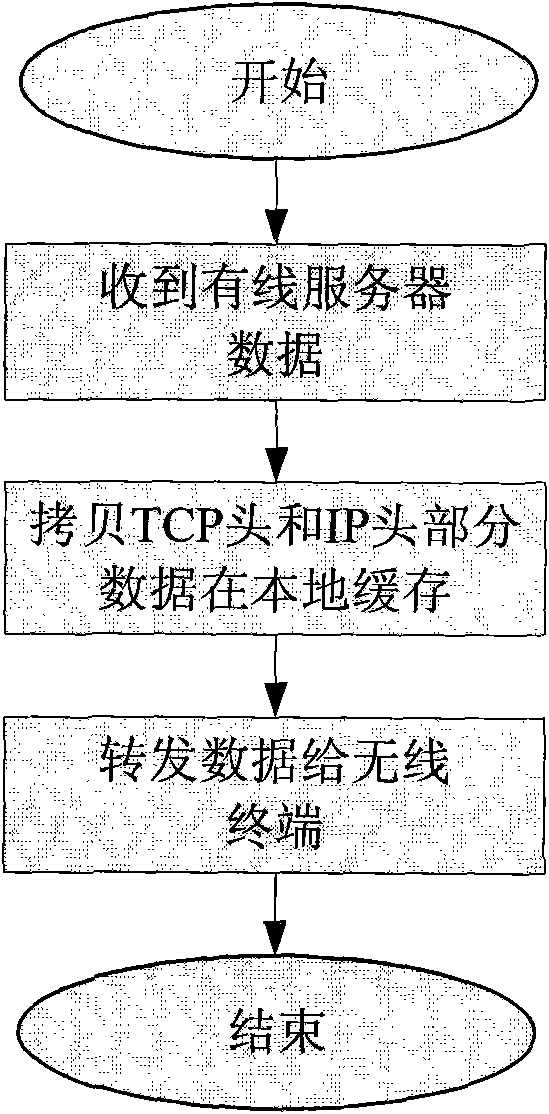
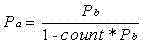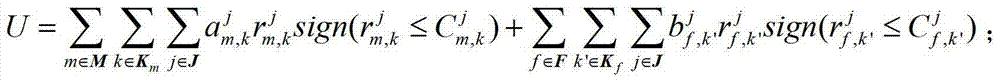Patents
Literature
111 results about "Cross layer design" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
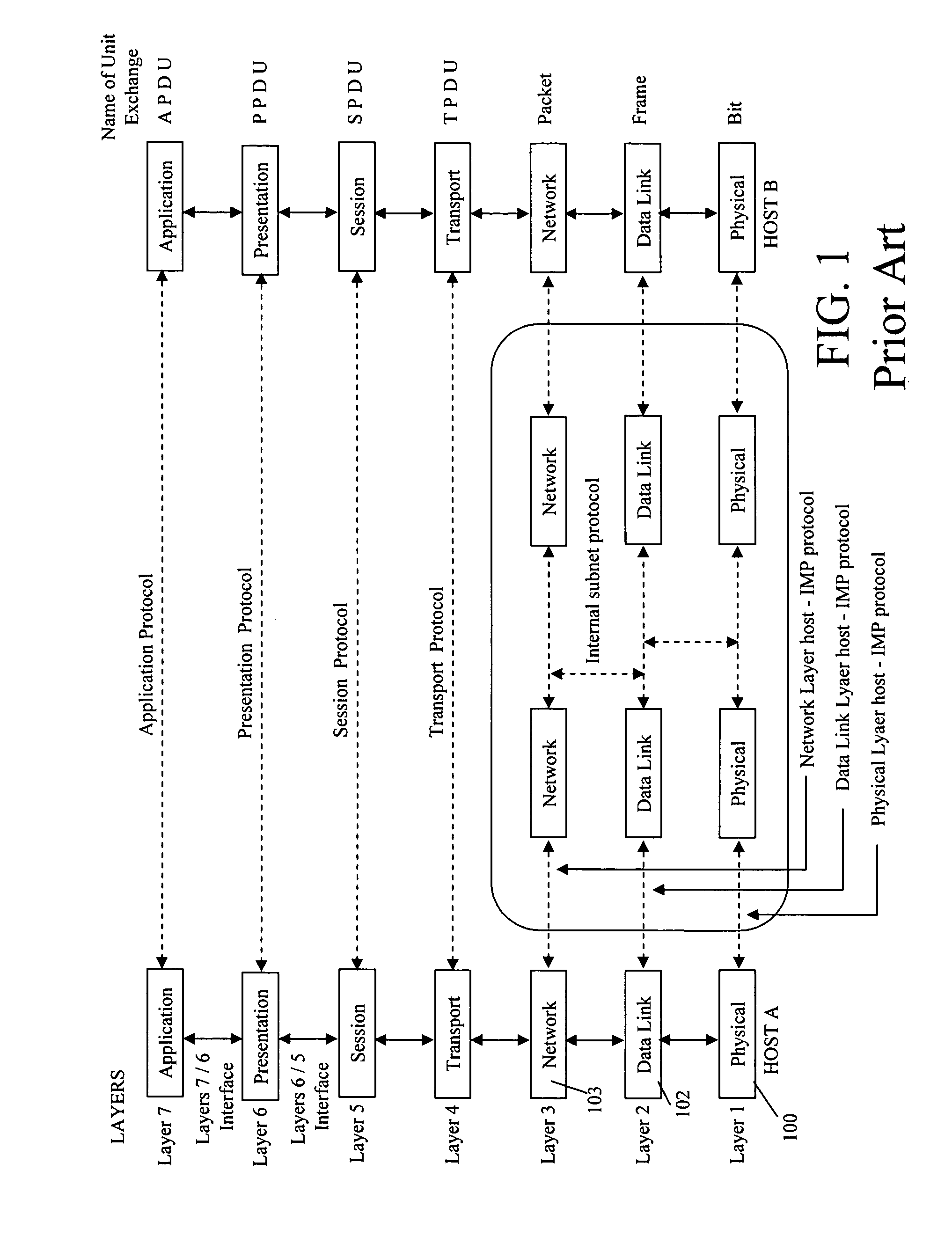
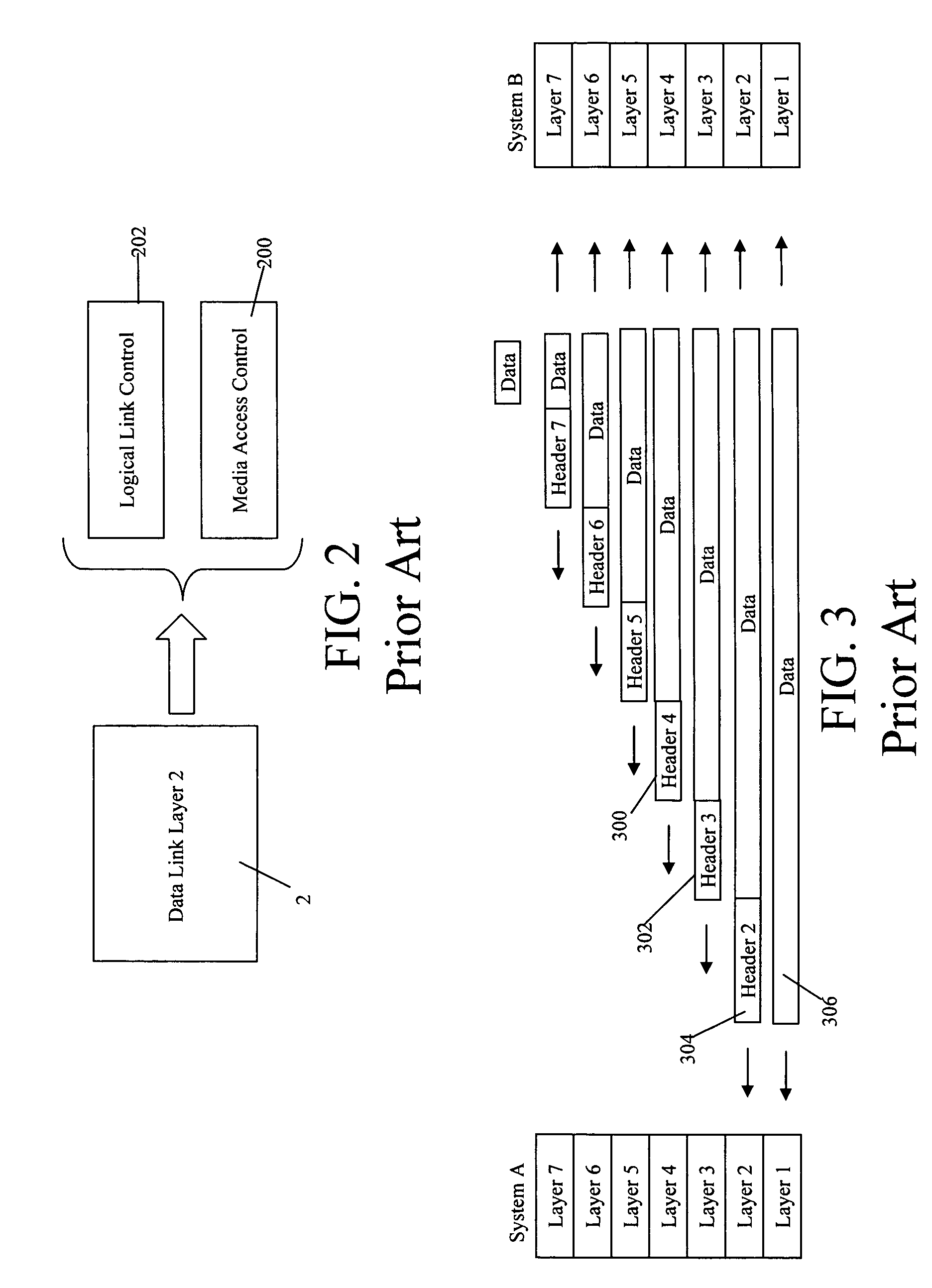
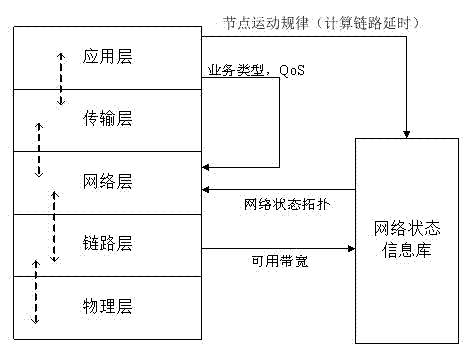
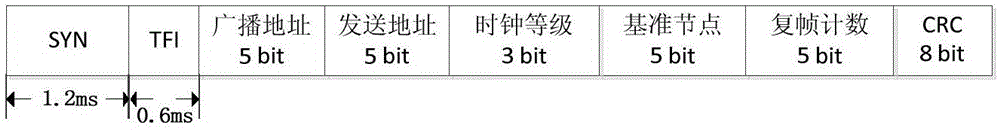
CROSS-LAYER DESIGN A DEFINITION OF CROSS-LAYER DESIGN. A layered architecture, like the seven-layer open systems interconnect (OSI) model [2, p. 20], divides the overall networking task into layers and defines a hierarchy of services to be provid- ed by the individual layers.
System, method, and computer program for superposition coded multicast with a single modulation scheme
InactiveUS20110222462A1Pulse modulation television signal transmissionModulated-carrier systemsSuperposition codingWireless data
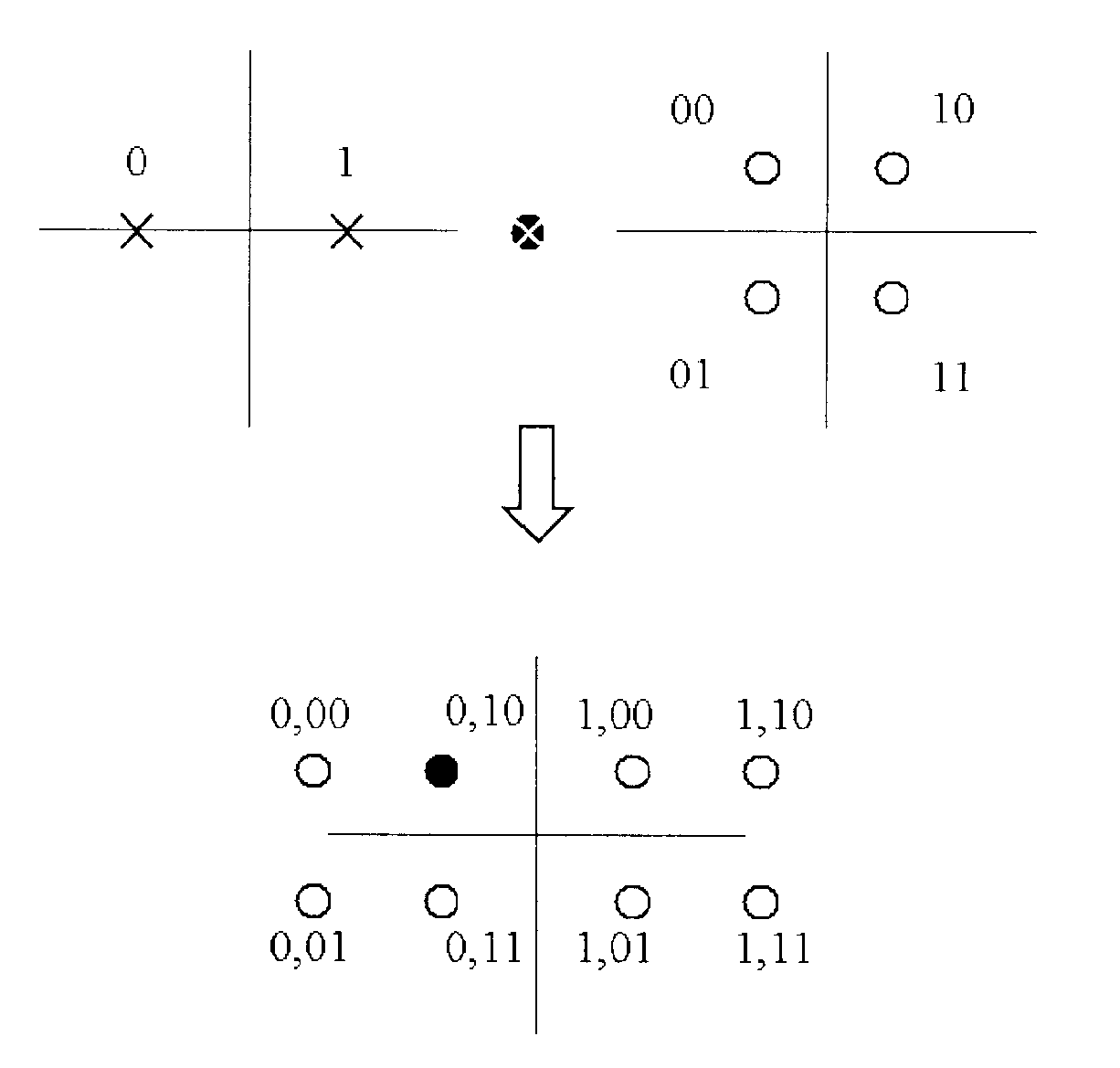
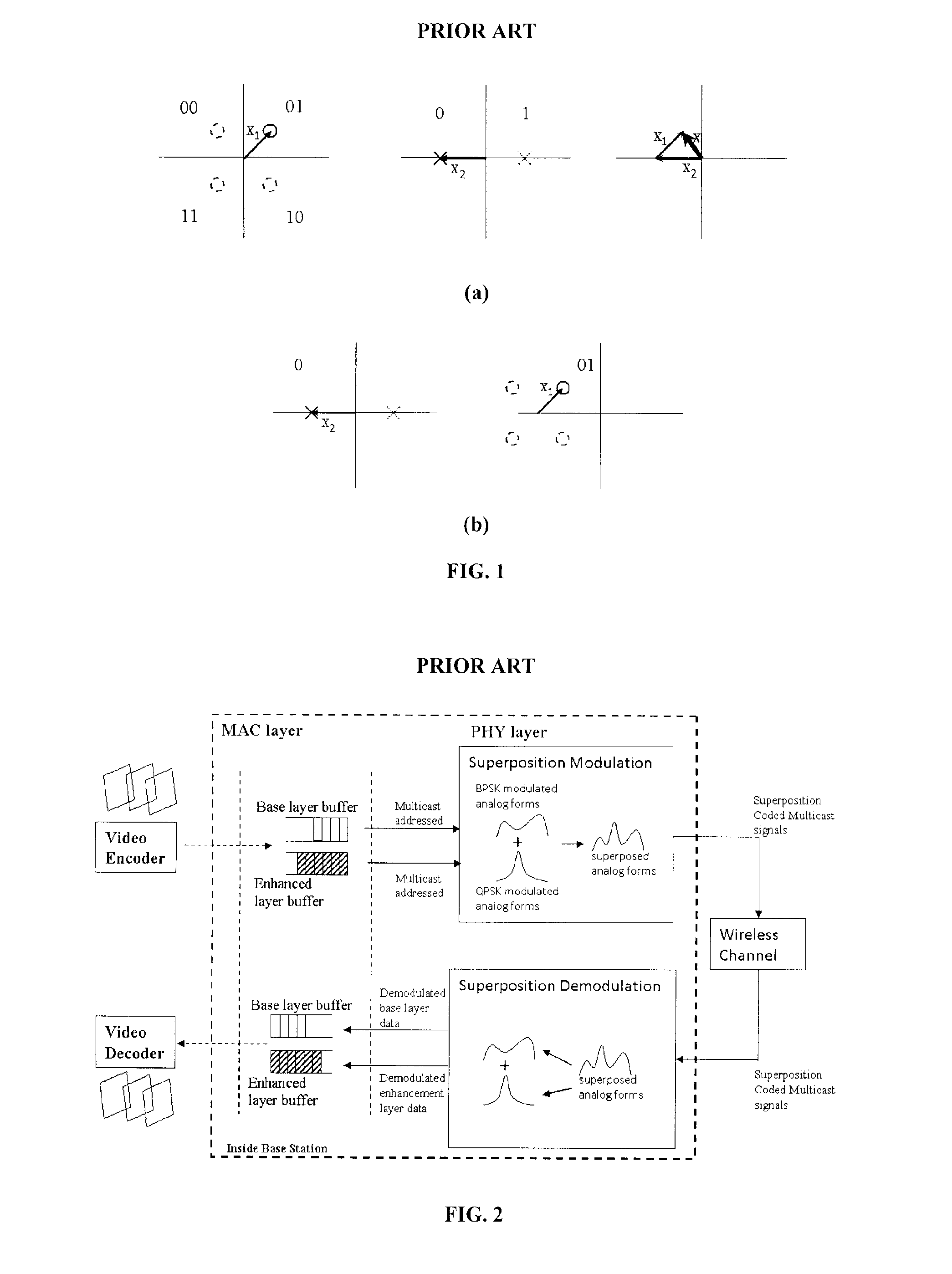
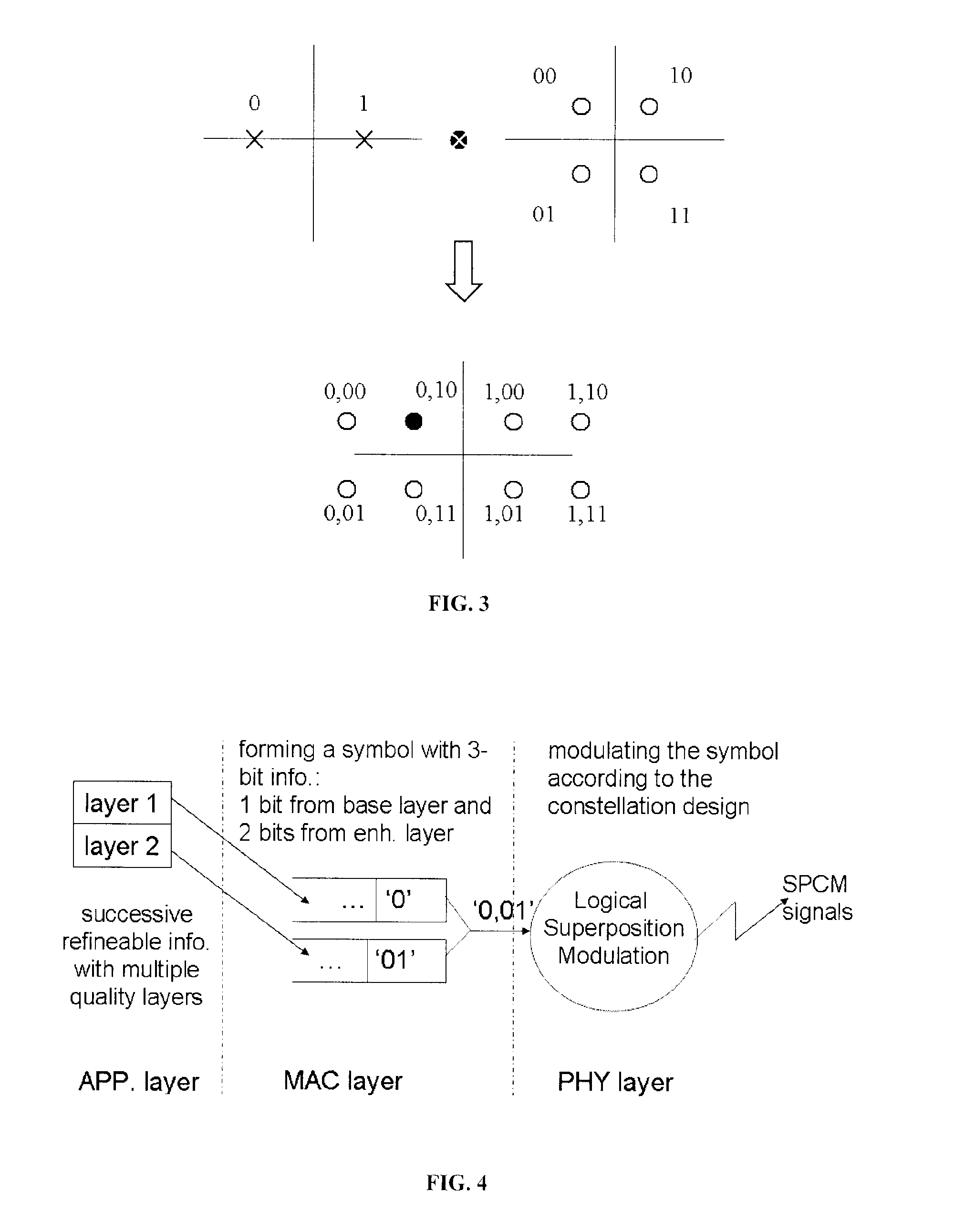
A cross-layer design architecture is provided for logical superposition coded (SPC) modulation for last-hop wireless data, aiming to overcome the effects of multi-user channel diversity in wireless video multicast. The proposed approach generates a logical SPC modulated signal by mapping successively refined information bits onto layered modulation through dynamic energy allocation and phase keying assignment, which mimics the superposition process for multiple modulated signals in convention hardware-based SPC modulation. At the receiver end, the received logical SPC signal is decoded by implementing a software-based approach on common demodulators without going through the signal-interference cancellation (SIC) process that is necessary in the conventional approach. The approach presented provides comparable or even better overall system throughput than by using the conventional hardware and SIC-based SPC modulation under various scenarios of different histograms of user channel conditions and power allocations for base and enhancement layer information.
