Method and apparatus for three-dimensional fabrication
A technology of equipment, three-dimensional objects, applied in the direction of manufacturing tools, additive manufacturing, opto-mechanical equipment, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach
[0012] In some embodiments of continuous liquid phase interface printing, the first layer or region is provided immediately above, or in contact with, the build plate. The build plate is transparent to radiation that initiates polymerization (e.g., patterned radiation), but the build plate is preferably semipermeable to the polymerization inhibitor and allows the polymerization inhibitor (e.g., oxygen) to pass through it partially or completely (e.g., for continuous effectively feeds the inhibitor into the "dead zone"). The build plate is preferably "fixed" or "stationary", meaning that it does not need to slide, indent, spring back, etc. to produce discrete or sequential steps (as in a layer-by-layer process). Of course, minor movement of the build plate in the x and / or y directions (without unduly interrupting the polymerization gradient, but still allowing continuous polymerization of the liquid interface) may still accommodate some embodiments, also discussed below.
[00...
Embodiment 1
[0145] Inhibitor transfer from separate feed surface to build surface
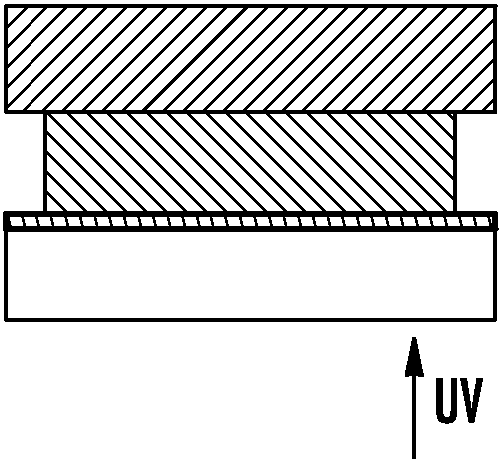
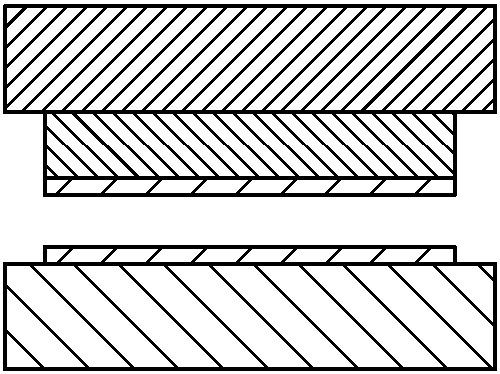
[0146]A drop of ultraviolet (UV) curable adhesive was placed on the metal plate and covered with a 10 mm thick plate of TEFLON™ AF fluoropolymer (amorphous glassy polymer) as shown in Figure 5a. UV radiation was delivered to the adhesive from the TEFLONAF side, as shown in Figure 5b. After UV exposure, the two plates were separated. It was found that no force was required to separate the two plates. After testing the samples, it was found that only the adhesive near the metal plate was cured, and a thin film of uncured adhesive was present on the TeflonAF fluoropolymer plate and also on the cured portion of the adhesive, as shown in Figure 5c .
[0147] Two comparative experiments were also performed, using clean glass (Fig. 5d-5f) and glass treated with a release layer (Fig. 5g-5i). It was demonstrated that considerable force was required to separate the clean glass from the metal, and the adhesive ...
Embodiment 2
[0150] Inhibitors are transferred from the build plate to the build surface
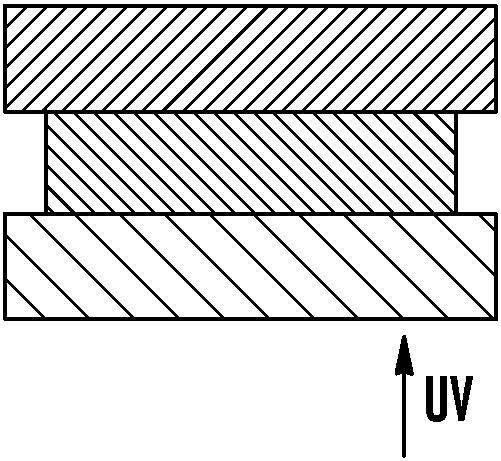
[0151] Samples 1 and 2 were prepared in a similar manner, where a drop of UV-curable adhesive was placed on a metal plate and covered with a 10 mm thick TEFLON™ AF fluoropolymer plate, as shown in Figure 6a. Both samples were exposed to a nitrogen environment to eliminate any oxygen present, as shown in Fig. 6b. The next two samples were placed in standard atmospheric environment, and sample 1 was exposed to UV radiation immediately, while sample 2 was exposed to UV radiation for 10 minutes after atmospheric environment. Both samples were exposed to the same amount of UV radiation as Figure 6C and Figure 6E shown. In sample inspection after UV exposure, it was found that the adhesive was fully cured in Sample 1, as Figure 6D shown, and in sample 2 the adhesive cures only close to the metal plate, as Figure 6F shown. A film of uncured adhesive was present on the Teflon AF fluoropolymer pla...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com