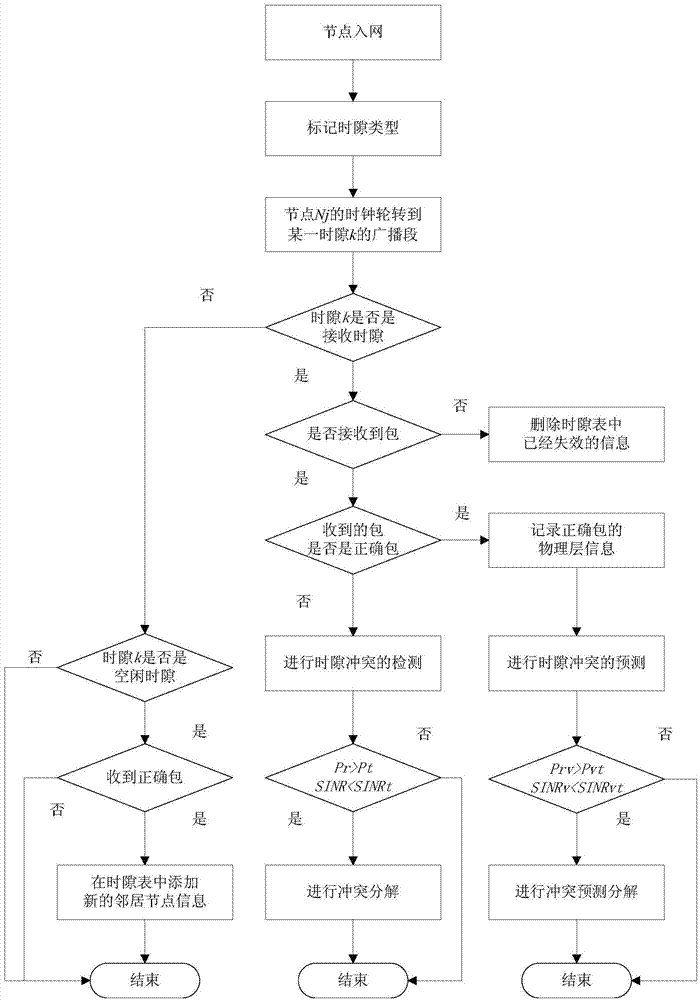
[0032] refer to figure 1 , the implementation steps of the present invention are as follows:
[0033] Step 1: Nodes join the network.
[0034] The node enters the network at a randomly set time point, establishes the time slot table of the node and listens to the channel, receives the broadcast packet sent by the one-hop neighbor node, and obtains the occupied time slot of the one-hop neighbor node and the own node contained in the broadcast packet. Occupied slots of two-hop neighbors.
[0035] Step 2: Mark the slot type.