Owner:HO PIN HAN +1
Interference-resilient joint MAC and routing scheme for wireless ad-hoc networks
InactiveUS7570593B1Reduce complexityImprove end-to-end network throughputError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsRouting decisionPath length
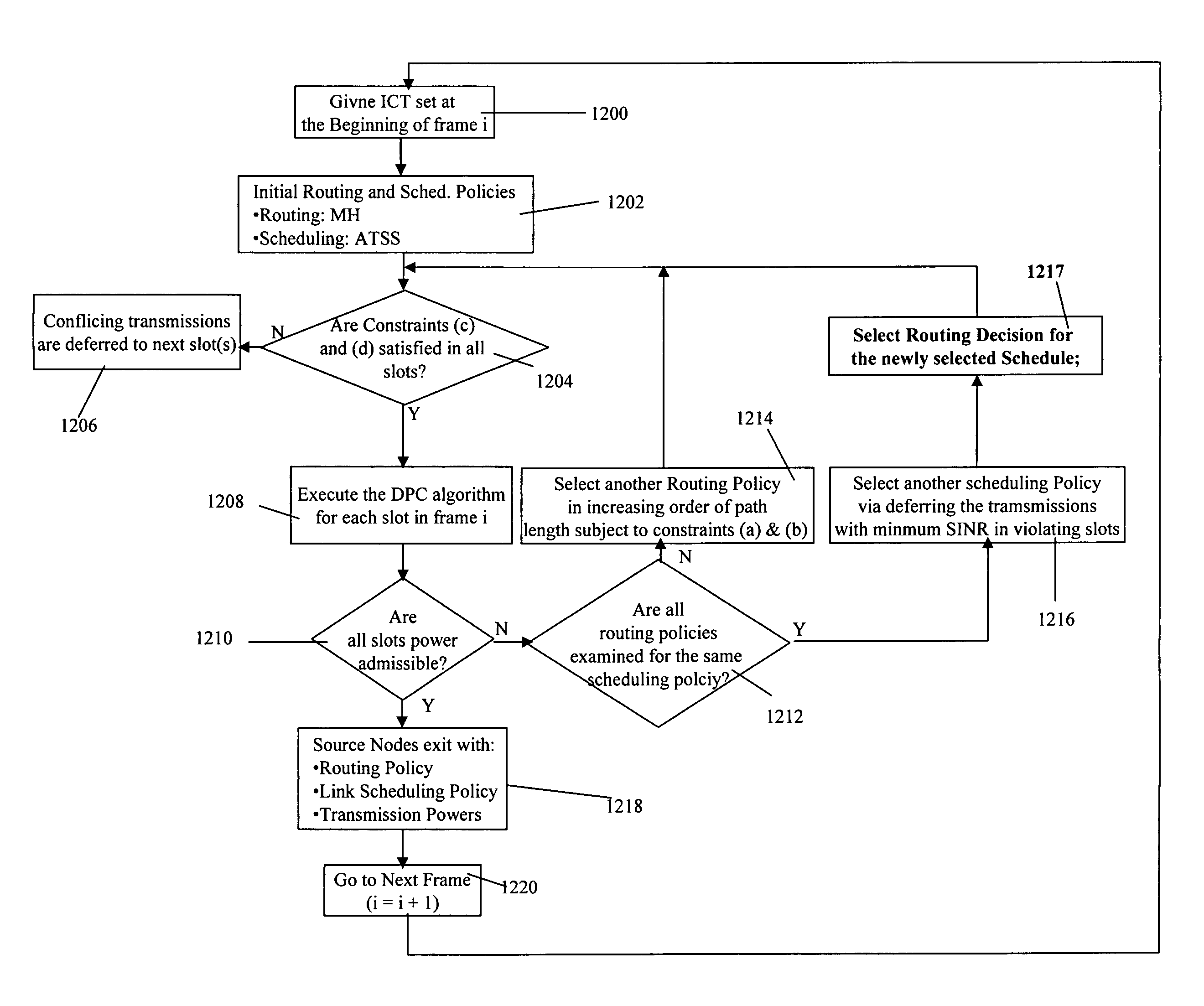
The present invention provides a cross-layer design framework for the multiple access and routing problems in interference-limited wireless ad-hoc networks. It identified interference as an essential factor that couples multiple access and routing decisions through the trade-off between MAC throughput and path length. It formulates an optimization problem that maximizes the multiple access throughputs subject to constraints on the path length, single-to-interference-and-noise-ratio, and transmission power. It incorporates interference into the routing metric and reduces problem complexity via the set-based routing concept that solves the problem for a set of spatially close source nodes. Accordingly, the present invention introduces a joint routing, scheduling and power control algorithm that handles intra-set interference. In addition, it adopted a simple set coordination scheme for handling inter-set interference.
Owner:HRL LAB
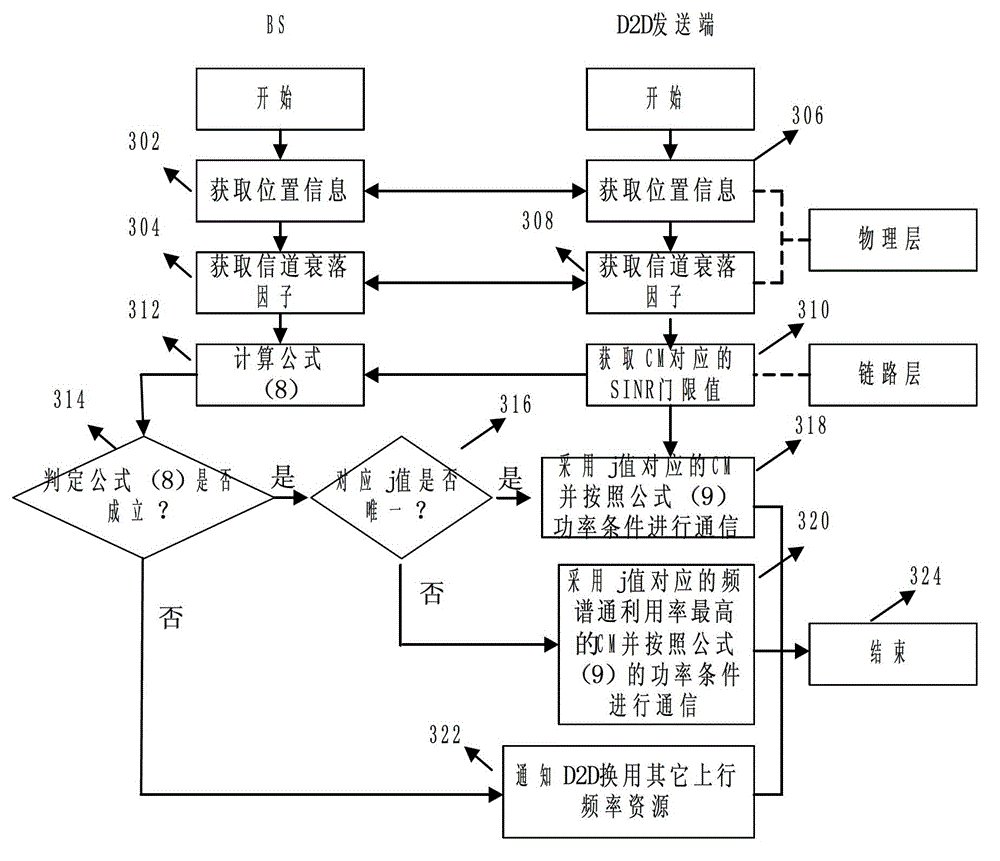
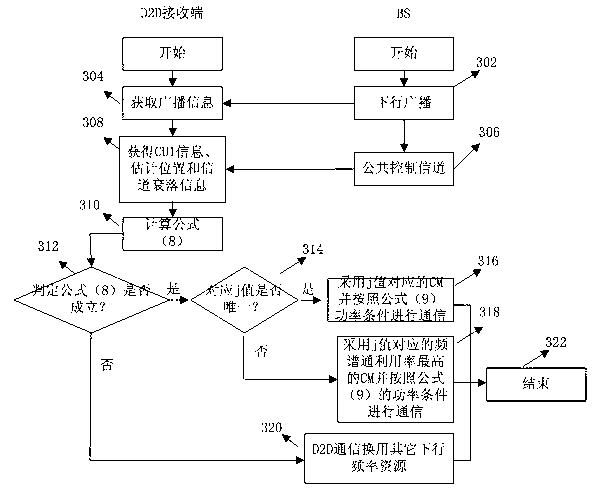
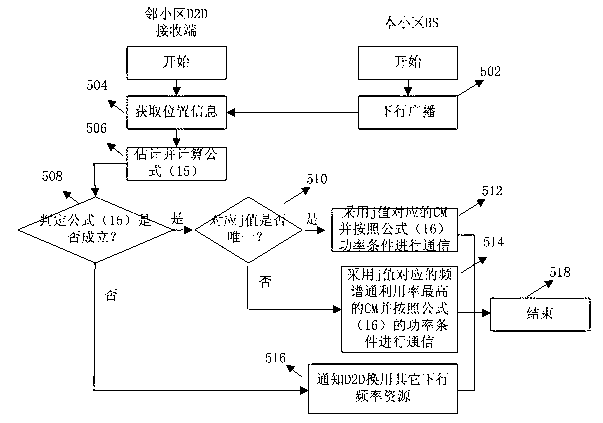
Cross layer design method of up resources of shared system by terminal direction connection technology
ActiveCN102883451AImprove resource utilizationImprove effectivenessWireless communicationPhysical layerHoneycomb
The invention relates to a cross layer design method of up resources of a shared system by the terminal direction connection technology. The method is used for conducting combined scheduling and optimization distribution on frequency, time, space and power resource by combining base stations, a D2D communication end physical layer, a link layer and a network layer. The method includes allowing D2D users to adopt the mode of simultaneously coordinating interference of the D2D client to a base state and interference of honeycomb users to the D2D client when the D2D users share up link resources of a honeycomb system to keep normal communication of a traditional user link and obtain effective gain brought by the D2D direction connection technology, and conducting cross layer resource distribution mode on the resources through the link self-adapting method. The cross layer design method is specifically applied to the following three scenes: 1) a single D2D communication pair and the honeycomb users coexist in a housing estate; 2) a plurality of D2D communication pairs and the honeycomb users coexist in the housing estate; and 3) a single D2D communication pair and the honeycomb users coexist between housing estates.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
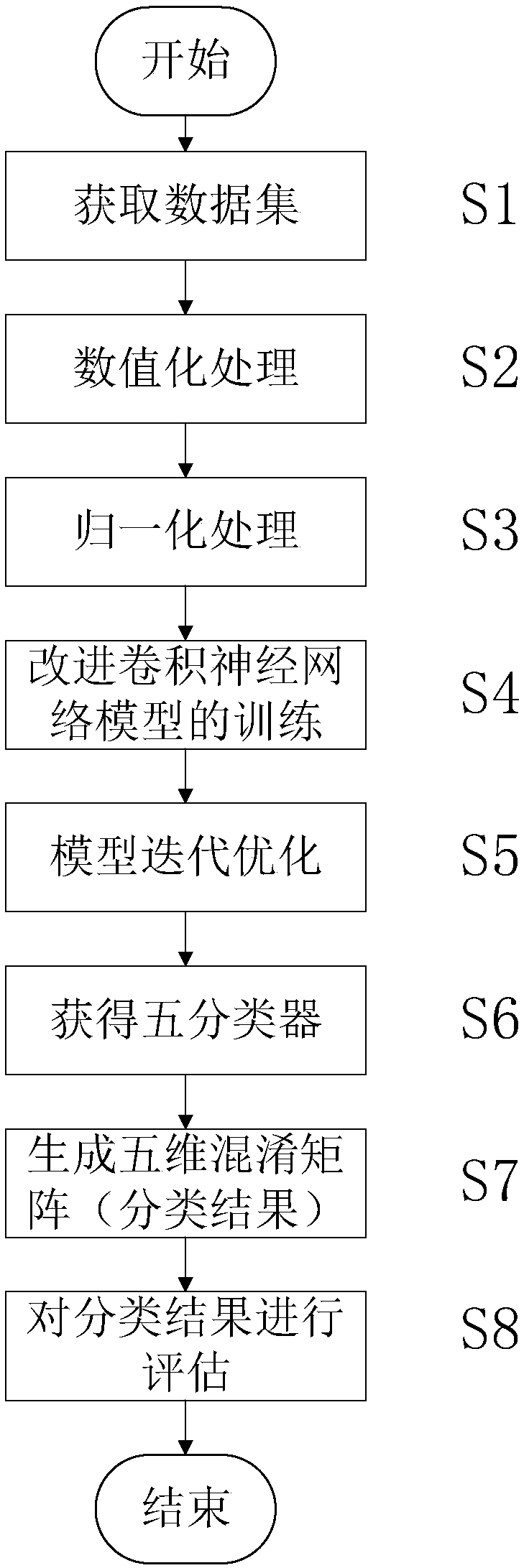
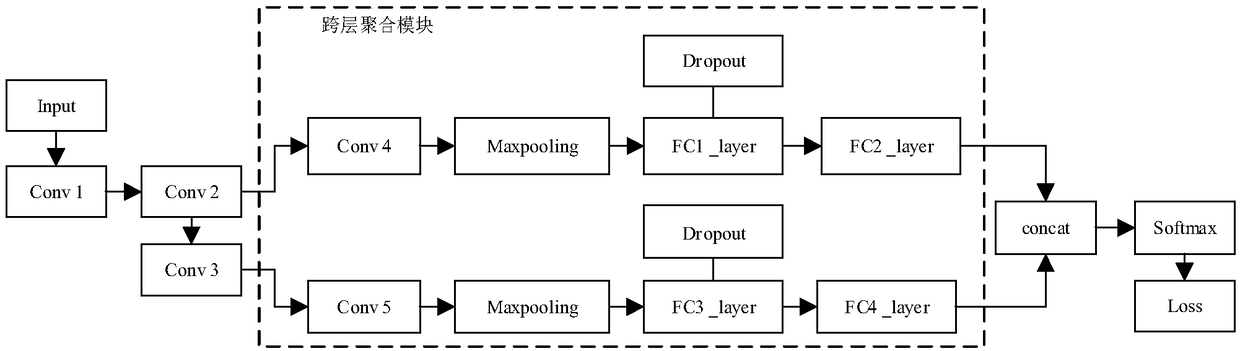
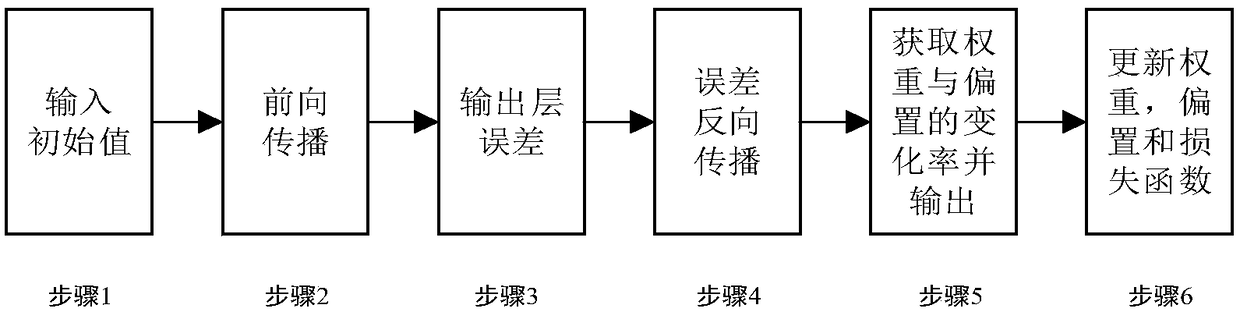
Network intrusion detection method based on improved convolutional neural network
ActiveCN109379379AFast convergenceHigh feasibilityNeural architecturesTransmissionData setFeature extraction
The invention provides a network intrusion detection method based on an improved convolutional neural network. The method comprises the steps of acquiring a data set, performing numeralization, performing normalization processing, improving convolutional neural network model training, performing iterative optimization of model parameters, acquiring five classifiers, outputting a five-dimensional confusion matrix to serve as a classification result, and evaluating the classification result; the network intrusion detection method based on the improved convolutional neural network provided by theinvention is based on an improved convolutional neural network model, model training is performed by using a preprocessed original sample data set in combination with a cross-layer design manner, themodel achieves a good convergence effect through continuous feature extraction and iterative optimization, and then a classification test is performed by using the trained classifier, so that the feasibility and effectiveness of an intrusion detection effect can be improved by the method.
