A Protection Method for SM2 Signature Algorithm Against Lattice-Based Error Attack
A technology of error attack and algorithm, applied in the field of information security, can solve the problem of not being found, and achieve the effect of protecting the private key from being leaked
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
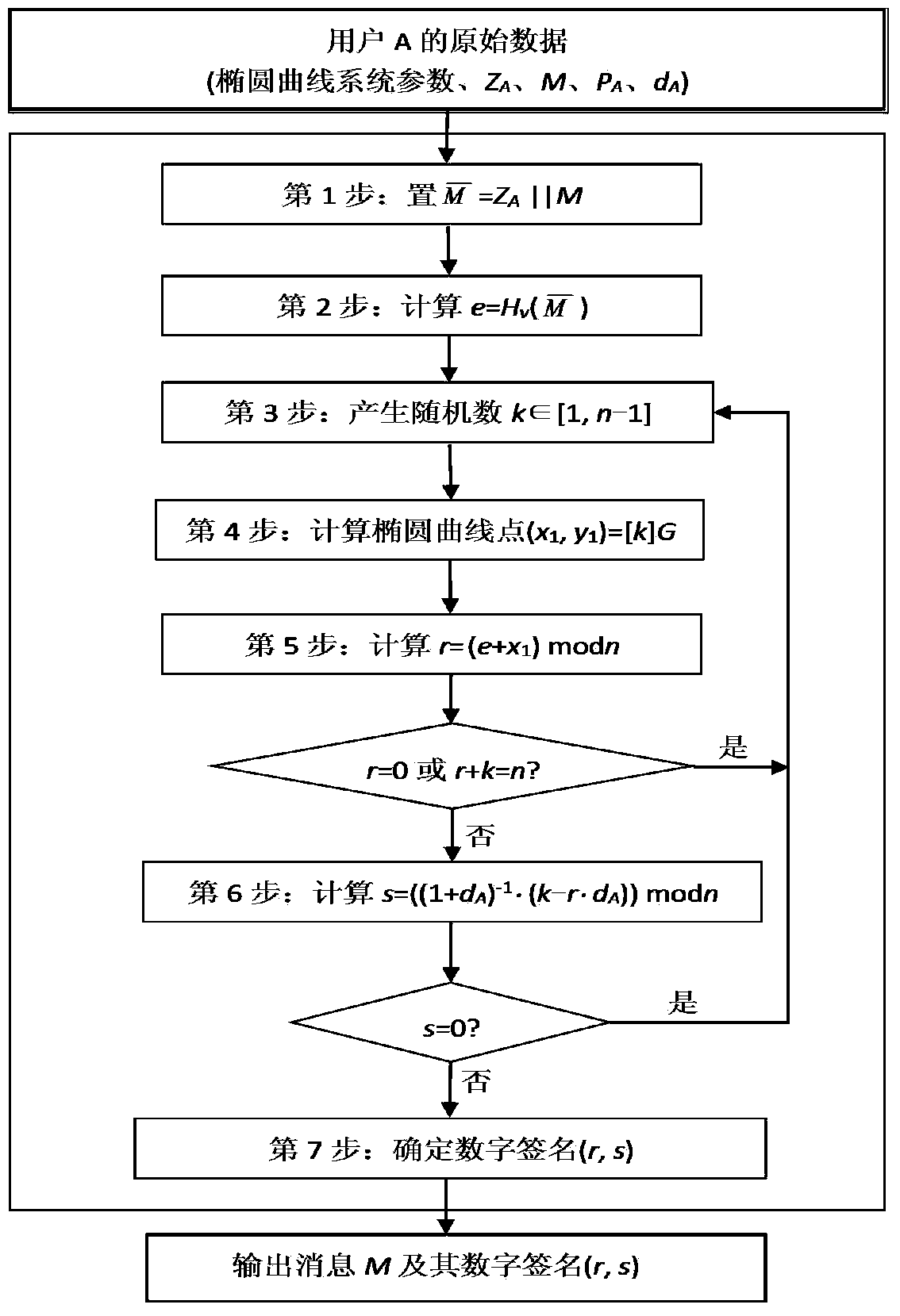
[0082] The following describes the present invention in further detail with reference to the accompanying drawings and an example, but does not limit the scope of the present invention in any way. In the embodiment, the validity of the present invention is illustrated by the demonstration and experiment of a lattice attack failure of an SM2 signature algorithm with the protection method of the present invention.
[0083] If the attacker learns N (N=50) random numbers k in the SM2 signature algorithm with protection by injecting wrong means i ,w i ∈[1,n-1] low-order l (l=32) bit a i And c i , And obtained N wrong signature results (r i ,s i ), i∈{1,2,...,N}. k=b i 2 l +a i , W=c i 2 l +d i , Where 0i , D i l .
[0084] Substitute the protected signature algorithm step 6 s=((1+d A ) -1 (k+(k 0 -r)d A )) modn is available:
[0085] 2 -l (r i +s i -c i )d A -2 -l (a i -s i )=b i +d i d A modn
[0086] Let t i = 2 -l (r i +s i -c i )modn, u i = 2 -l (a i -s i ) modn, the above formula can...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com