A treatment method for rapid sealing of top water when water-stopping failure occurs in expansion joints of gravity dams
A treatment method and technology of expansion joints, applied in water conservancy projects, marine engineering, construction, etc., can solve problems such as rapid sealing of invalid top water, water-stop damage of gravity dam expansion joints, etc., and achieve low-loss rapid repair projects and removal projects Hidden dangers, the effect of solving engineering problems
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0035] Include the following steps:
[0036] 1. Drilling and testing seepage conditions
[0037] 1. Drilling
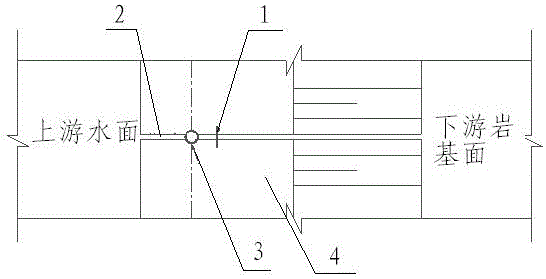
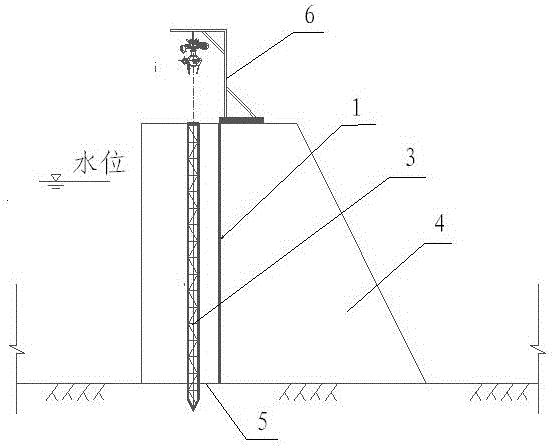
[0038] In the direction of the water-facing surface of the dam 4, and 30 cm before the original expansion joint waterstop 1, a hole 3 is drilled downward along the expansion joint 2. The diameter of the hole is 90 mm. The principle of drilling holes and grouting is to facilitate the drilling depth. 5 in 50 cm;
[0039] 2. Test the seepage water in the hole
[0040] Test with a flow meter or a long round wooden rod. The diameter of the wooden rod should be slightly larger than the width of the expansion joint. When there is a large seepage flow, the wooden rod will be affected by the seepage pressure and its movement will be affected. s position;
[0041] 2. Expansion joint closure
[0042] 1. Adopt auxiliary seepage reduction measures
[0043] When the seepage water is serious, it means that the expansion joints are seriously damaged and cannot be directly block...
Embodiment 2
[0065] Include the following steps:
[0066] 1. Drilling and testing seepage conditions
[0067] 1. Drilling
[0068] In the direction of the water-facing surface of the dam 4, and 40 cm in front of the original expansion joint waterstop 1, drill a hole 3 downward along the expansion joint 2, with a diameter of 100 mm, in order to facilitate drilling and grouting, and the drilling depth is to go deep into the structural foundation 5 in 75 cm;
[0069] 2. Test the seepage water in the hole
[0070] Test with a flow meter or a long round wooden rod. The diameter of the wooden rod should be slightly larger than the width of the expansion joint. When there is a large seepage flow, the wooden rod will be affected by the seepage pressure and its movement will be affected. s position;
[0071] 2. Expansion joint closure
[0072] 1. Adopt auxiliary seepage reduction measures
[0073] When the seepage water is serious, it means that the expansion joints are seriously damaged and ...
Embodiment 3
[0093] Include the following steps:
[0094] 1. Drilling and testing seepage conditions
[0095] 1. Drilling
[0096] In the direction of the water-facing surface of the dam 4, and 50 centimeters in front of the original expansion joint waterstop 1, a hole 3 is drilled downward along the expansion joint 2. The diameter of the hole is 109 mm. The principle is to facilitate drilling and grouting, and the depth of the drilling is to go deep into the structural foundation. 5 in 100 cm;
[0097] 2. Test the seepage water in the hole
[0098] Test with a flow meter or a long round wooden rod. The diameter of the wooden rod should be slightly larger than the width of the expansion joint. When there is a large seepage flow, the wooden rod will be affected by the seepage pressure and its movement will be affected. s position;
[0099] 2. Expansion joint closure
[0100] 1. Adopt auxiliary seepage reduction measures
[0101] When the seepage water is serious, it means that the exp...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com