Owner:CIVIL AVIATION UNIV OF CHINA
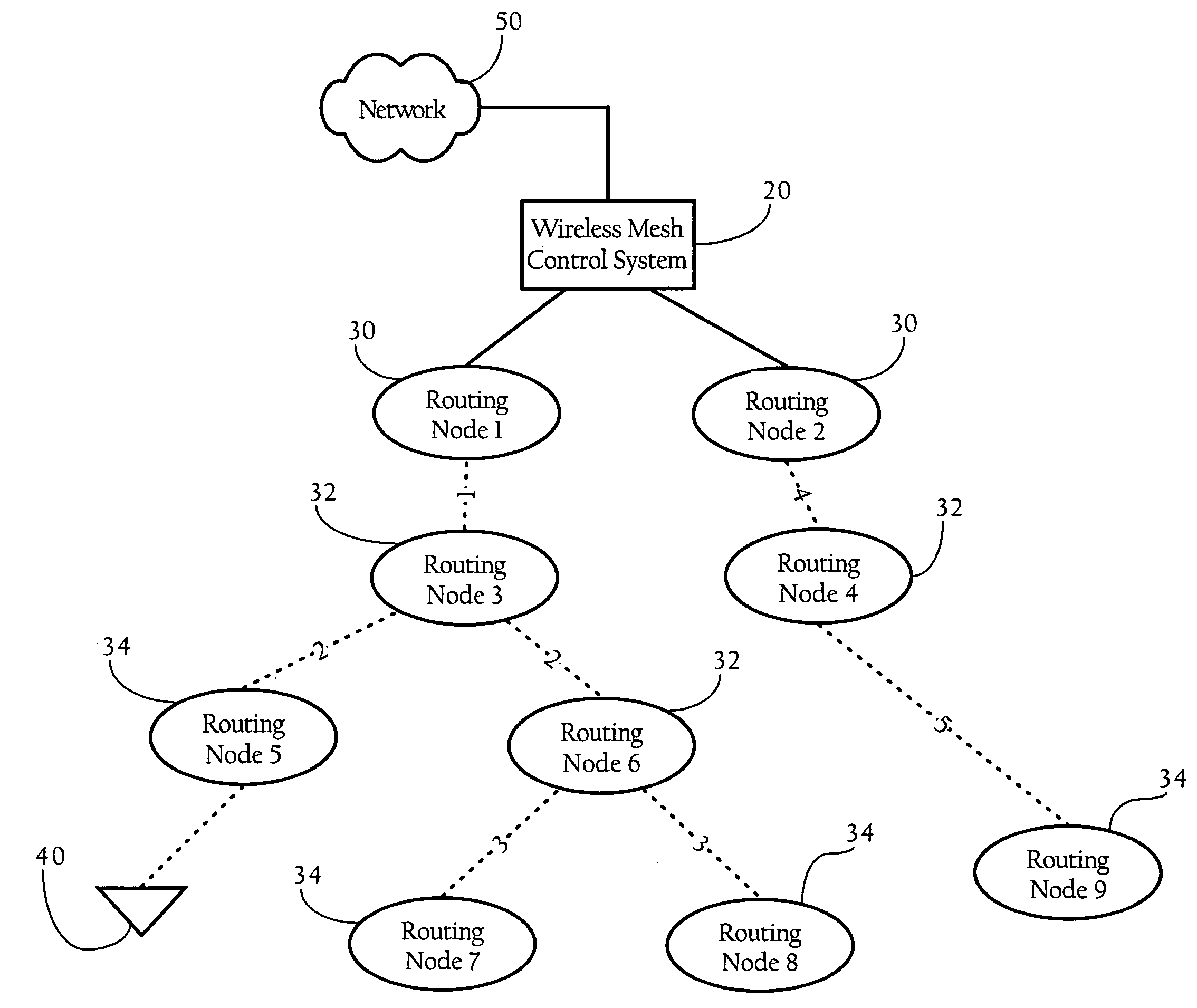
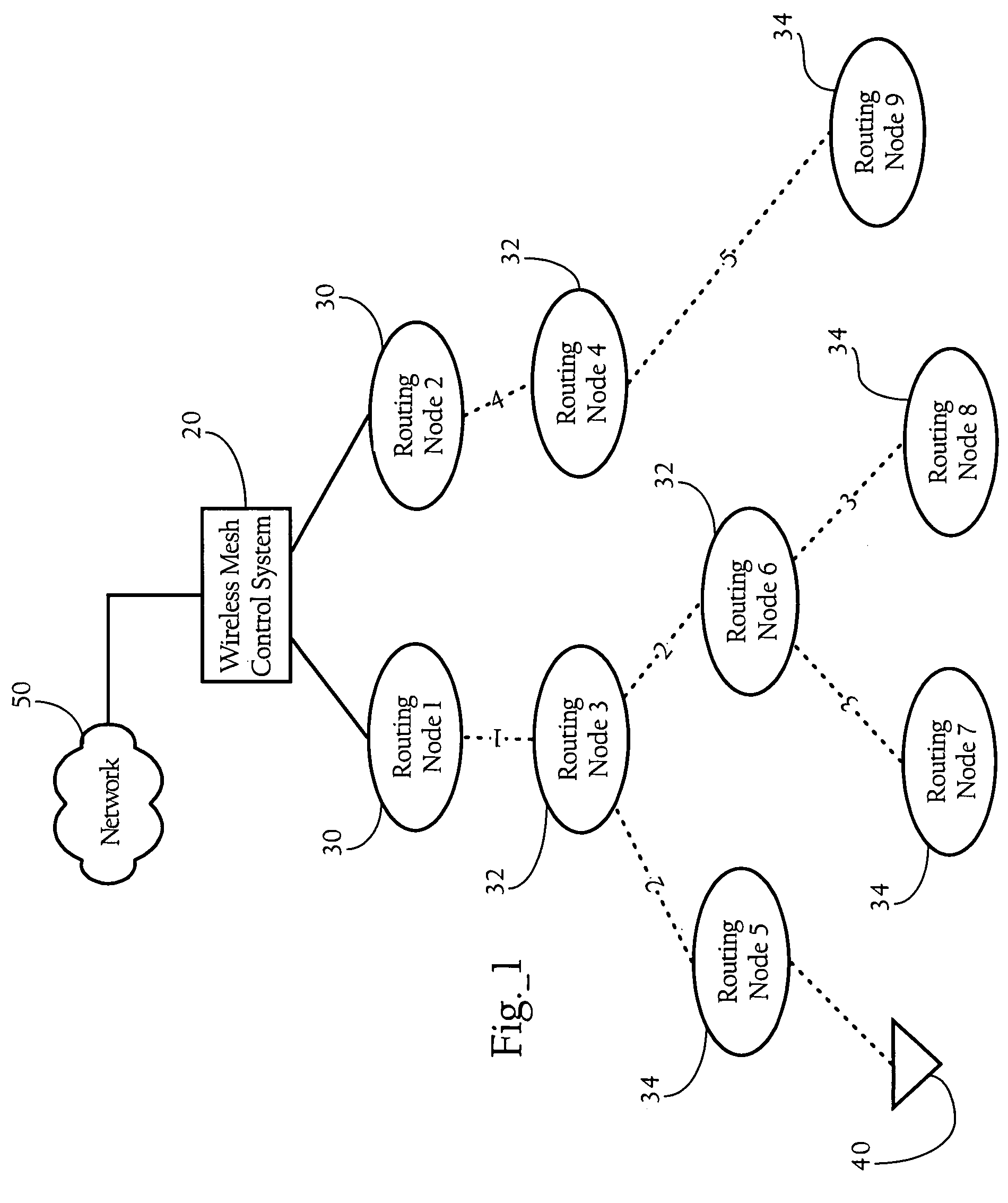
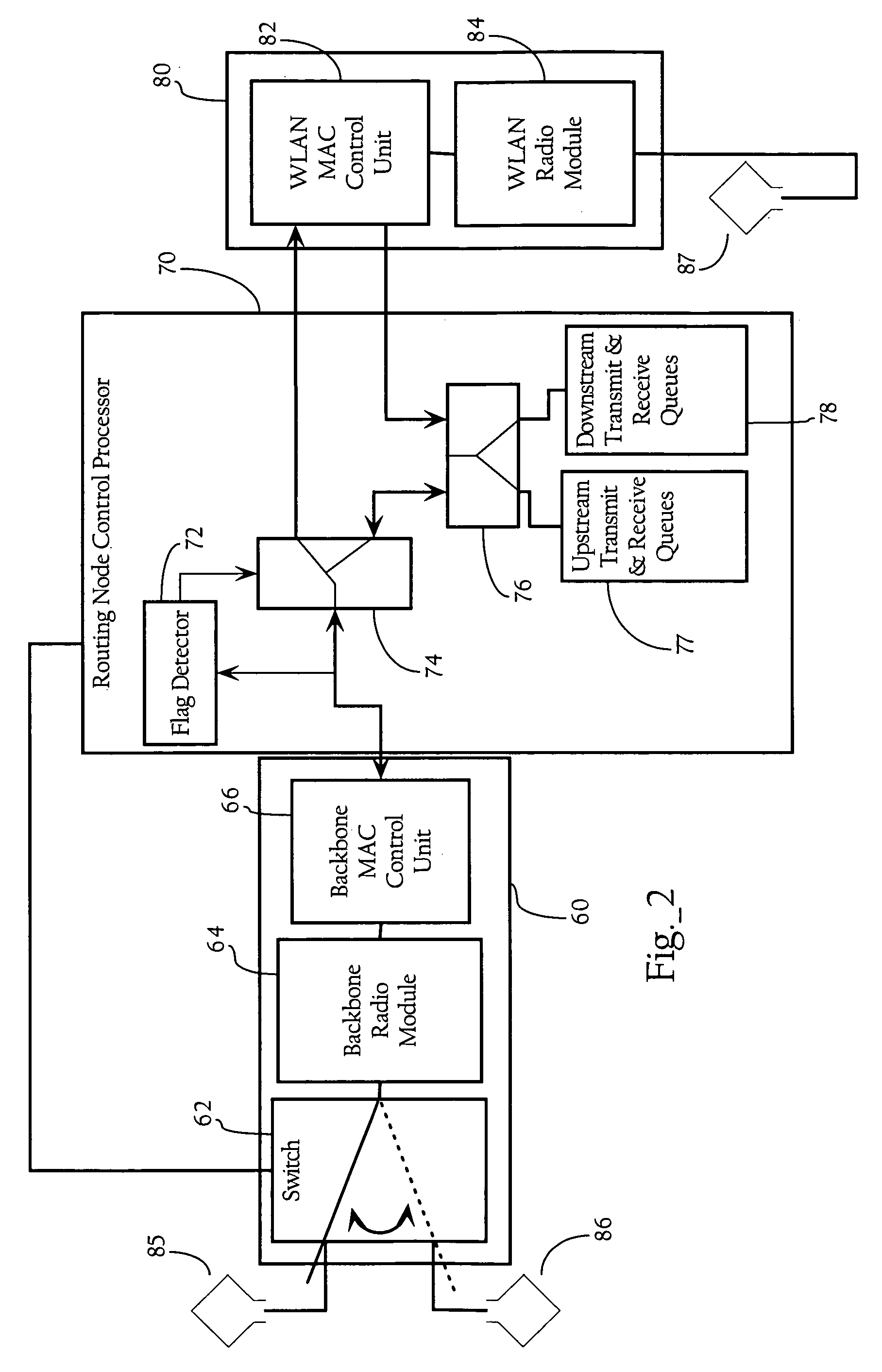
Cross-layer design techniques for interference-aware routing configuration in wireless mesh networks
Methods, apparatuses and systems directed to facilitating increased throughput in wireless mesh networks. Generally, according to one implementation of the present invention, routing nodes in a wireless mesh network combine metrics corresponding to the link and network layers to select a route to a root node in the wireless mesh network. In one implementation, for each neighbor, a given routing node computes a routing metric, which is based on the computed route cost and hop count, and selects a preferred neighbor as the parent routing node based on the best routing metric.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
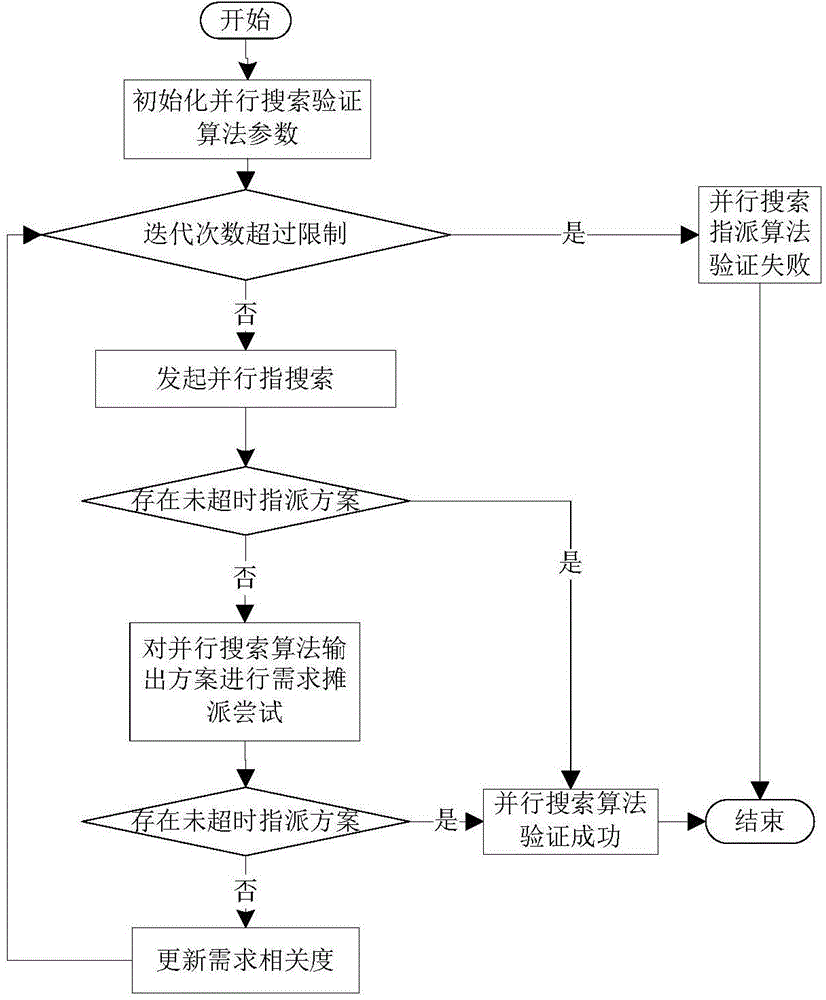
Implementation method of cross-layer routing capable of perceiving congestion
ActiveCN101674630AImprove throughputImprove latencyData switching networksWireless communicationRouting decisionWireless mesh network
The invention relates to an implementation method of cross-layer routing capable of perceiving congestion, which is suitable for the implementation of a routing protocol of a wireless Mesh network. The method provides two quality messages which are obtained from an MAC layer and can perceive the congestion condition of the network for a network layer through a cross-layer design: an expectation transmission success rate for perceiving link congestion and a residual load rate for perceiving node congestion. The expectation transmission success rate and the residual load rate of a path can be obtained through a routing discovery process, the two path quality messages are integrated so as to form a routing decision function, and routing is decided according to the routing decision function. The invention solves the problems that a network service load cannot be effectively balanced in the wireless Mesh network, and the fairness of the transmission of multiple traffic streams is poor.
