Variable-rigidity elastic joint of cam structure
An elastic joint and variable stiffness technology, applied in the field of robotics, can solve the problems of complex joint structure, poor variable stiffness characteristics, and large energy consumption of variable stiffness robots, achieving continuous and reliable variable stiffness process, stable variable stiffness process, and easy manufacturing and processing. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
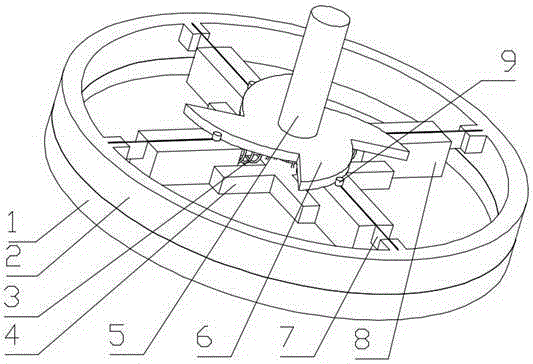
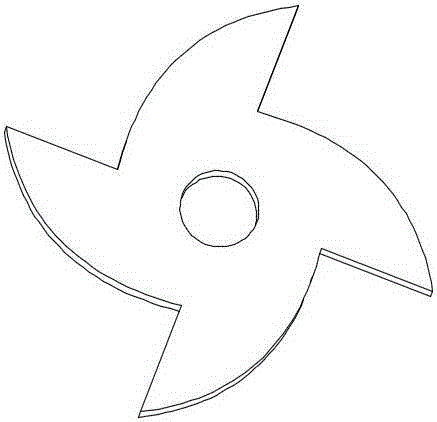
[0037] A variable stiffness elastic joint with a cam structure, consisting of a casing (1), a shaft (5) and an outer ring (2); it is characterized in that the shaft (5) is set at the center of rotation of the casing (1), and is connected to the casing ( 1) are fixedly connected, and the casing (1) and the outer ring (2) are connected by a rotating pair; the outer ring (2) is radially installed with a plurality of symmetrical spring pieces (7), and each spring One end of the piece (7) is fixedly connected to the outer ring (2), and the other end is fixedly connected to the shaft (5) through the spring (3); one end of the spring (3) is connected to the shaft (5), and the other end is connected to the sliding on the block (8); the sliding block (8) is installed in the middle of the spring leaf (7), distributed symmetrically with the spring leaf (7), and is slidingly connected with the spring leaf (7); the shaft (5 ) is installed with a cam disc (6), the cam disc (6) is a centrall...
Embodiment 2
[0042] Such as Figure 12 As shown, the variable stiffness robot elastic joint in this example is installed at the leg joint of the hexapod bionic robot, the input end 12 of the bionic robot leg is fixedly connected with the shell 1 of the elastic joint, and the outer ring 2 is connected to the output end 13 of the bionic robot leg Fixed connection. In the application process, the stiffness characteristics of the elastic joint are set in advance according to the working condition information. During the walking process of the bionic robot, when the motor drives the input end 12 of the leg of the bionic robot to rotate, the external load will affect the output end 13 of the leg of the bionic robot. When an impact occurs, the elastic joint in this example will produce a buffering effect through the elastic action of the spring leaf 7, so that there is an elastic action between the outer ring 2 and the shell 1, which effectively protects the leg joints of the bionic robot and imp...
Embodiment 3
[0044] Such as Figure 13 As shown, the elastic joint of the robot with variable stiffness in this example is installed at the leg joint of the human prosthesis. The elastic joint is installed at the joint between the thigh and the lower leg of the human prosthesis. The input end of the driving lower leg is fixedly connected with the shell 1 of the elastic joint. The ring 2 is fixedly connected to the prosthetic leg 15. During the application process, the stiffness characteristics of the elastic joint are set in advance according to the working condition information. When the prosthesis is walking, when the motor drives the input end of the prosthetic leg 15 to rotate, the external load will affect the prosthesis. The calf 15 produces an impact, and the elastic joint of this example will produce a buffering effect through the elastic action of the spring leaf 7, so that there is an elastic action between the outer ring 2 and the shell 1, effectively protecting the prosthetic le...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com