[0036]Record the time slots occupied by the one-hop and two-hop neighbor nodes in the time slot table of this node, and randomly select a time slot in the time slot table that is not repeated with all the time slots occupied by the one-hop and two-hop neighbor nodes , marked as the sending slot;
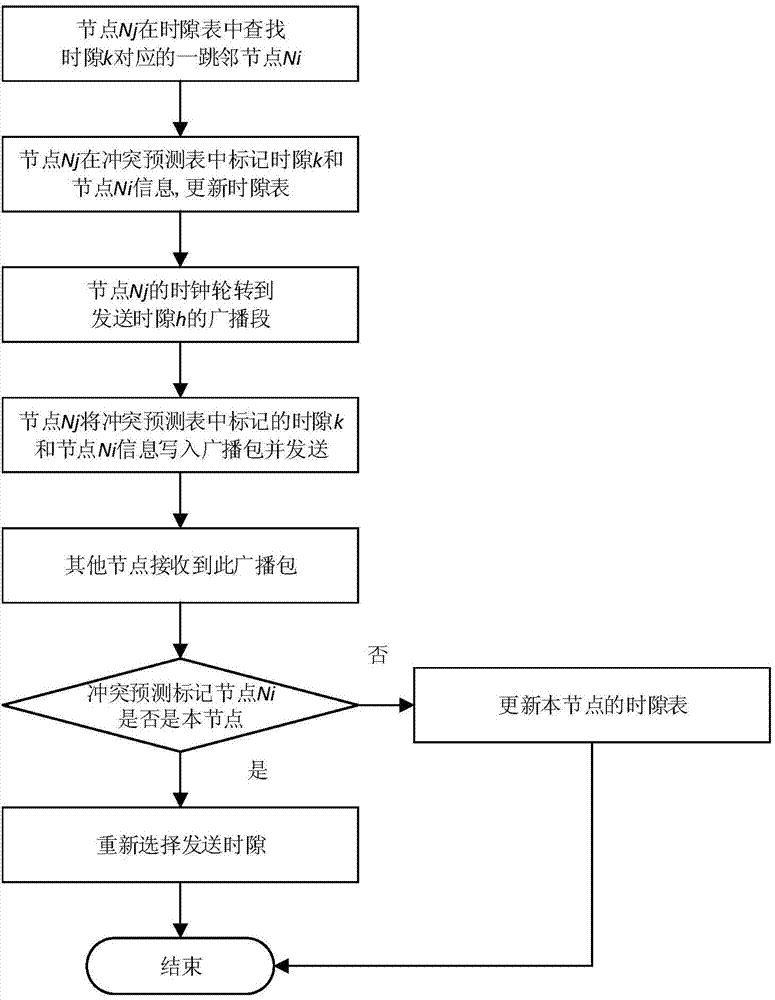
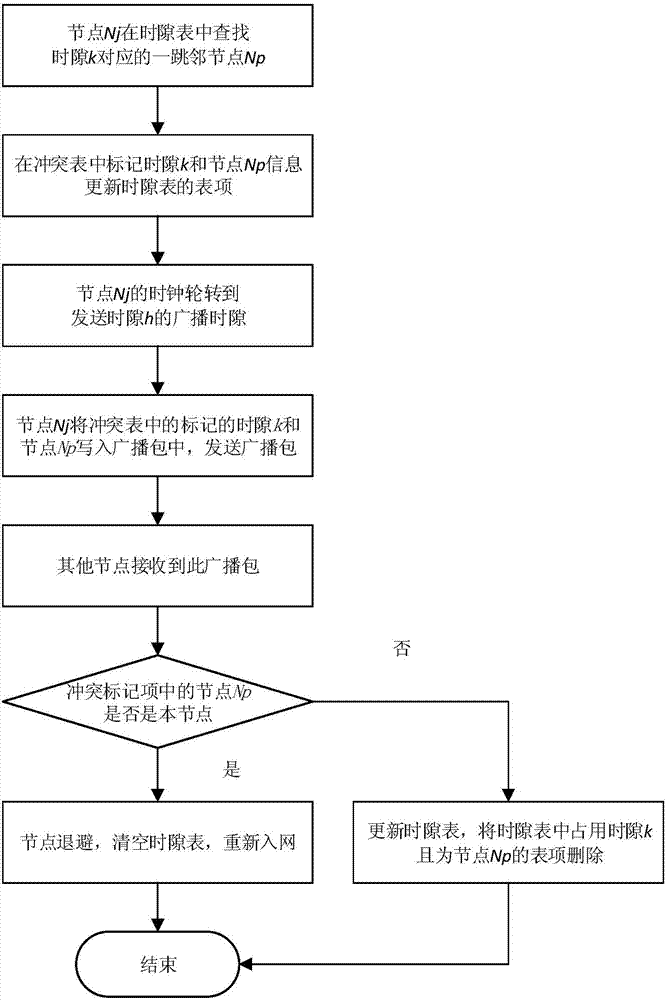
[0037] Mark the time slot occu...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com