Owner:GUANGDONG XUNTONG TECH
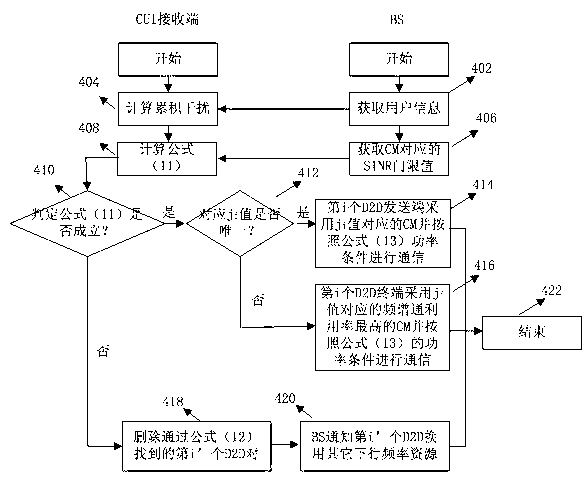
Cross-layer design method for downlink resources in D2D (device-to-device) technology sharing system
ActiveCN103024914AImprove resource utilizationImprove effectivenessWireless communicationCross layerWireless resources
The invention relates to a cross-layer design method for downlink resources in D2D (device-to-device) technology sharing system, in particular to a method and an algorithm for allocation and scheduling cross-layer resources in downlink resources of a cellular subscriber multiplexing cellular system with D2D terminals in an IMT-Advanced (international mobile telecommunications-advanced) system. A considered system model comprises an intra-cell application scenario and an inter-cell application scenario. D2D subscribers existing in a wireless cellular network system in the form of self-organization and cellular network subscribers co-exist in the form of underlay and share the same downlink radio resources (including channels, timeslot, power and space). Allocation and scheduling on the resources are discussed to solve the problems of interference coordination and suppression. The intra-cell application scenario and the inter-cell application scenario are considered respectively, common features of the different application scenarios are found, and personality factors of the different application scenarios are also considered. For characteristics of a D2D and cellular network system, the defects in existing resource allocation schemes are overcome and the resource-based cross-layer optimization, allocation and scheduling method is provided.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
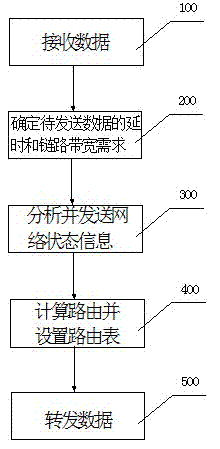
Aerospace information network information transmission method and system based on cross-layer resource optimization
ActiveCN102271368AReduce wasteAchieve optimal utilizationNetwork traffic/resource managementCross-layer optimizationSky
The invention relates to a cross-layer-resource-optimization-based space-sky information network information transmission method and a cross-layer-resource-optimization-based space-sky information network information transmission system. a route meeting service needs is calculated according to the states of a network and a node of a bottom layer for different service needs of an application layer by utilizing a cross-layer designing concept, the wasting of network resources is reduced in ways of realizing the balanced allocation of network bandwidth resources, avoiding congestion and reducing network control information, and the optimized utilization of the network resources is realized at the same time of ensuring the accurate transmission of data.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH SHENZHEN GRADUATE SCHOOL
Cross-layer communication method for OFDM link physical layer and MAC layer of underwater acoustic communication network
ActiveCN106788782AAchieve interactionAchieve sharingError prevention/detection by using return channelTransmission rate adaptationFrequency spectrumDiversity scheme
The invention provides a cross-layer communication method for an OFDM (Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing) link physical layer and an MAC (Media Access Control) layer of an underwater acoustic communication network. Based on the purposes of reasonably allocating channel resources and improving the throughput of the network, the performance of the network is optimized by a cross-layer data interaction method for a physical layer and an MAC layer. The physical layer adaptively adjusts the modulation order, coding rate and frequency diversity order according to an underwater acoustic channel environment, thus realizing data transmission of different rates to adapt to a fast time-varying underwater acoustic channel; the MAC layer adopts an improved CSMA (Carrier Sense Multiple Access ) / CA (Collision Avoidance) protocol, thus improving the retransmission success rate of data packets and reducing the data transmission delay; and the cross-layer design between the physical layer and the MAC layer solves the problems of high packet loss rate and low transmission efficiency caused by fast time variation, long transmission delay and other factors of the underwater acoustic channel, thus improving the throughput of the underwater acoustic communication network and the spectral efficiency of the system.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
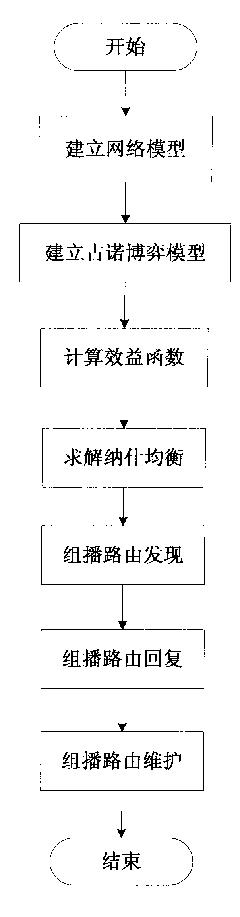
Energy optimization-based cognitive radio multicast routing method
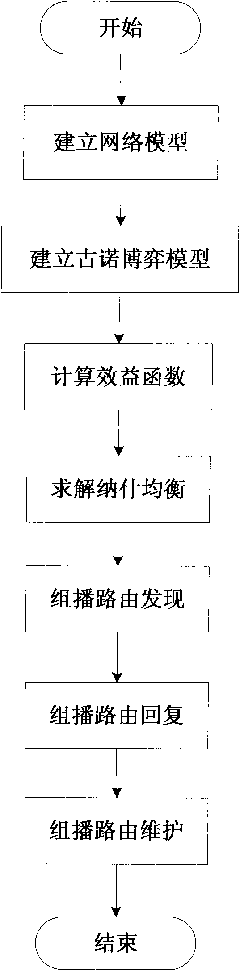
The invention belongs to the field of cognitive radio CR and in particular relates to multicast routing protocols in a CR network. The method provides an energy optimization-based CR multicast routing method. The method comprises the following steps of: establishing a network model; establishing a Cournot game model; calculating a profit function; solving Nash equilibrium; and establishing a multicast tree. The invention provides an energy optimization-based multicast routing algorithm in the CR network and efficient spectrum allocation rate is achieved by establishing a spectrum allocation model in the CR network according to a classical Cournot static model. And simultaneously, the problem of dynamic spectrum selection is solved by utilizing a mode of routing selection and spectrum allocation cross-layer design according to energy optimization and the thought of minimum increment capacity MIC and on-demand drive, and the multicast routing algorithm which is suitable for the characteristics such as diversity, dynamic and differentiation of the frequency spectrum of the CR network is designed.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
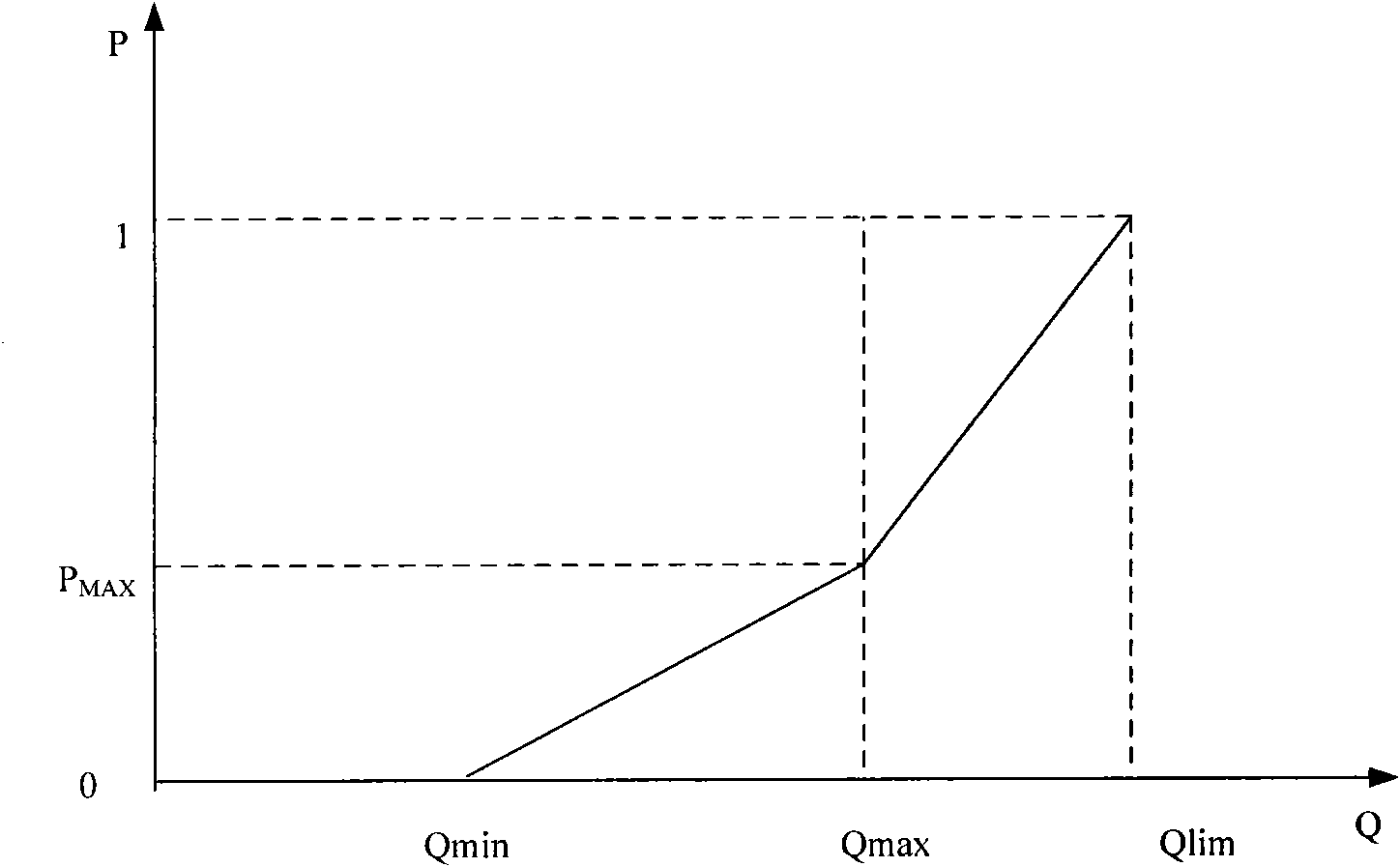
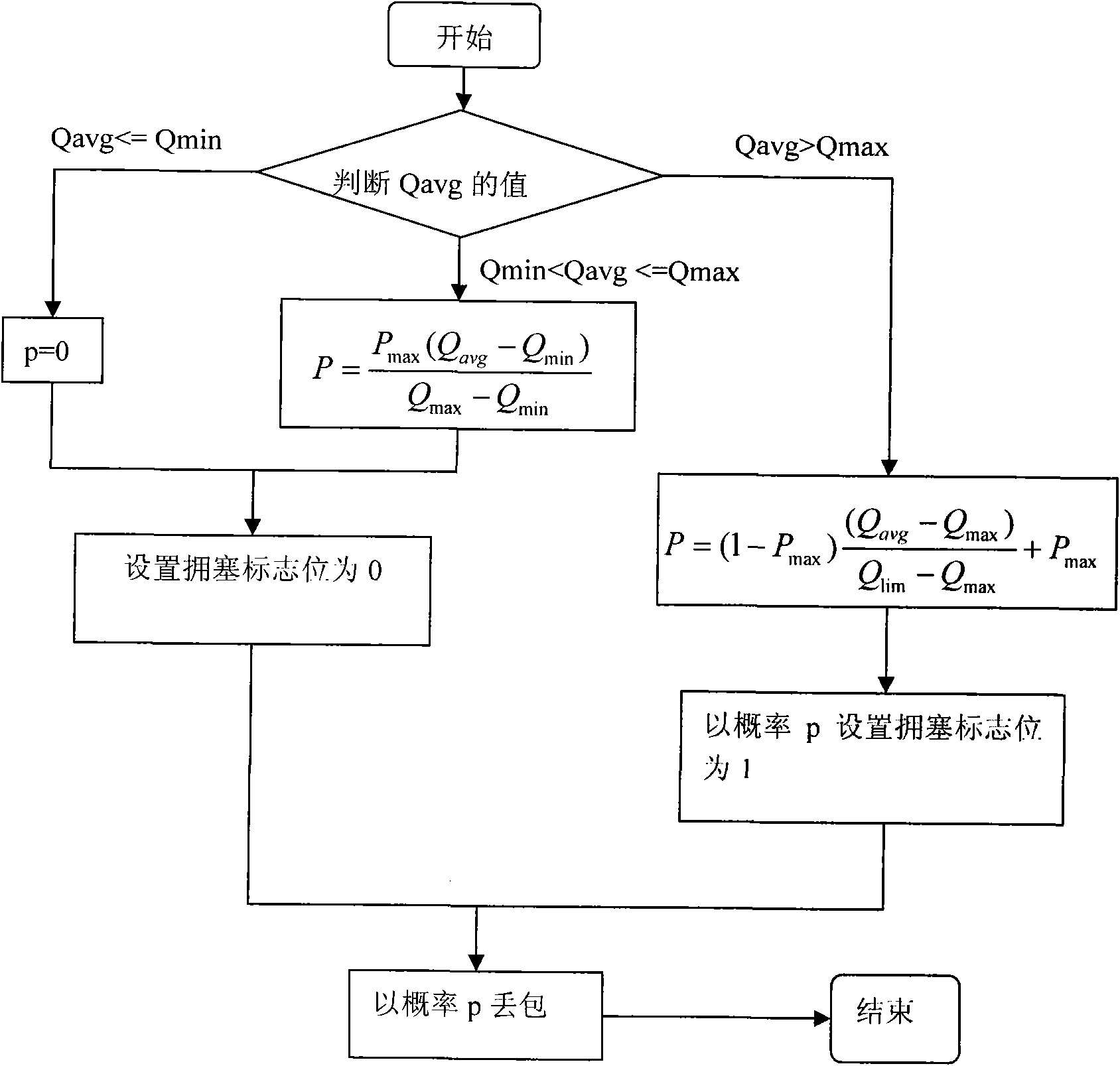
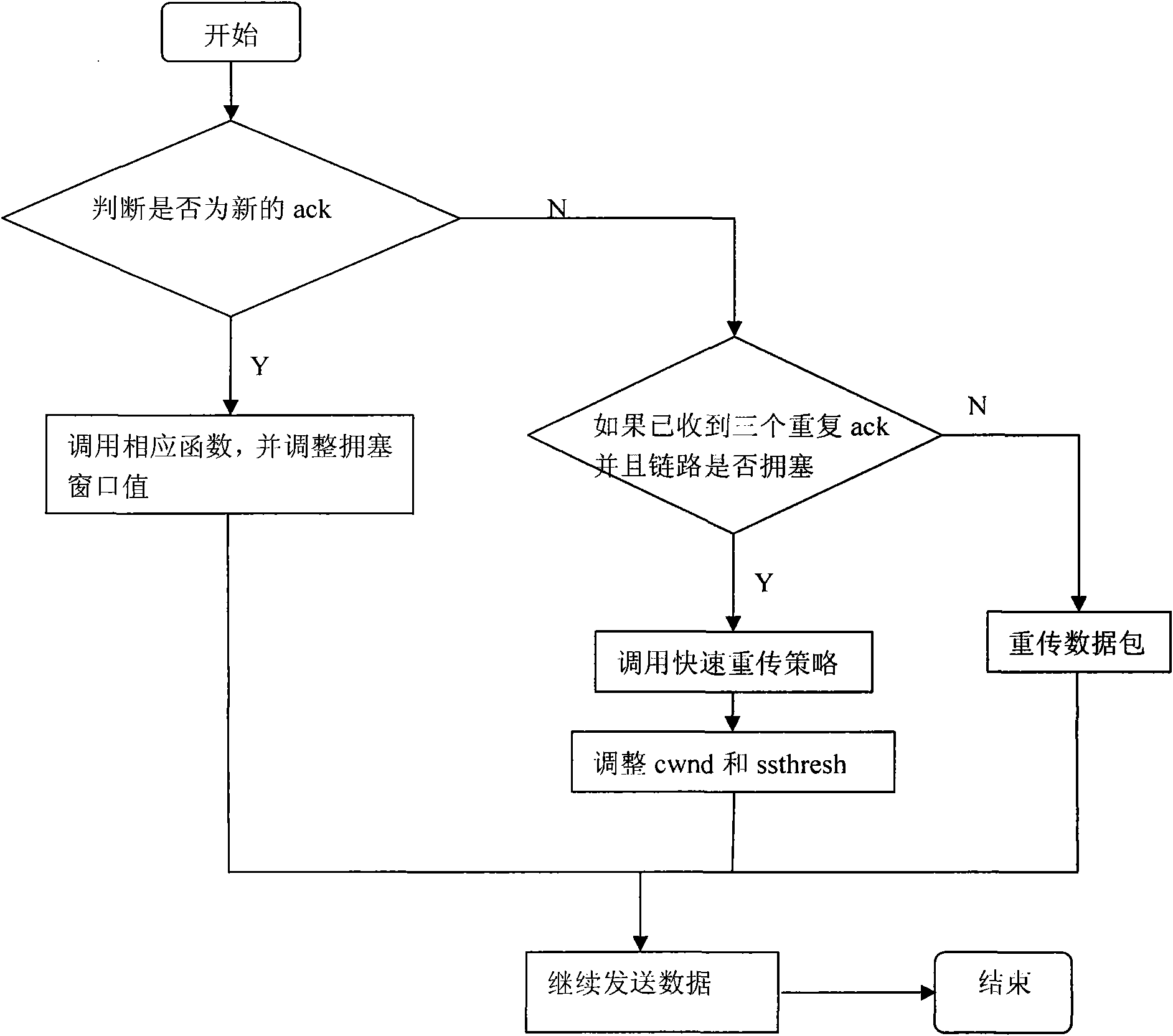
A Cross-Layer Congestion Control Method in Satellite Networks
InactiveCN102291389ALoss of correct judgmentImprove throughputData switching networksComputer networkTelecommunications
The design method of cross-layer congestion control in satellite network is a solution to enhance TCP performance by using cross-layer design in satellite network. It is mainly used to solve the impact of the high bit error environment of satellite network on TCP, so that TCP can predict congestion in time and correctly judge the packet loss caused by network congestion and bit error, which belongs to the field of congestion control of satellite network. It should have the following features: the present invention enables the TCP layer and the link layer to realize cross-layer interaction, so that the queue state in the link layer can be passed to the TCP layer, so that the TCP layer can judge the congestion status of the link according to the state of the queue , so as to adopt corresponding strategies, and finally achieve the effect of improving TCP performance.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Overlayer design based wireless sensor network energy-saving method
