Coverage Hole Repair Method and System for Failure Nodes in Internet of Things
A technology that covers holes and failed nodes, applied in network topology, advanced technology, electrical components, etc., can solve problems that are not suitable for large-scale applications, affect the quality of service in the monitoring area, increase node costs, etc., to prolong the network survival time, good The effect of network coverage quality and guaranteed communication quality
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
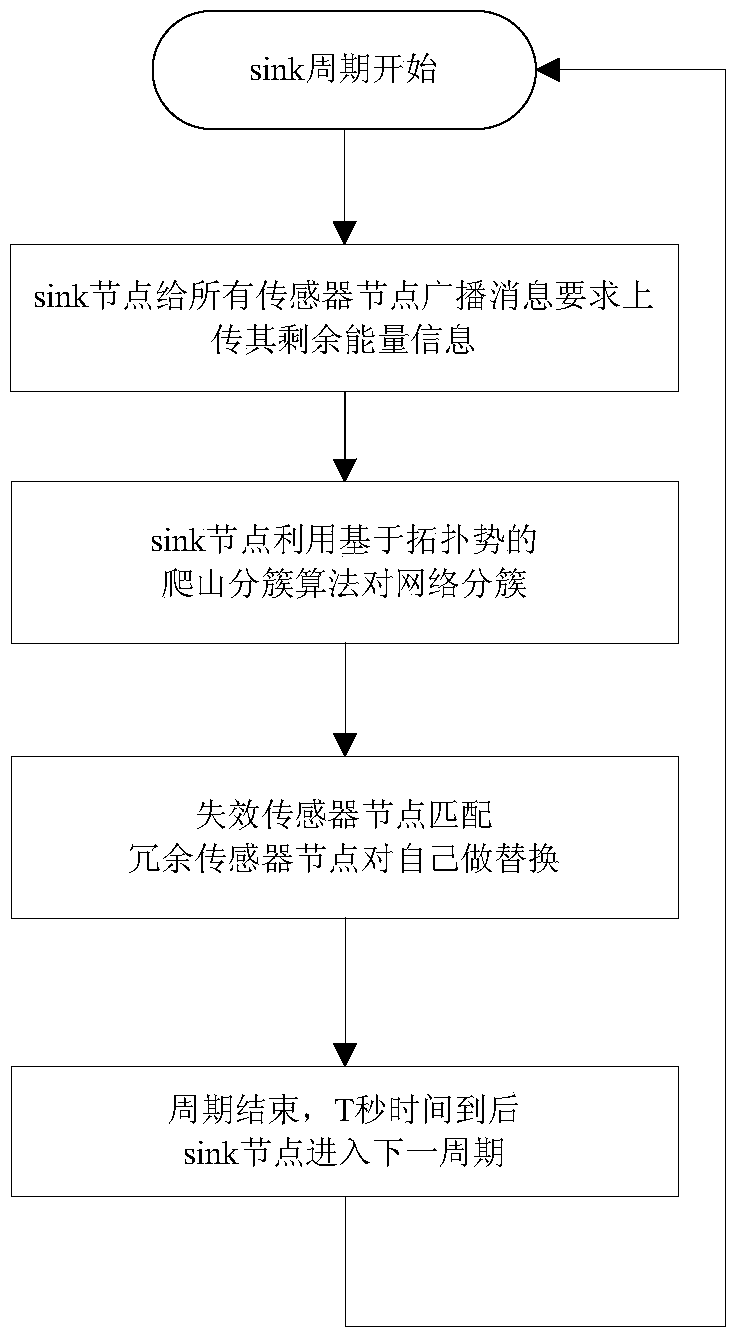
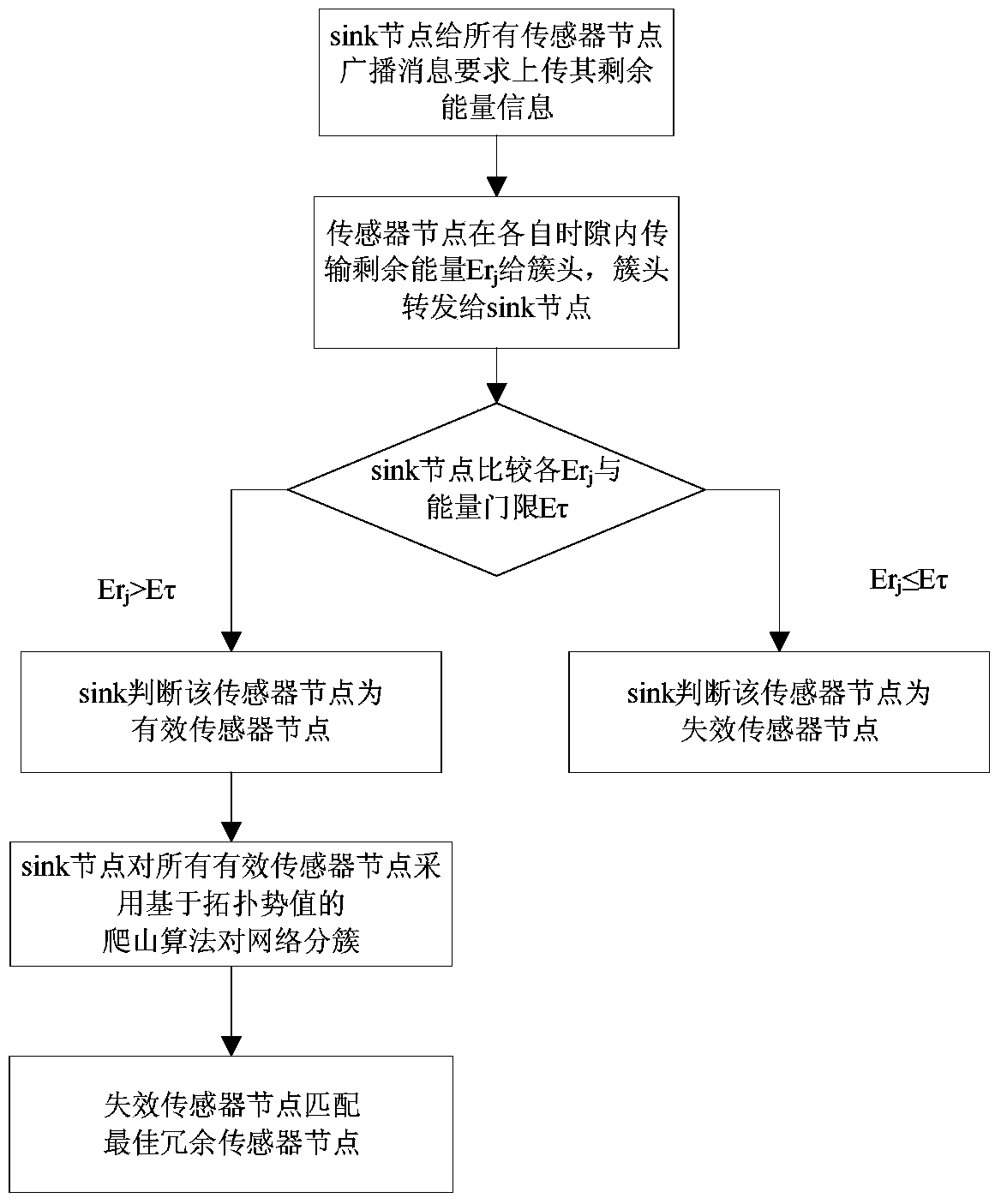
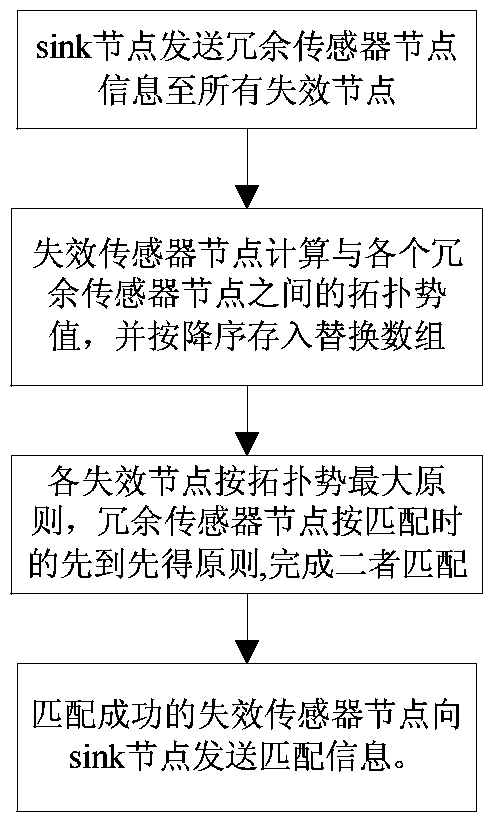
[0045] The implementation process of the present invention will be described in detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and specific embodiments.
[0046] The hybrid sensor network includes static sensor nodes responsible for sensing events and redundant sensor nodes with mobile capabilities that can be used for scheduling. The two coordinate with each other to complete the deployment of the network. Both are identical in terms of communication, computing power and the amount of energy they carry. During the initial deployment, the network is fully covered by all static sensor nodes, and other redundant sensor nodes are deployed in the area covered by the designated static nodes in a partially redundant coverage manner. After normal operation, the static sensor node is responsible for sensing data, while the redundant sensor node only exchanges residual energy information with the static sensor node where it is located, and is not responsible for sensing dat...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com