Polymer-based composite material sensing civil engineering structure super-deformation, and preparation method and application thereof
A technology of civil engineering structures and composite materials, which is applied in the field of polymer-based composite materials and its preparation, can solve the problems of small deformation and unreported research on material sensitization, and achieve the effects of easy acquisition, convenient preparation, and easy realization
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
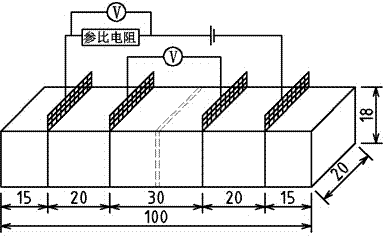
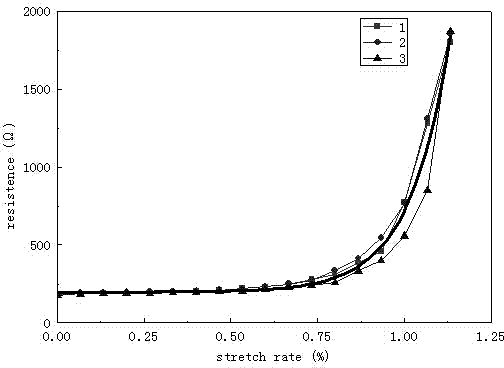
[0024] Embodiment 1: This embodiment provides a polymer-based composite material capable of sensing super large deformation in civil engineering and its preparation method. The deformation sensing performance and preparation method of the composite material will be described one by one below.
[0025] 1. Preparation of composite materials
[0026] The preparation steps of materials, the consumption of each material and the preparation process are described as follows in the present embodiment:
[0027] In the raw materials used in the composite material in this embodiment, water: polyacrylamide: montmorillonite = 10:3:5, carbon fiber in carbon-based materials: carbon nanotubes: carbon black = 3:15:20, the amount of methyl cellulose The amount of polyacrylamide and montmorillonite is 0.4% of the total amount of polyacrylamide and montmorillonite, the amount of polyvinylpyrrolidone is 20% of carbon nanotubes, and the amount of carbon-based materials is 2.8% of the total amount o...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0035] Embodiment 2: The difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 is that water: polyacrylamide: montmorillonite=10:3:4, carbon fiber in carbon-based materials: carbon nanotubes: carbon black=2:10: 25. The amount of methylcellulose is 0.3% of the total amount of polyacrylamide and montmorillonite, the amount of polyvinylpyrrolidone is 18% of carbon nanotubes, and the amount of carbon-based materials is 2.6% of the total amount of polyacrylamide and montmorillonite %.
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0036]Specific embodiment three: the difference between this embodiment and specific embodiment one is that water: polyacrylamide: montmorillonite = 10:4:3, carbon fiber in carbon-based materials: carbon nanotubes: carbon black = 4:20: 15. The amount of methyl cellulose is 0.5% of the total amount of polyacrylamide and montmorillonite, the amount of polyvinylpyrrolidone is 22% of carbon nanotubes, and the amount of carbon-based materials is 3.2% of the total amount of polyacrylamide and montmorillonite %.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com