InactiveCN101119254AReduce energy consumptionProlong survival timeEnergy efficient ICTTransmission systemsWireless dataEngineering
The present invention discloses a wireless sensor network energy conservation method which is designed basing on the cross-layer, a MCU Active mode and a MCU Sleep mode are arranged on the processor MCU in the wireless sensor network, an ADC Active mode and an ADC Sleep mode are arranged on an analog-to-digital converter ADC, a MTRU Sleep mode, a WTRU Tx mode and a WTRU Rx mode are arranged on a wireless date sending module / receiving module respectively, and sent from a surveillance center according to the control command designed by the primitive to control the accesses of the different modes after being sent by the processor MCU, so as to conduct a cross-layer energy conservation optimization from an application layer, a network layer, a link layer and a physical layer of the wireless sensor network. Under the premise of not influencing the application performance and function, the present invention reaches the effect of reducing the whole energy consumption of the nodes, and greatly prolongs the use life of the batteries used on the nodes and greatly lengthens the life span of the network.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Long-distance line type wireless sensor network cross-layer communication method
ActiveCN104038991AReduce energy consumptionSolve the problem of long delayPower managementSynchronisation arrangementWireless sensor networkingCross layer design
The invention discloses a long-distance line type wireless sensor network cross-layer communication method. The long-distance line type wireless sensor network cross-layer communication method includes the following steps that: at first, a wireless sensor network adopts a double-chain topologic structure, and each aggregation node only communicates with two sensor nodes; and then, the aggregation nodes perform whole-network periodic time synchronization; and finally, the sensor nodes synchronously perform periodic monitoring and sleep, wherein the periodic monitoring and sleep includes a monitoring phase and a sleep stage, in the monitoring phase, the sensor nodes compete time slot deployment of the whole-network sensor nodes through transmitting time slot deployment requests, and in the sleep stage, the sensor nodes perform data transmission according to the time slot deployment of the sensor nodes their own. According to the long-distance line type wireless sensor network cross-layer communication method of the invention, the characteristics of the long-distance line type wireless sensor network are considered; a cross-layer design method is adopted, and communication decision threshold and time slot deployment modes are adopted in combination, and therefore, the network can be more suitable for cross-layer protocols; and the problem of long time delay caused by periodical monitoring and sleep can be solved.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV
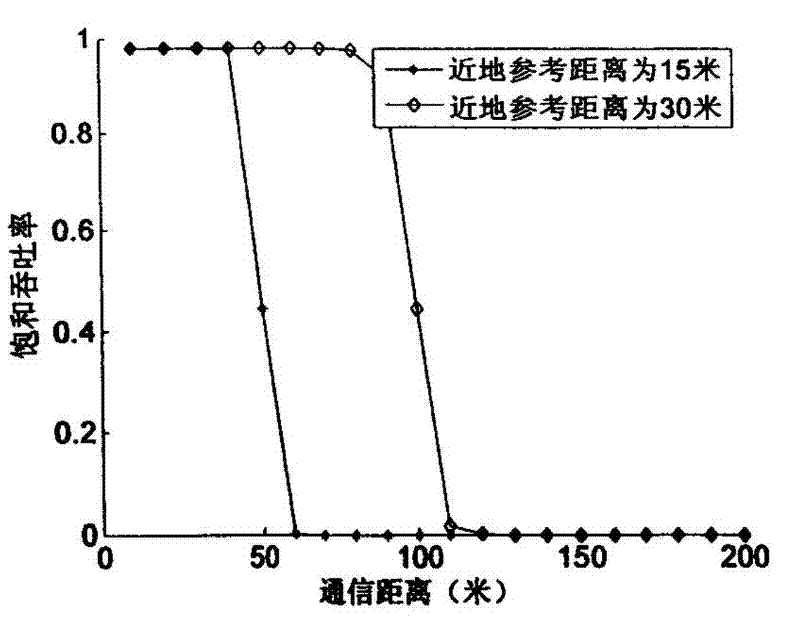
Adaptive error control method applied to wireless sensor network
InactiveCN102333344AImprove reliabilityImprove throughputEnergy efficient ICTNetwork traffic/resource managementQos quality of serviceWireless mesh network
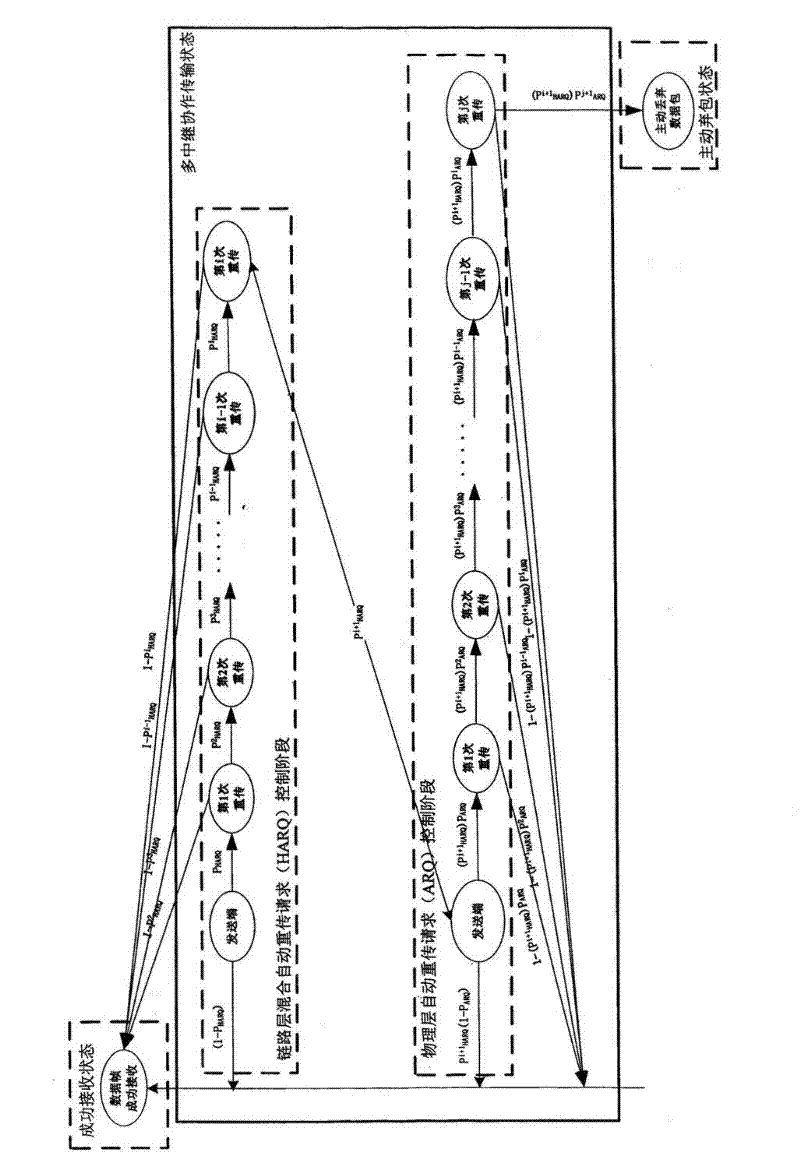
The invention discloses a hybrid automatic repeat request (HARQ)-automatic repeat request (ARQ)-cross-layer-interactive-cooperation-based adaptive error control method applied to a wireless sensor network, and belongs to the technical field of adaptive error control for cooperative communication in the wireless sensor network. In the method, a cross-layer design is adopted, hybrid automatic repeat request (HibridARQ) is adopted in a data link layer, automatic repeat request (ARQ) is adopted in a physical layer, the repeat number i of the hybrid automatic repeat request of the link layer and the repeat number j of the automatic repeat request of the physical layer are adaptively selected according to different requirements of an application server on quality of service (QoS), and an optimal error control scheme is determined; and simultaneously, a relay node number and a communication distance threshold value which are required by the cooperative communication are determined according to a communication distance between a transmitter and a receiver, a next-hop relay node is selected, and a multi-relay cooperative transmission path is adaptively created. The method has the advantages of ensuring the high transmission reliability of the wireless sensor network, simultaneously shortening time delay and achieving relatively higher throughput and energy efficiency.
Owner:CHANGSHU INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
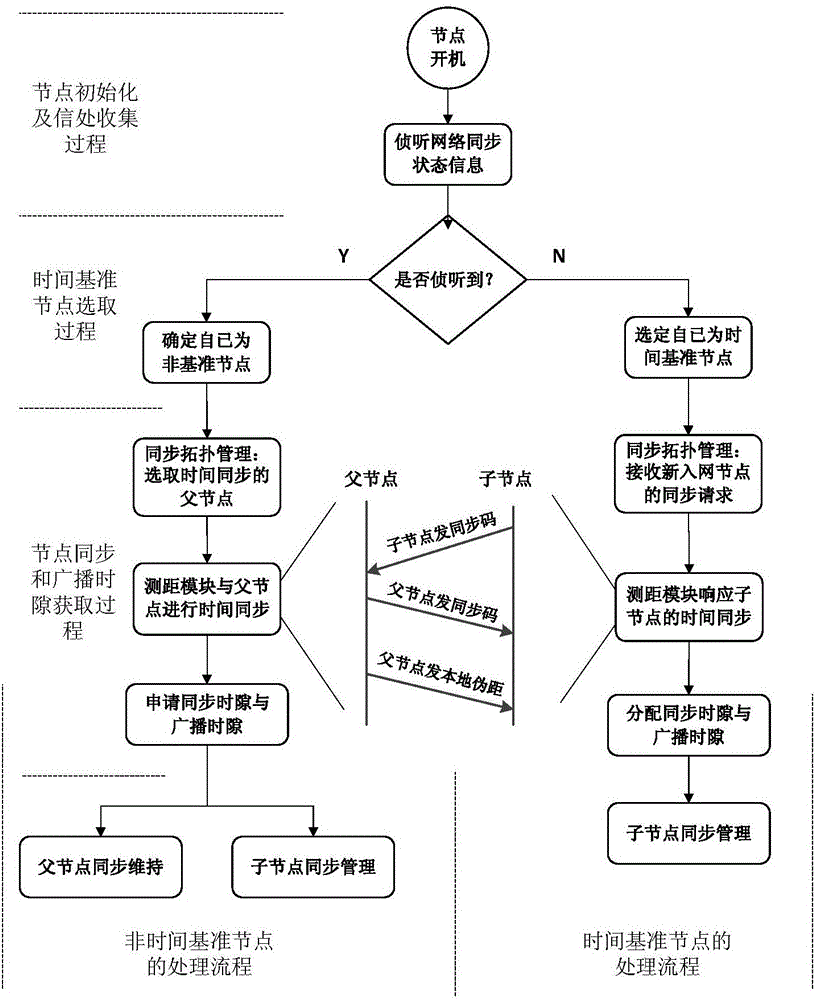
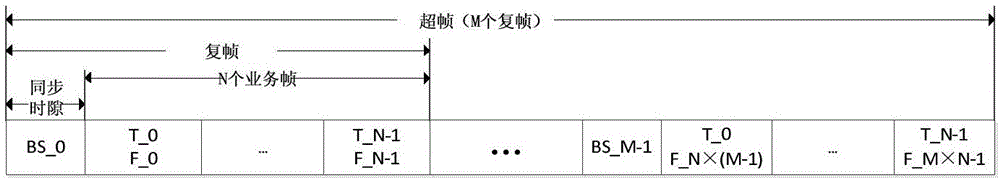
Satellite group network time synchronization method based on cross-layer design
ActiveCN106452645ASave communication resourcesHigh synchronization accuracyTime-division multiplexRadio transmissionData synchronizationTopology management
The invention discloses a satellite group network time synchronization method based on a cross-layer design. A spread spectrum signal mechanism is employed in a physical layer. A clock difference between a son node and a father node is calculated in a semi-two-way inter-satellite distance measurement mode, thereby finishing high-precision time synchronization between the nodes. Network synchronization management is employed in an MAC layer, synchronization state information is broadcasted in a network and synchronization topology management is carried out. A time synchronization father node selection result is provided for the physical layer for inter-node synchronization, thereby finishing time synchronization among the nodes of the whole network. The method provided by the invention is applicable to inter-satellite time synchronization demands of various satellite groups; there is no special demand for a satellite system; the universality is high; the application range is wide; on-satellite processing is simple; and the method has good application prospect.
