Method for configuring capacity of asynchronous wind power plant reactive power compensation device under grid fault
A technology for compensating equipment and power grid faults, applied in reactive power compensation, reactive power adjustment/elimination/compensation, circuit devices, etc., can solve problems that do not involve reactive power compensation equipment capacity allocation, etc., to improve low voltage ride-through capability , Improving the effect of feasibility and economy
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0027] The specific implementation of the present invention will be described in detail below in conjunction with calculation examples and drawings.
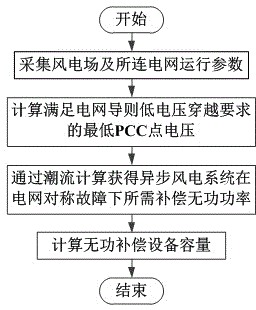
[0028] Combine figure 1 As shown in the calculation process, the specific implementation steps of the capacity configuration method for reactive power compensation equipment of asynchronous wind farms under grid failure are as follows:
[0029] (A) Collect the operating parameters of the wind farm and the connected grid:
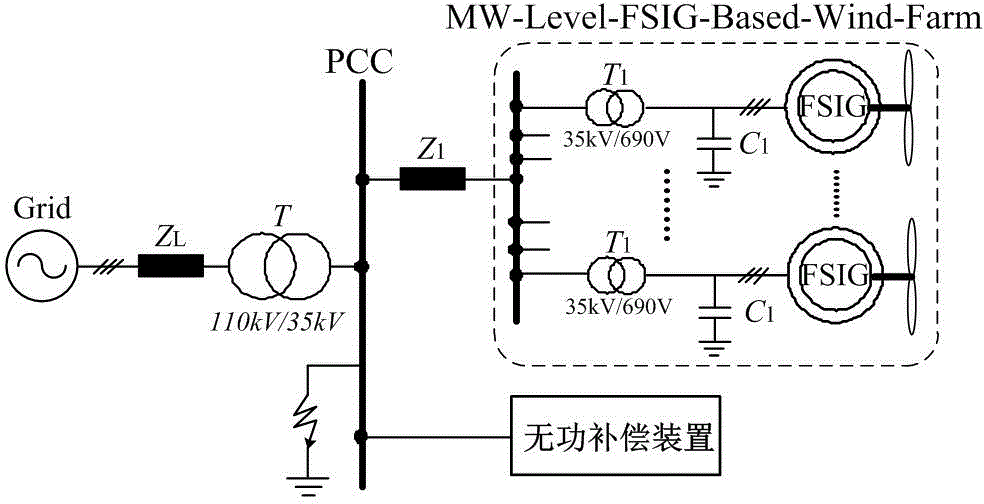
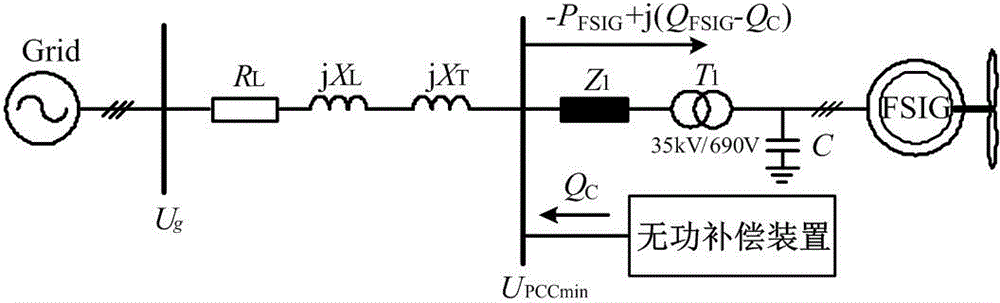
[0030] In this example, the wind farm is composed of 30 single fixed-speed asynchronous wind turbines with a rated power of 1MW in parallel. The system topology is as follows figure 2 Shown. The output voltage of the asynchronous motor is 0.69kV, which is connected to the internal power grid of the wind farm through a 0.69 / 35kV transformer. After being connected to a 35 / 110kV booster station through a 2km transmission line, it is connected to the local 110kV grid through a 100km transmission line, and reactive powe...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com