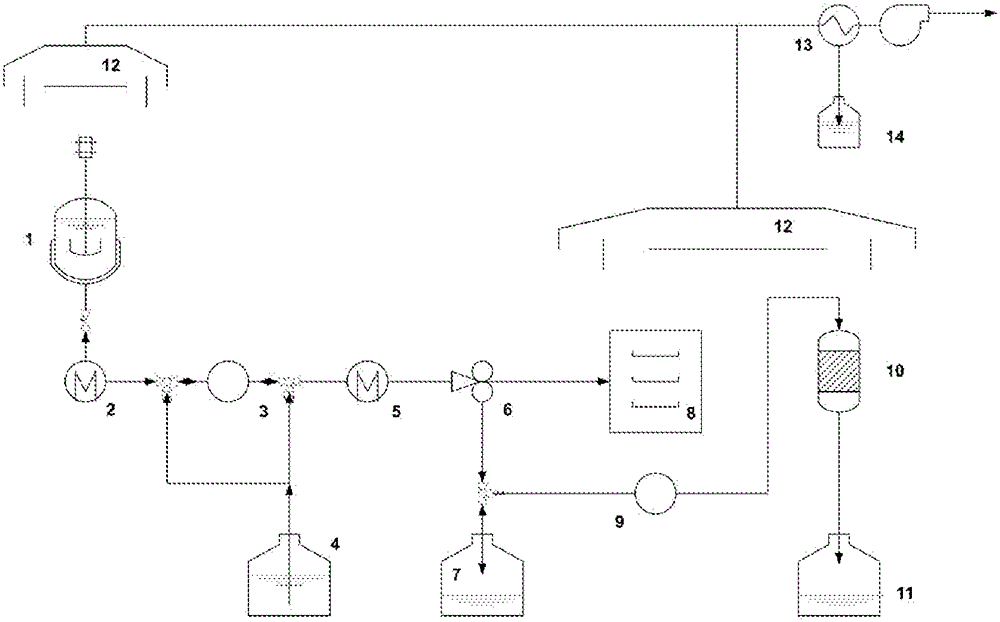
Process for the extraction of polyhydroxyalkanoates from biomass
A technology of biomass and biomass particles, applied in solid solvent extraction, fermentation, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 8
[0113] EQ-5
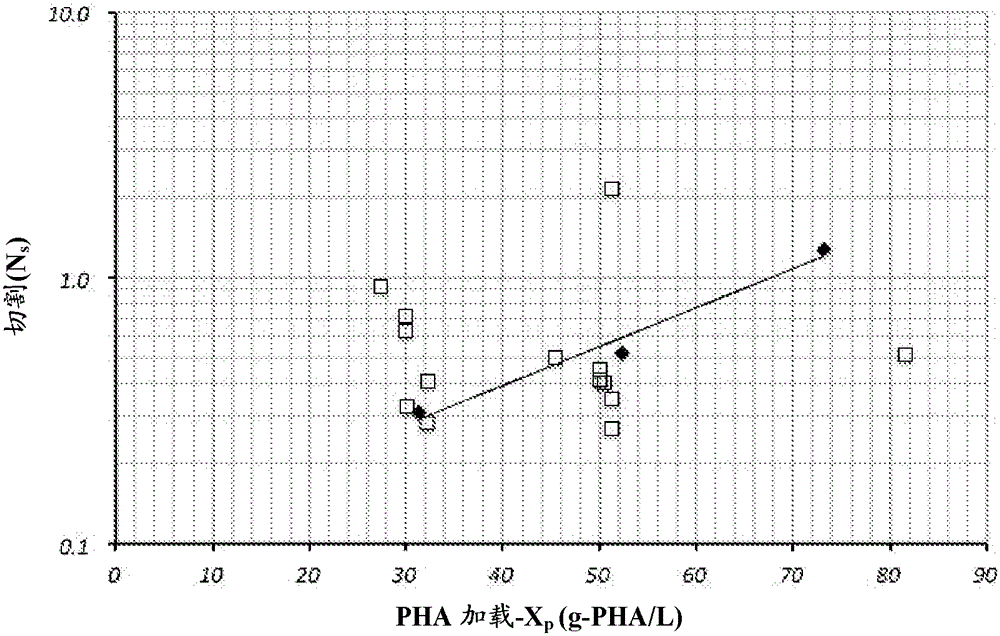
[0114] where X n is the non-PHA component of the biomass loaded into the extraction process. Thus in a calibrated system specifying the extraction temperature and solvent (Example 8), the loading dependence versus the off-rate can be described. We found that the assessment of polymer off-rate during recovery is important to accommodate batch-to-batch variability in PHA-enriched biomass quality with batch-specific adjustments to the PHA process recovery operating parameters.