Owner:XIAN INSTITUE OF SPACE RADIO TECH
Routing method for distributed cognition radio network based on layer-striding design
InactiveCN101437273AOptimize adjacent hop interferenceMinimize routing hopsTransmission monitoringWireless communicationRadio networksFrequency spectrum
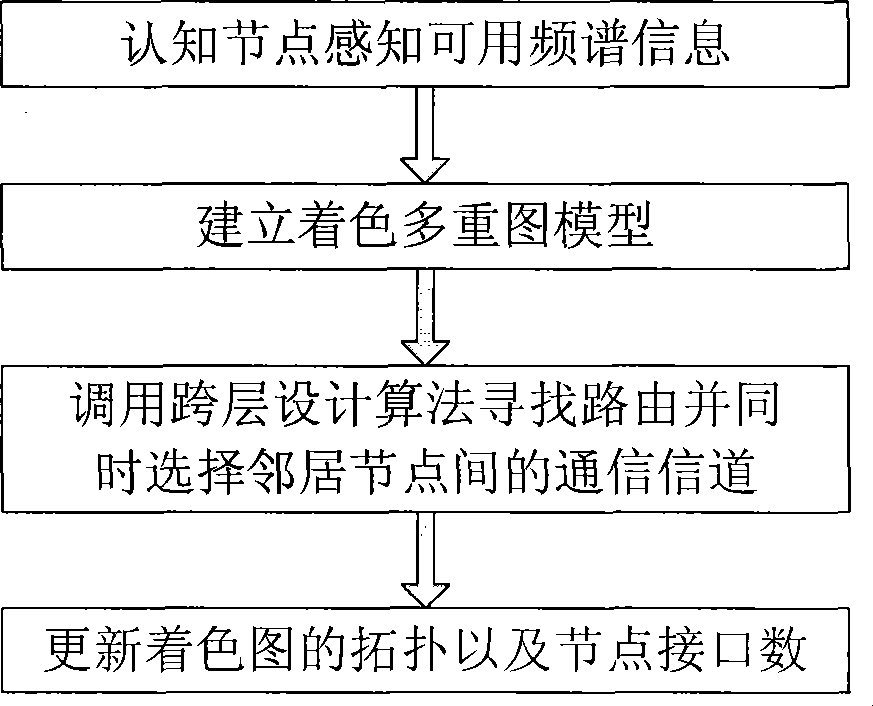
The invention discloses a method for distributed type cognitive radio network routing based on cross-layer design, which belongs to the technical field of cognitive radio network. The method comprises the following steps: establishing a coloring multi-graph model according to useable frequency spectrum information acquired by node perception; transferring a cross-layer design routing algorithm to search the routing between a source node and a target node, and simultaneously selecting communication signal channels between adjacent nodes; and updating the topology of coloring multi-graph and interface number of the nodes. The routing method adopts the cross-layer design on the routing selection of a network layer and an MAC layer, and concretely optimizes routing hop number and adjacent hop interfere under the condition of lower time complexity. The method is applicable to radio network, next generation heterogeneous network and so on.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
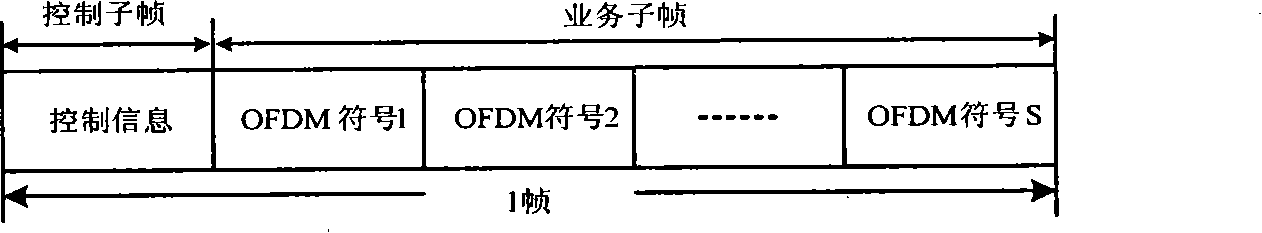
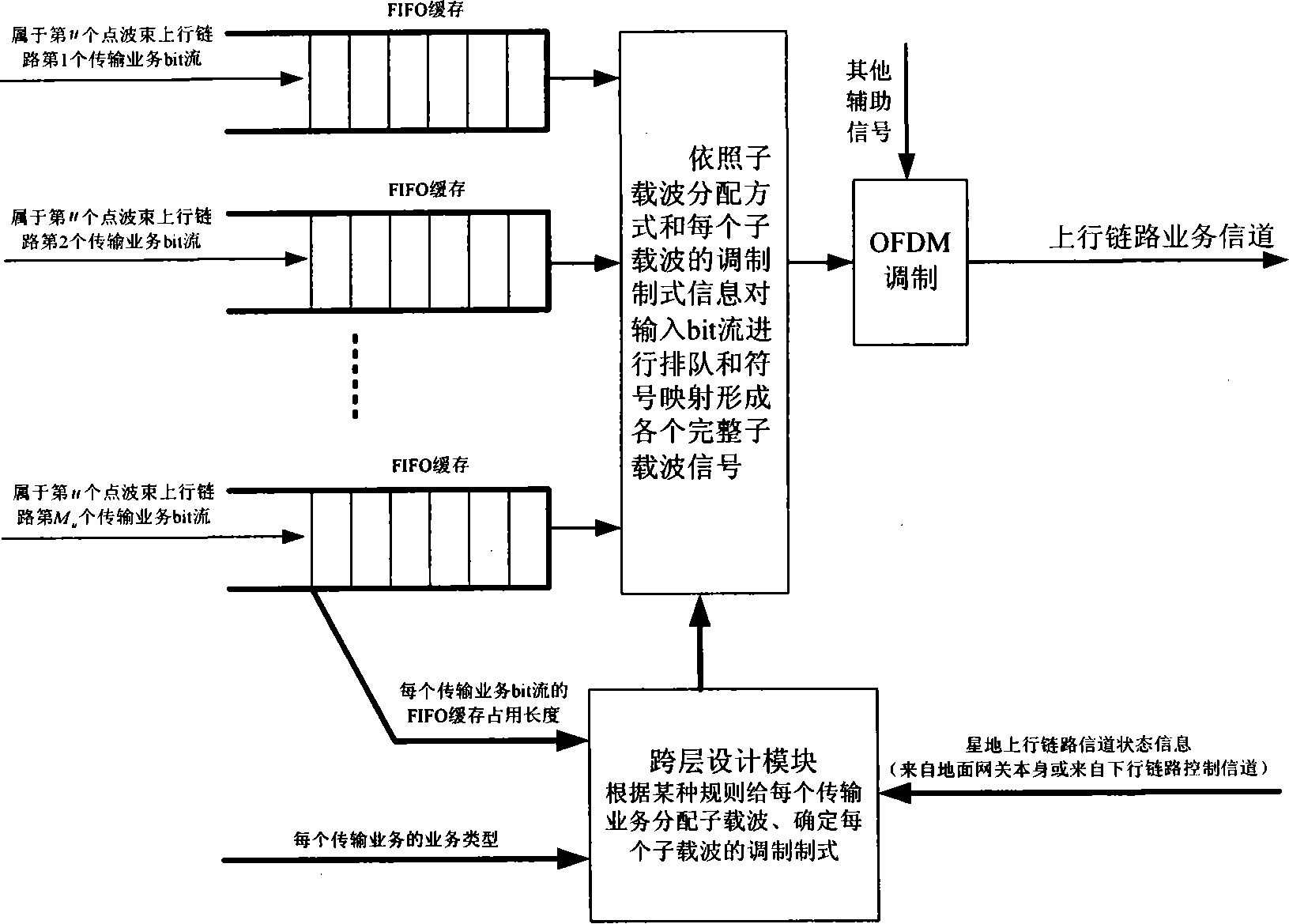
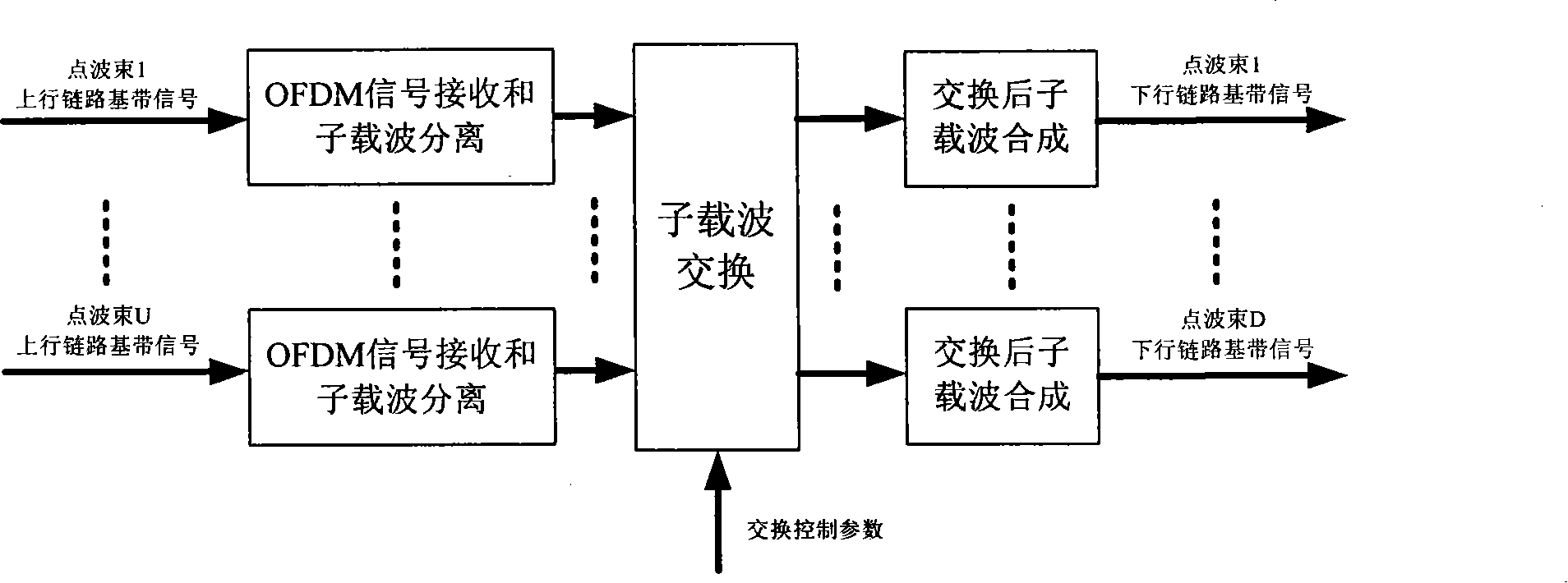
Star loading exchanging method based on OFDM and cross layer design
InactiveCN101252384AImplement statistical multiplexingReduce mutual interferenceRadio transmissionMulti-frequency code systemsMultiplexingCommunications system
The invention belongs to the satellite spaceborne switching technical field and relates to the spaceborne switching method based on the OFDM and the cross-layer design. The method includes that each spot-beam on the satellite and each corresponding ground gateway adopt the OFDM technique to process the satellite-ground uplink and downlink business transmission; each ground gateway determines the modulation mode of each sub-carrier in the spot-beam satellite-ground uplink and distributes the sub-carriers for each satellite-ground uplink business, and modulates all sub-carriers to OFDM signals which are transmitted to the satellite; the satellite processes sub-carrier separation and switching towards each OFDM signal of the spot-beam satellite-ground uplink, determines the modulation mode of each sub-carrier of the spot-beam satellite-ground downlink and distributes the sub-carriers for each satellite-ground downlink business, and modulates all sub-carriers to OFDM signals which are transmitted to the corresponding ground gateways. The spaceborne switching method can realize the statistical multiplexing of the spectrum resources and have no correlation with the concrete communication system so that the method has good adaptability and provides the transmission business with QoS guarantee.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
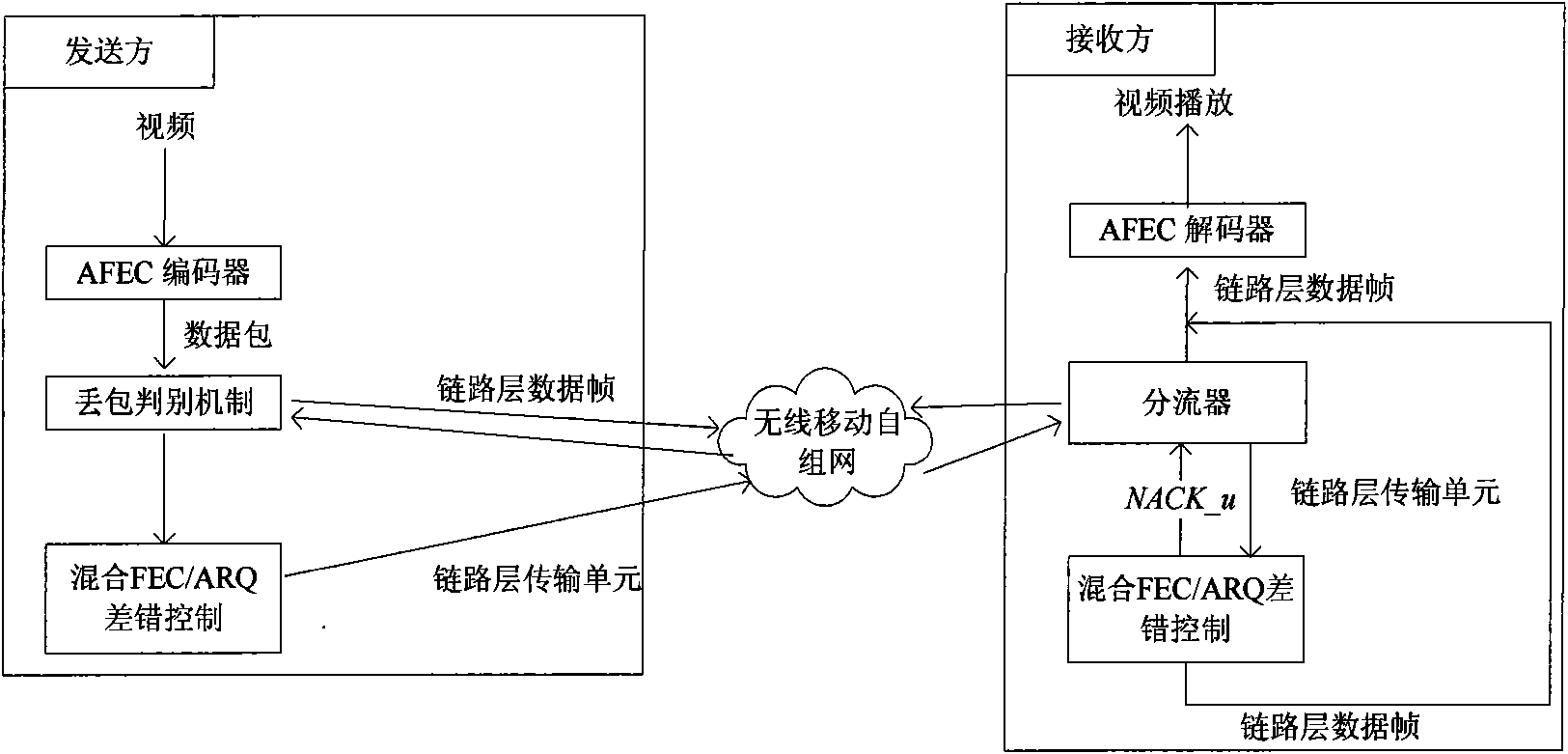
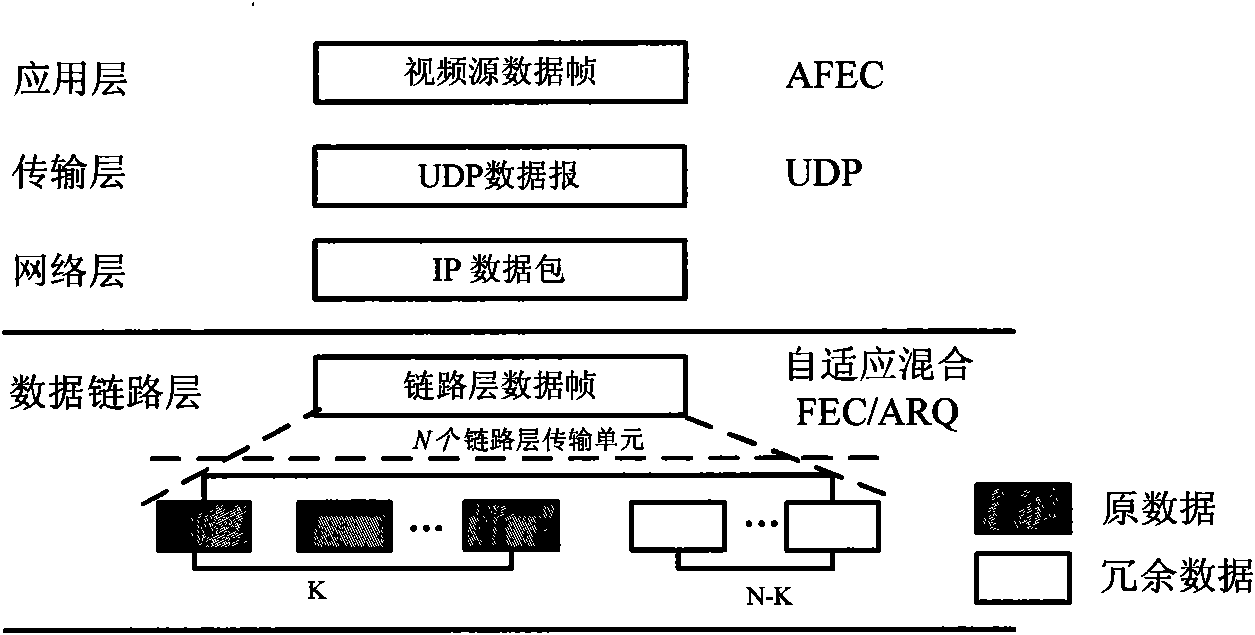
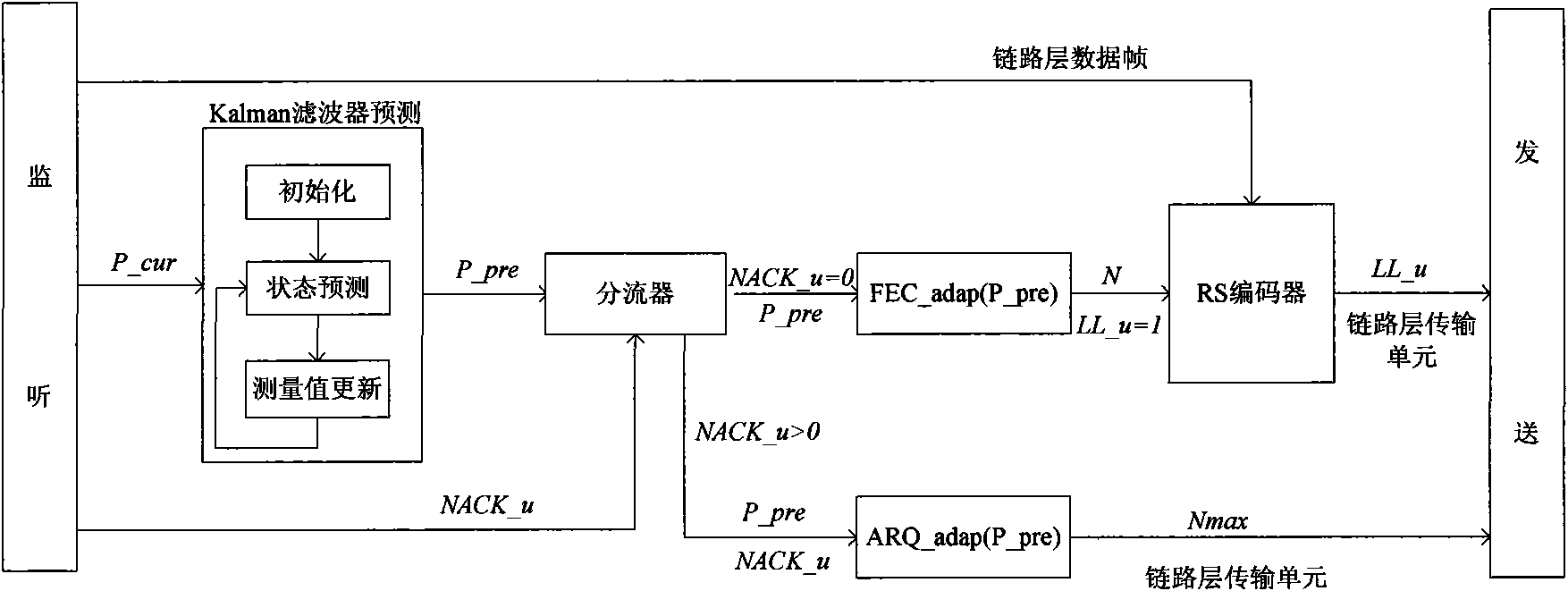
Control method of wireless streaming media self-adapting mixing FEC/ARQ based on Kalman filtering
InactiveCN101588597AImprove reliabilityImprove real-time performanceError prevention/detection by using return channelNetwork traffic/resource managementPacket lossData link layer
The invention discloses a control method of wireless streaming media adaptive mixing FEC / ARQ based on Kalman filtering, belongs to multimedia communication adaptive error control field in wireless dynamic network. The method uses cross-layer design and uses Kalman filter to predict current network status (packet loss ratio) in data link layer, adaptively regulates forward error correction (FEC) parameter of link layer and automatic repeat request (ARQ) parameter of link layer; on the other hand, uses adaptive FEC strategy in application layer, adaptively regulates sending speed of video frame according to current network status, and distributes network bandwidth dynamically between the video source data and the redundant data. The invention provided method can make receiver obtain maximum playback frame rate and improves reliability and real time of streaming media transmission effectively.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
Hybrid MAC protocol method for cluster-structure multi-carrier acoustic sensor network
ActiveCN104796959AReduce energy consumptionGuaranteed service qualityTransmissionHigh level techniquesQuality of serviceTransfer mode
The invention discloses a hybrid MAC protocol method for a cluster-structure multi-carrier acoustic sensor network. The hybrid MAC protocol method comprises the following steps: fusing a scheduling type MAC protocol with a competitive type MAC protocol into a hybrid acoustic communication network MAC protocol, realizing MAC protocol dynamic switching for all nodes in the network by virtue of a global synchronization time, and classifying data with different attributes through a cross layer design thought and then transmitting. Two transmission modes of free burst IBT and active polling IPT are adopted, data messages transmitted in the two different transmission modes are periodic messages and burst messages respectively, IBT time slots and IPT time slots are alternately carried out, and the length of the free burst IBT time slots is dynamically adjustable, so that the needs of transmission for the various messages in the sensor network can be met, the communication energy consumption of the sensor network can be reduced simultaneously when the service quality of the network can be ensured.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Method for designing transmission control protocol (tcp) cross-layer in satellite network
InactiveCN101854297ALoss of correct judgmentImprove throughputError prevention/detection by using return channelData switching networksPacket lossCross layer design
The invention discloses a method for designing a tcp cross-layer in a satellite network, which is a solution for enhancing tcp performance by using a cross-layer design in the satellite network. The method is mainly used for solving the influence of a high error code environment of the satellite network on a tcp so that the tcp can accurately judge data packet loss caused by network congestion and error code; and the method belongs to the field of congestion control of the satellite network. The method has the following characteristics that: the tcp layer and a link layer realize cross-layer interaction so that a queue state in the link layer can be transferred to the tcp layer, the tcp layer judges the congestion condition of a link according to the queue state, furthermore, the tcp can accurately judge the data packet loss caused by the network congestion and the error code, and the effect of improving the tcp performance can be finally achieved.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
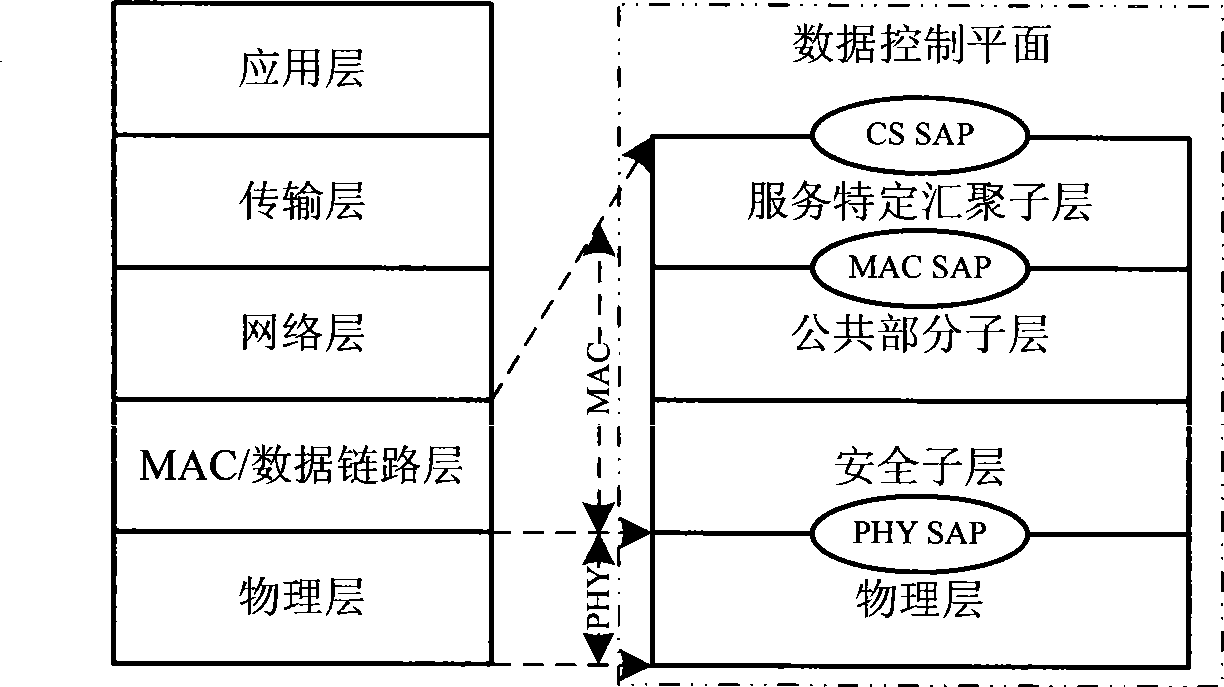
Cross-layer structure for guaranteeing QoS in WiMAX and QoS combination control method
