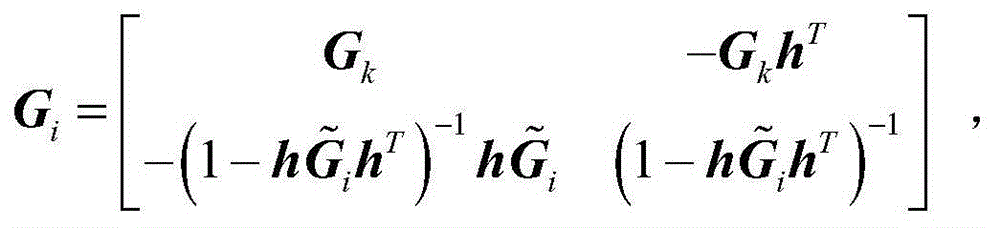Global satellite navigation system receiver constellation optimal selection method
A global satellite navigation and satellite navigation system technology, applied in satellite radio beacon positioning systems, radio wave measurement systems, measurement devices, etc., can solve the problems of large amount of calculation, dependence, and no consideration of the influence of time deviation, etc., to reduce the search time time, reduce the amount of calculation, and reduce the effect of the number of satellite combinations
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach
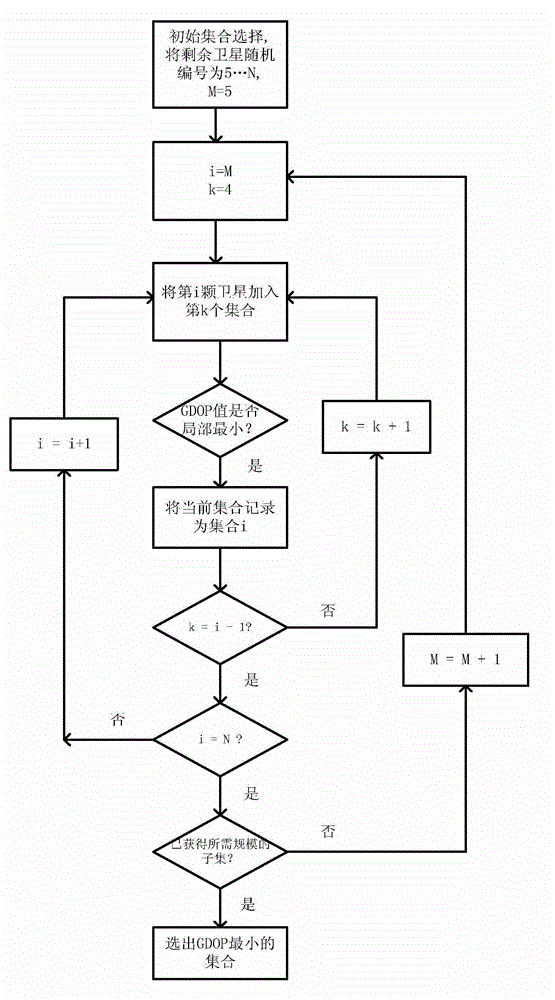
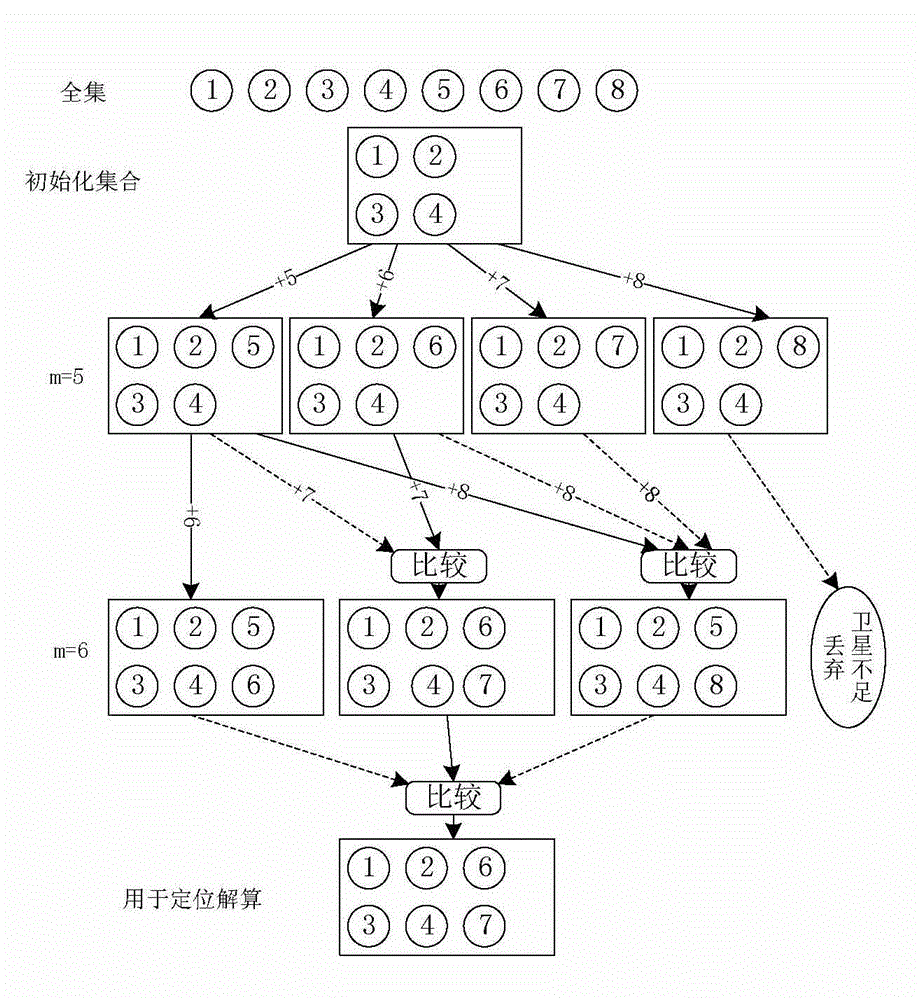
[0036] Such as figure 2 Shown is a running sample process of a method for selecting a constellation of a global satellite navigation system receiver according to the present invention. There are 8 visible satellites in total, numbered 1 to 6 are GPS satellites, and numbers 7 to 8 are Beidou satellites, from which 6 satellites need to be selected as the preferred subset of the constellation.
[0037] The initial set selects 4 satellites from the GPS system according to the geographic location, and randomly numbers the other satellites as 5-8.
[0038] Add the 5th satellite to the initial set, the newly added satellite belongs to the GPS system, use the formula (1) to calculate the GDOP of the set, at this time k=i-1, and there is only one set containing the 5th satellite, so Make it the new set (5, 5). Add the sixth satellite to the initial set in the same way to obtain set 6(6,5).
[0039] Add the seventh satellite to the initial set. The newly added satellite belongs to t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com