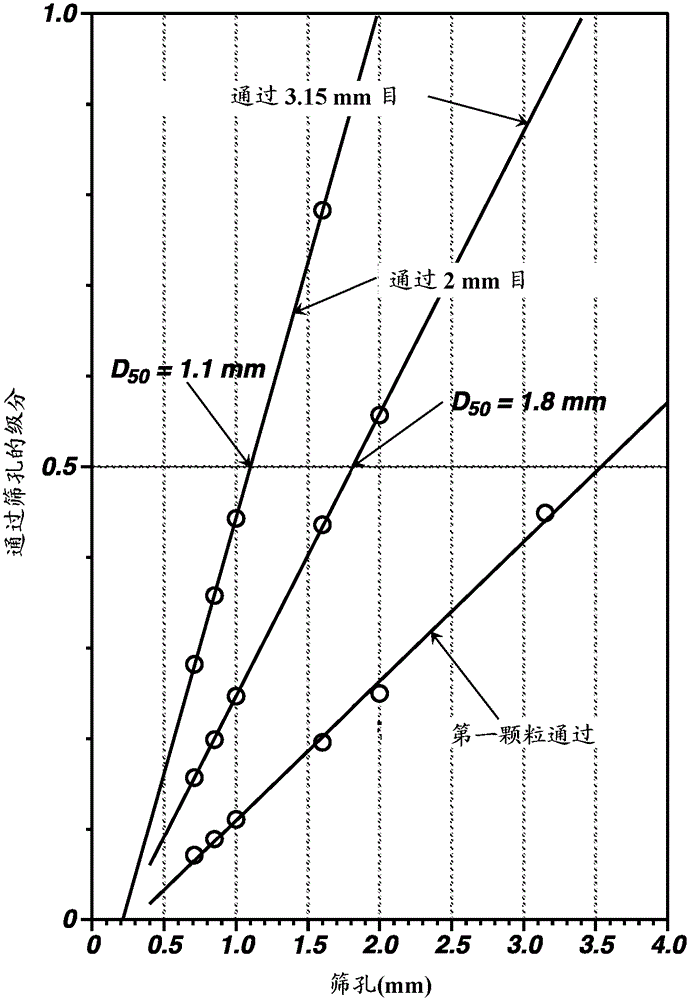
[0115] Based on more information on the molecular weight distribution of PHA-containing biomass (Example 5) and extraction time, biomass solvent loading limits can be defined with the expectation that the recovered polymer will remain above the specified lower product quality limit for molecular weight (Example 5). Example 9). The biomass loading constraints can be compared to the resulting PHA solvent loading to be used, as this relates to practical process constraints for product reco...
Embodiment 1
[0181] Embodiment 1—general analysis method and material
[0182] Thermogravimetric Analysis (TGA)
[0183] Between 2 and 10 mg of finely ground dry PHA-enriched biomass sample was weighed and heated from room temperature to 550°C under an inert nitrogen atmosphere. The sample temperature was raised to 105°C at a rate of 10°C and the weight was equilibrated at 105°C for 10 minutes. The samples were evaluated for moisture loss at 105°C. The temperature was again increased at a rate of 10°C until 550°C and weight loss was recorded. The ash content of the sample was evaluated from weight loss while maintaining the sample at 550° C. for 30 minutes in air. Polymers in both biomass and extracted PHA resins were quantitatively evaluated by this standard method. The weight loss and the change in the rate of weight loss with temperature were taken into account. These trends inform the thermal decomposition temperature (T d )PHAT d , the PHA content of the biomass and the pur...
Embodiment 2
[0202] Example 2 - Kinetics of PHA Dissolution
[0203] It is practical to measure the natural dissolution rate of poly(3-hydroxybutyrate) (PHB) in PHA-poor solvent as a benchmark. PHB is considered a "worst case scenario". Due to the tendency for higher crystallinity with PHB, it is considered to be more difficult to dissolve, especially in PHA-poor solvents. The dissolution trend of finely divided pure PHB powder (>98% purity) as a function of temperature was studied. Weigh PHB powder into a 12mL test tube and mix with 5mL equivalent 2-butanol to form a 50g-PHB / L solution. The tubes were sealed with Teflon-lined screw caps and introduced into a constant temperature heater at the selected temperature. The contents of the tube were vortexed every 3 minutes, and immediately after mixing, the solution optical density and color were measured. The relative change in solution color was used to indicate the progress of PHB dissolution in solution ( figure 1 , according to th...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thermal decomposition temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| decomposition temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com