InactiveCN101431811ASecure cross-layer architectureSimple structureWireless network protocolsTransmissionService flowControl signal
The invention discloses a layer-crossing structure for assuring the QoS in the WiMAX and a compound control method of the QoS. The layer-crossing design is used to divide the basic data control plane into two planes of QoS resource management and data service delivery. The QoS resource managing plane delivers the multiple media communication service flow by applying the layer to the MAC layer; controlling the PHY layer be gathered by the AMC channel mode selection information to the MAC layer transmission, security system to achieve cross-layer QoS control of the joint management of data services and access to the QoS flow control performance indicators set by the user in the system the threshold value; data streaming services to submit sub-plane containing a variety of norms to follow IEEE 802.16 data services stream processing module, the management of their resources in accordance with sub-QoS management plane carries control signaling information data services for all types of flow classification and scheduling to achieve layer by layer submitted. The present invention system in maintaining a high throughput at the same time being able to service a number of QoS flow limit indicators within the target threshold, taking into account a fair rate of customers.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Robust cooperative relaying in a wireless lan: cross-layer design
ActiveUS20110110290A1Facilitate cooperative communication of dataSite diversityFrequency-division multiplex detailsControl layerChannel statistics
A distributed and opportunistic medium access control (MAC) layer protocol for randomized distributed space-time coding (R-DSTC), which may be deployed in an IEEE 802.11 wireless local area network (WLAN), is described. Unlike other cooperative MAC designs, there is no need to predetermine, before packet transmission, which stations will serve as relays. Instead, the MAC layer protocol opportunistically recruits relay stations on the fly. Network capacity and delay performance is much better than legacy IEEE 802.11g network, and even cooperative forwarding using one relay station. Avoiding the need to collect the station-to-station channel statistics considerably reduces overhead otherwise required for channel measurement and signaling.
Owner:POLYTECHNIC INSTITUTE OF NEW YORK UNIVERSITY
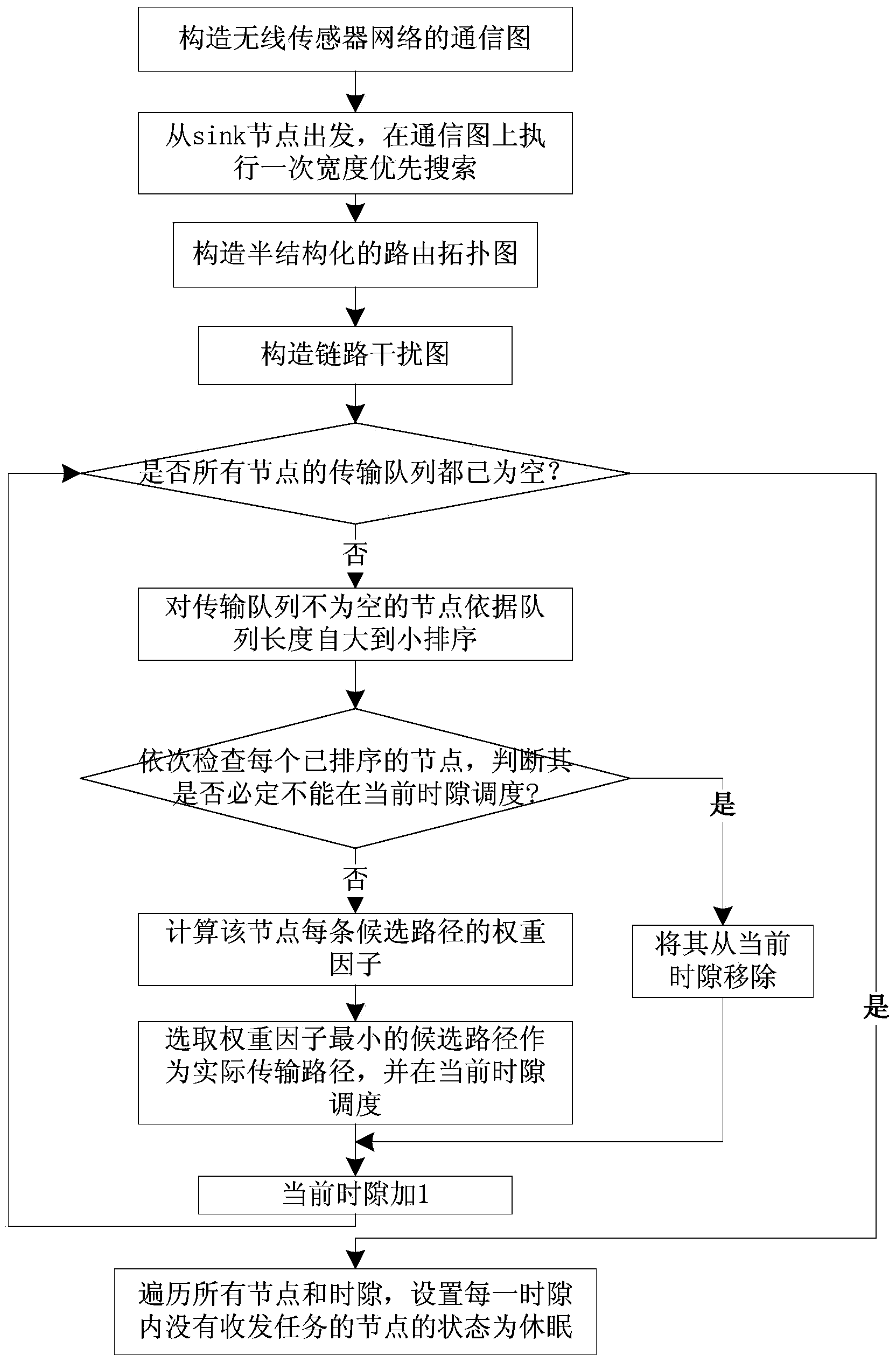
Semi-structured transmission dispatching method orienting wireless sensor network data collection
ActiveCN104301966AReduce energy consumptionExtend the life cyclePower managementHigh level techniquesSemi-structured dataInterference factor
The invention discloses a semi-structured transmission dispatching method orienting wireless sensor network data collection. The method is characterized by comprising the steps that 1, breadth-first search is carried out on a network communication graph, so that a slack semi-structured data collection route topological graph is constructed; 2, a link interference graph is constructed according to the main interference and subsidiary interference relation between transmission links in a network; 3, link weight interference factors are defined, so that the interference intensity caused to other links of the network from transmission loads of sending nodes and sending links is comprehensively weighed; 4, the dynamic link selection and time slot allocation strategy based on preference of the minimum weight is carried out; 5, a node dormant state is controlled in an explicit mode, and a data collection period is adjusted in a self-adaptive mode. According to the method, routing and dispatching are designed in a unified mode on the basis of a cross-layer design idea, the time slot utilization rate of dispatching is increased by fully utilizing the redundancy of a path, time delay of data collection is shortened, and the handling capacity of the network is improved. The method is applied to the wireless sensor network with the high requirement for the real-time property.
Owner:中科水研(江西)科技股份有限公司
Routing method based on scheduling and link quality in wireless sensor network
ActiveCN101854696AImprove reliabilityMeet scheduling requirementsNetwork topologiesLine sensorWireless mesh network
The invention relates to a routing method based on time slot scheduling mechanism and communication link quality in a wireless sensor network, relating to the wireless sensor network. The invention realizes the wireless sensor network routing technology with high reliability by adopting a cross layer design idea, combining with a full-network time slot scheduling mechanism and bottom layer communication link evaluation, selecting transmission delay and link quality as standards of route selection, introducing a front k optimal route algorithm and selecting one optimal communication route meeting two route selection standards simultaneously. An ISA 100.11a network is taken as an example. A system manager in the ISA 100.11a network is used for carrying out centralized management on mesh topological communication sub-networks. When a route application of source equipment is received, the route algorithm is operated to select one route with optimal communication link quality under the condition of meeting the full-network scheduling requirement; and meanwhile, route information is sent to all nodes on the route for data communication so as to verify the feasibility of the algorithm.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
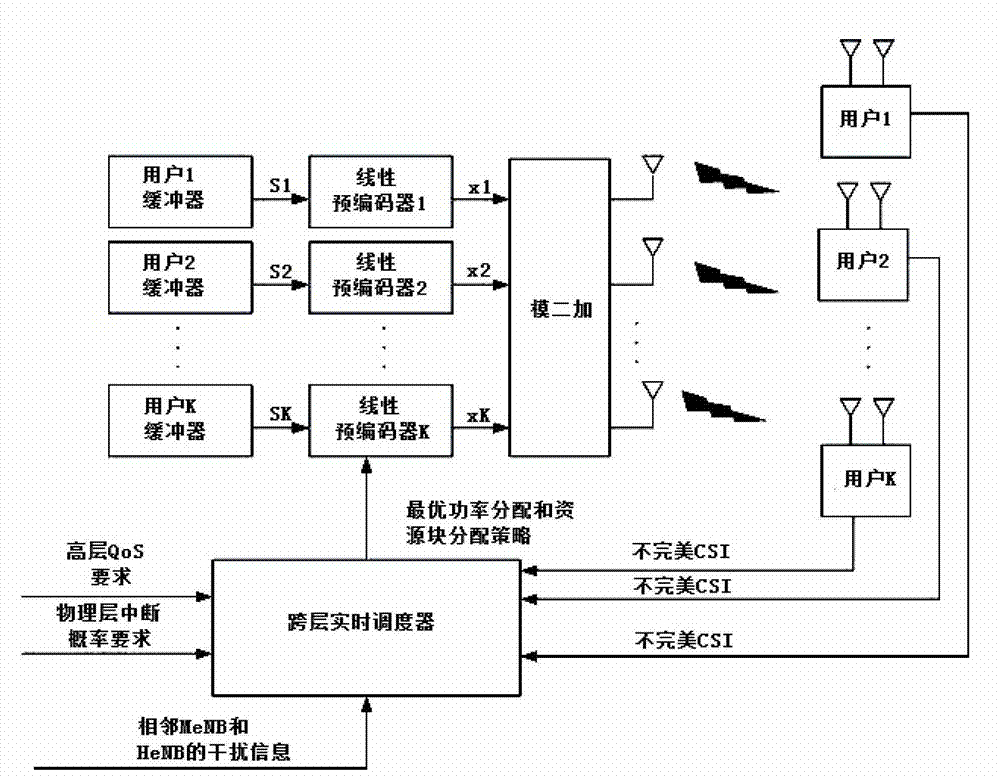
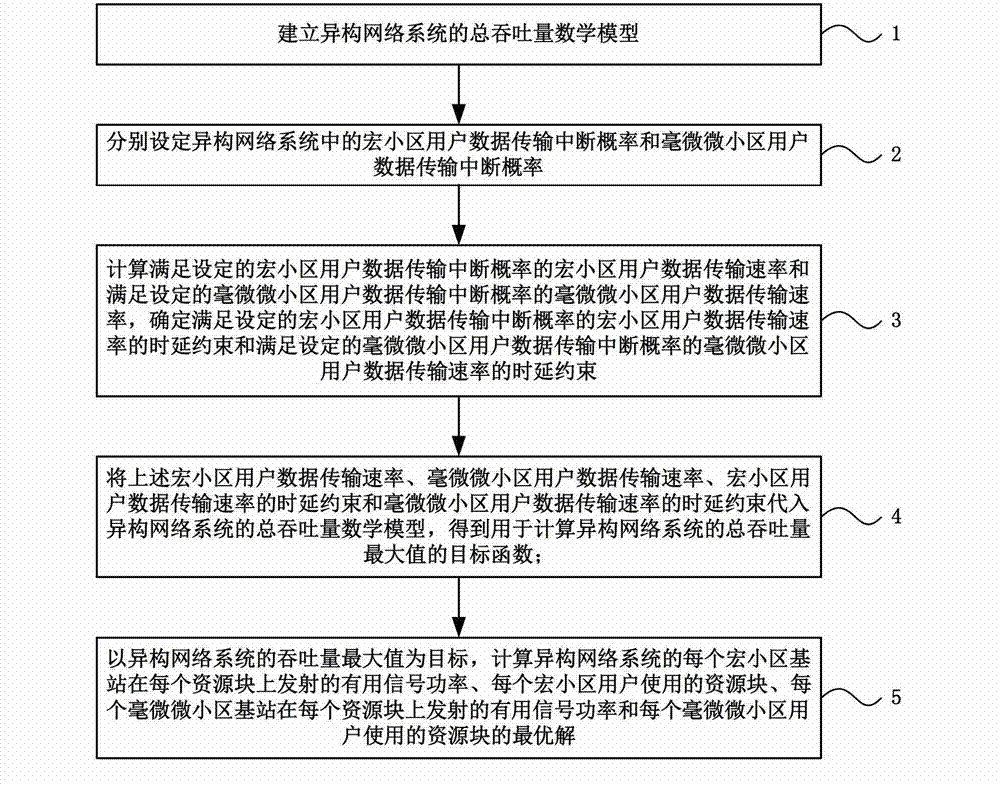
Resources allocation method based on cross-layer scheduling mechanism under imperfect CSI condition
The invention discloses a resources allocation method based on a cross-layer scheduling mechanism under an imperfect CSI (customer satisfaction index) condition and belongs to the technical field of wireless communication design. The method comprises the following steps: building a total throughput mathematical model of a heterogenous network system; setting user data transmission interruption probability; calculating macrocell user data transmission rate and femto cell user data transmission rate which meet the set interruption probability, and setting delay constraint of the micro-cell user data transmission rate and the delay constraint of the femto cell user data transmission rate; substituting the data transmission rates and the delay constraints into the total throughput mathematical model of the heterogenous network system, so as to obtain an objective function for calculating the greatest value of the total throughput; and calculating available signal power of a base station, which is transmitted at each resource block, and the optimum solution of a resource block used by a user. According to the invention, imperfect channel state information is described by using interruption probability, and a cross-layer design mechanism is guaranteed to be suitable for an actual wireless communication network.
Owner:BEIJING JIAOTONG UNIV
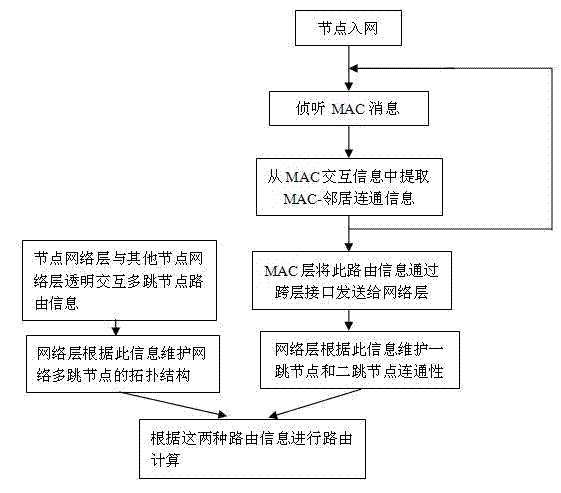
Routing information acquisition and transmission method for wireless mesh network
InactiveCN102238683AImprove efficiencyReduce overheadWireless communicationWireless mesh networkResource utilization
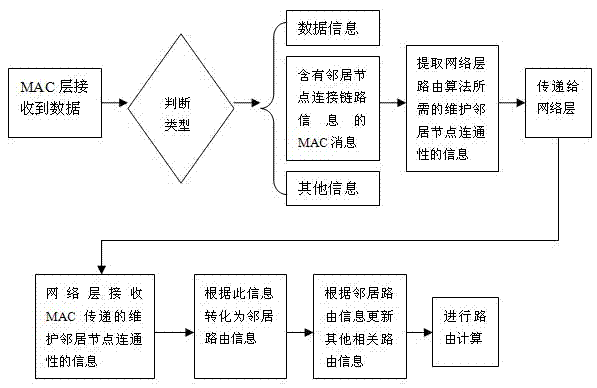
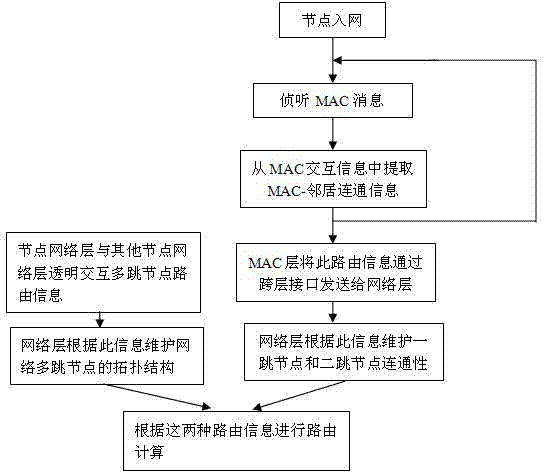
The invention discloses a routing information acquisition and transmission method for a wireless mesh network. In the method, the realization process of information interaction required by maintaining link connectivity among adjacent nodes in a wireless Mesh network media access layer and the realization process of inter-node routing information interaction in a network layer are combined together by using a cross-layer design, thereby reducing total overhead in bandwidth resources and operation time in the information interaction processes and increasing the utilization rate of network resources by improving the routing information acquisition and transmission efficiency.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
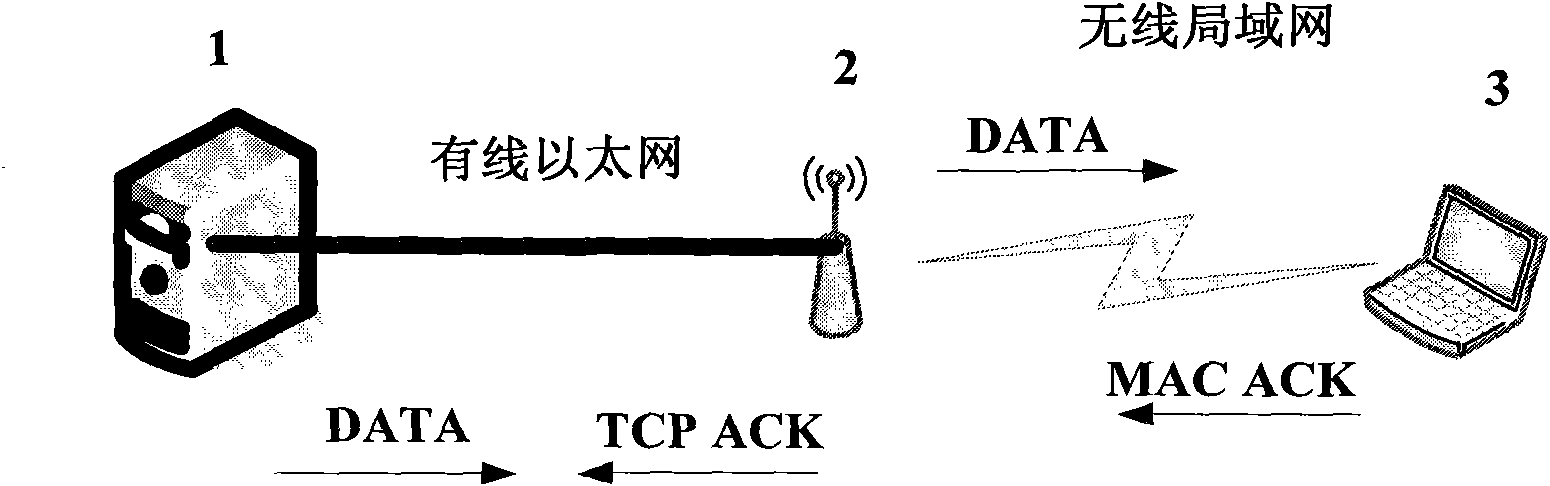
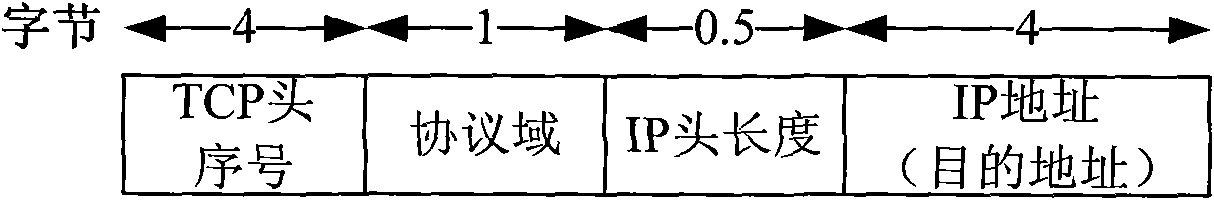
Cross-layer method for reducing TCP repeated response under wireless local area network
InactiveCN102186207AReduce duplicate responsesError prevention/detection by using return channelNetwork traffic/resource managementCross layer designWireless access point
The invention discloses a cross-layer design method for reducing TCP repeated response under a wireless local area network. In the method, few frame formats and flow treatments only need to be rectified in the wireless local area network. A wireless access point (AP) caches the head local information of TCP / IP that is sent to a destination terminal by a sending terminal. A wireless terminal part caches a suggestion sending window of the TCP head at the MAC layer; simultaneously the sub-domain remained by the MAC head frame control domain marks whether the TCP layer carries out response and answering to the MAC layer within the specified time; and when the MAC layer is being sent, the MACACK is sent to the AP in a way of taking the slightly changed TCP suggestion window as the MAC load. After the AP receives the MAC ACK sent by the destination terminal, the TCP ACK agent destination terminal is established to carry out TCP response to the sending terminal according to the TCPACK response marking of the MAC head frame control domain and the previously cached TCP / IP head local information of the sending terminal.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
Method for allocating resources optimally in distributed mode by self-organizing cognitive wireless network
InactiveCN101534557AEffective distributionAvoid mutual interferenceNetwork topologiesCross layer designResource allocation
The invention provides a method for allocating resources optimally in a distributed mode by a self-organizing cognitive wireless network, and relates to a problem of self-organizing (Ad Hoc) network resource allocation based on cognitive radio. The method designs a link cost function, LCF for short, performs a cross layer design on the allocation of network resources according to the function, and achieves the optimal allocation of the resources through a distributed algorithm. The routing is carried out according to the link cost function LCF provided by the invention, so that the transmission rate of various links in the Ad Hoc network obtained through the distributed algorithm is made to be more close to an optimal value obtained through a centralized algorithm. Therefore, the resources of the whole network are allocated optimally.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Method for rapidly decomposing time gap conflicts in distributed type TDMA protocol
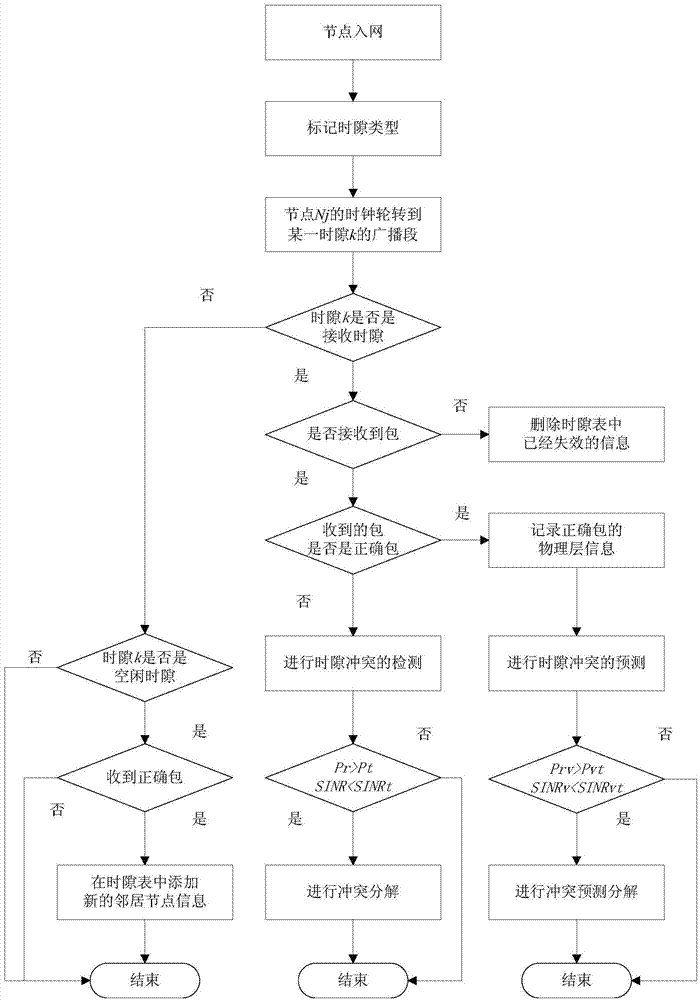
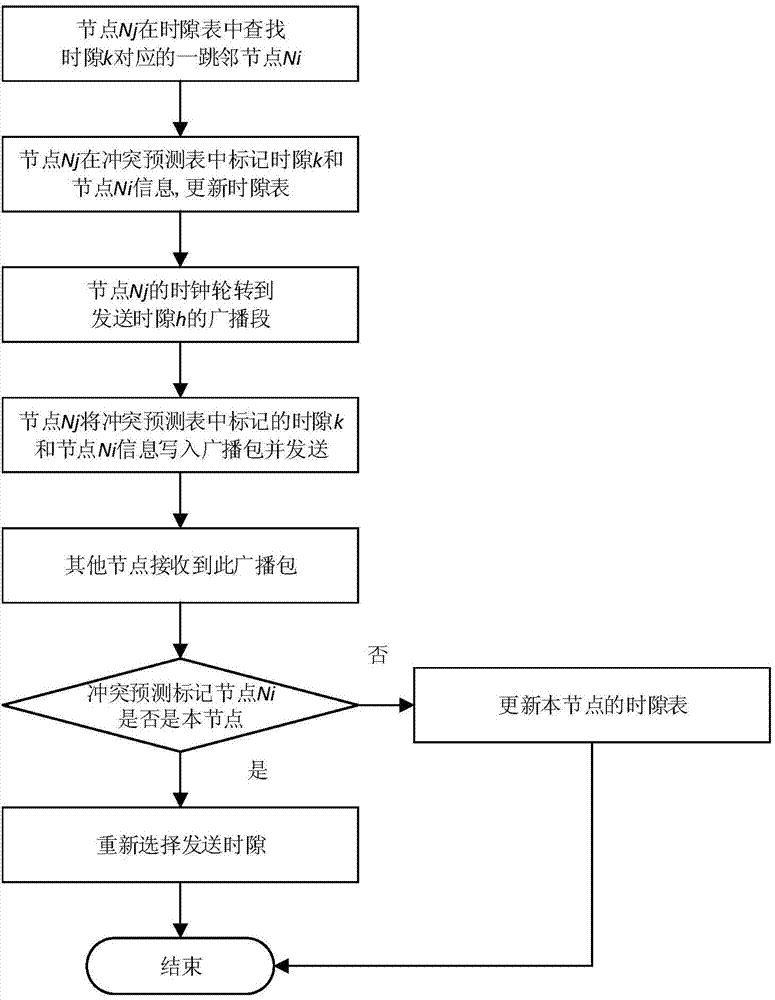
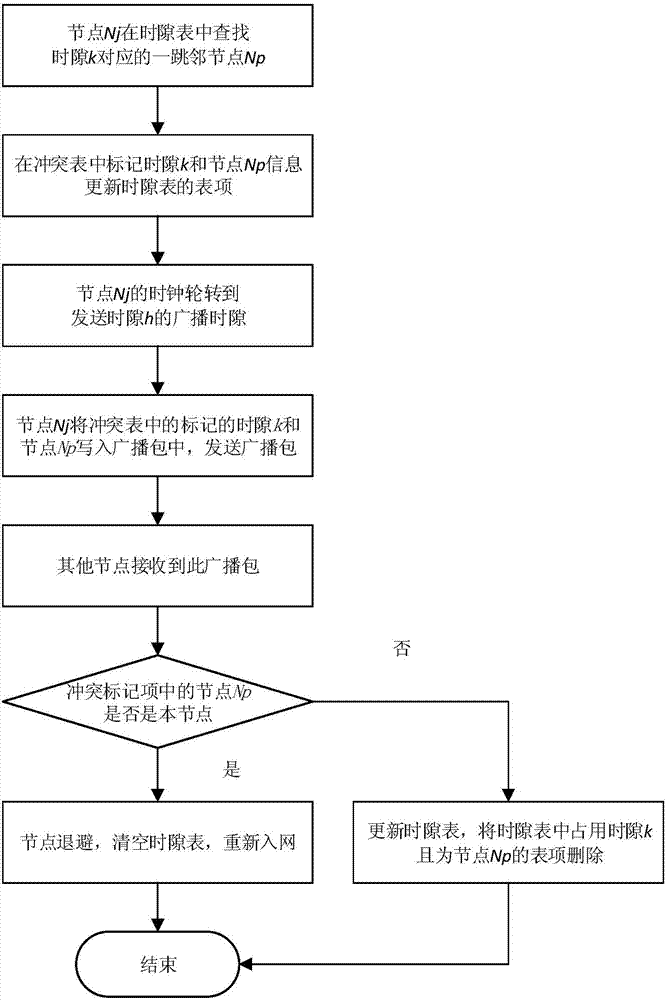
InactiveCN104734798AImprove transmission performanceSlot collision avoidanceTime-division multiplexWireless network protocolsIdle timeDecomposition
The invention discloses a method for rapidly decomposing time gap conflicts in a distributed type TDMA protocol. The method mainly solves the problem that in an Ad Hoc network, due to the time gap conflicts, the transmission efficiency and channel utilization rate are decreased. The method includes the steps that firstly, a node has access to a network and is marked with a time gap type; secondly, when receiving a correct packet during a receiving time gap, the node calculates prediction parameters according to the physical layer parameters of the packet and conducts conflict forecasting decomposition if the prediction parameters meet the conflict prediction conditions; thirdly, when receiving a wrong packet during the receiving time gap, the node conducts conflict decomposition if physical layer parameters of the packet meet the conflict conditions; fourthly, when receiving no packet during the receiving time gap or receiving a correct packet during an idle time gap, the node renews a time gap list. The cross-layer design is introduced, and therefore the time gap conflicts are more efficiently predicted and detected, the network transmission efficiency and channel utilization rate are increased, and the method can be used for the distributed type self-organized network.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Self-adaptive wireless sensor network routing method based on cross-layer optimization
InactiveCN102595550AAddressing energy managementAddress reliabilityHigh level techniquesWireless communicationLine sensorTransmitted power
The invention discloses a self-adaptive wireless sensor network routing method based on cross-layer optimization. In a physical layer, an energy supplement and power control mechanism is adopted to transfer energy information and transmitting power parameters of a wireless sensor node in a wireless sensor network to an MAC (media access control) layer; in the MAC layer, the information transferred by the physical layer is utilized to carry out sleep scheduling to regulate network connectivity and a sleep rate; and a network layer adapts to parameter change of each of above layers and adopts a double-bounce greedy path to carry out routing selection. The method achieves an integrative optimization aim of prolonging the service life of the network and improving data transmission reliability and timeliness by utilizing the interaction of the parameter information of each layer of a network; and on the basis of comprehensively considering the energy supplement and power control technology of the physical layer, the sleep scheduling of the MAC layer and the routing of the network layer in a network system structure, the cross-layer design structure applicable to the wireless sensor network is provided, so as to better describe the interaction among all the layers. The overall performance of the wireless sensor network is effectively improved finally.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV CHANGZHOU
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com