Treatment agent for synthetic fibers and use of same
A synthetic fiber and treatment agent technology, which is applied in fiber treatment, fiber type, textiles and papermaking, etc., can solve the problems of not being able to provide synthetic fiber treatment agents that actively use esters, and difficult to obtain esters, so as to suppress scum or broken Head generation, excellent quality, and excellent migration stability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
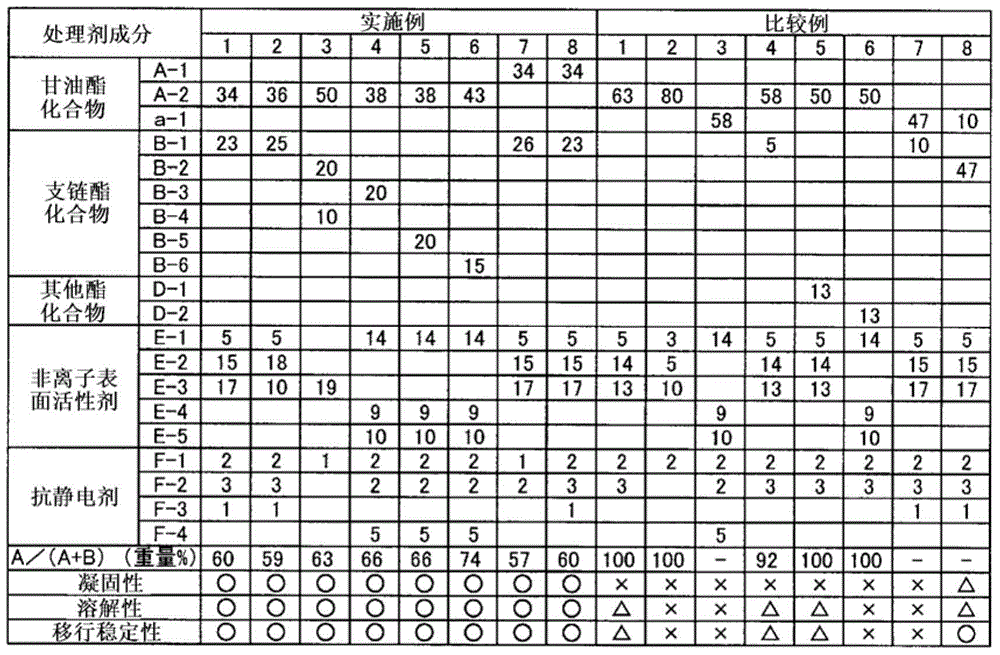
Embodiment 1~8、 comparative example 1~8
[0117] (treatment agent of embodiment 3, 7, comparative example 2)
[0118] The ingredients listed in Table 1 were mixed and stirred until uniform to prepare the treatment agent I. The prepared treatment agent I was diluted with a low-viscosity mineral oil having 11 to 15 carbon atoms to prepare a treatment agent II having a non-volatile component concentration of 80% by weight.
[0119] (Examples 1, 2, 4-6, 8, comparative examples 1, 3-8 treatment agent)
[0120] The ingredients listed in Table 1 were mixed and stirred until uniform to prepare the treatment agent I. Slowly add the prepared treatment agent I into the ion-exchanged water under stirring. After the addition, it was stirred for 60 minutes until it became a homogeneous state, and a treatment agent II (O / W type emulsion state) having a non-volatile matter concentration of 18% by weight was prepared.
[0121] Using each of the treatment agents I prepared above, coagulation and solubility were evaluated by the foll...
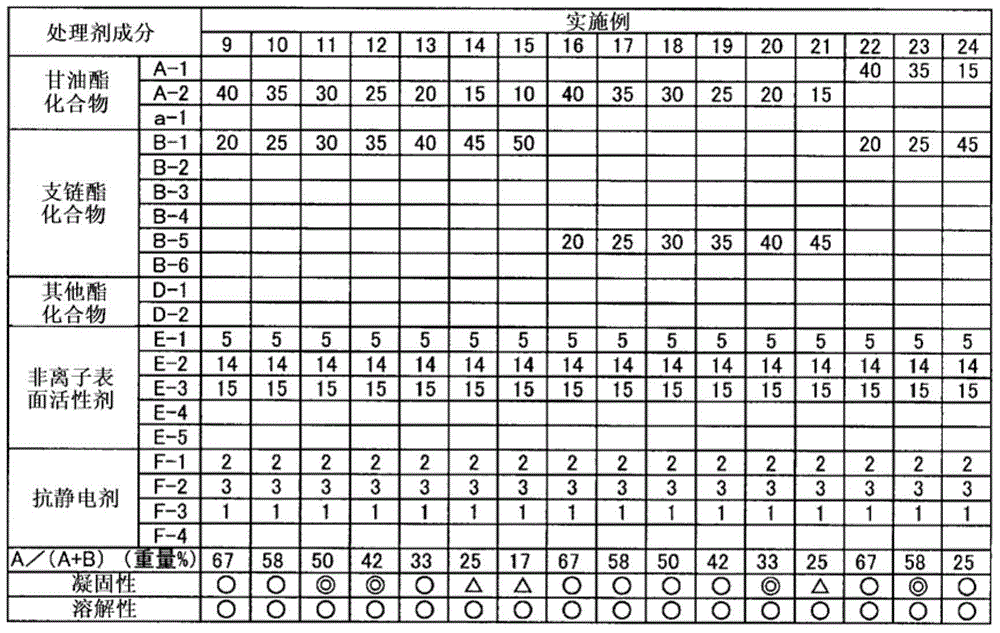
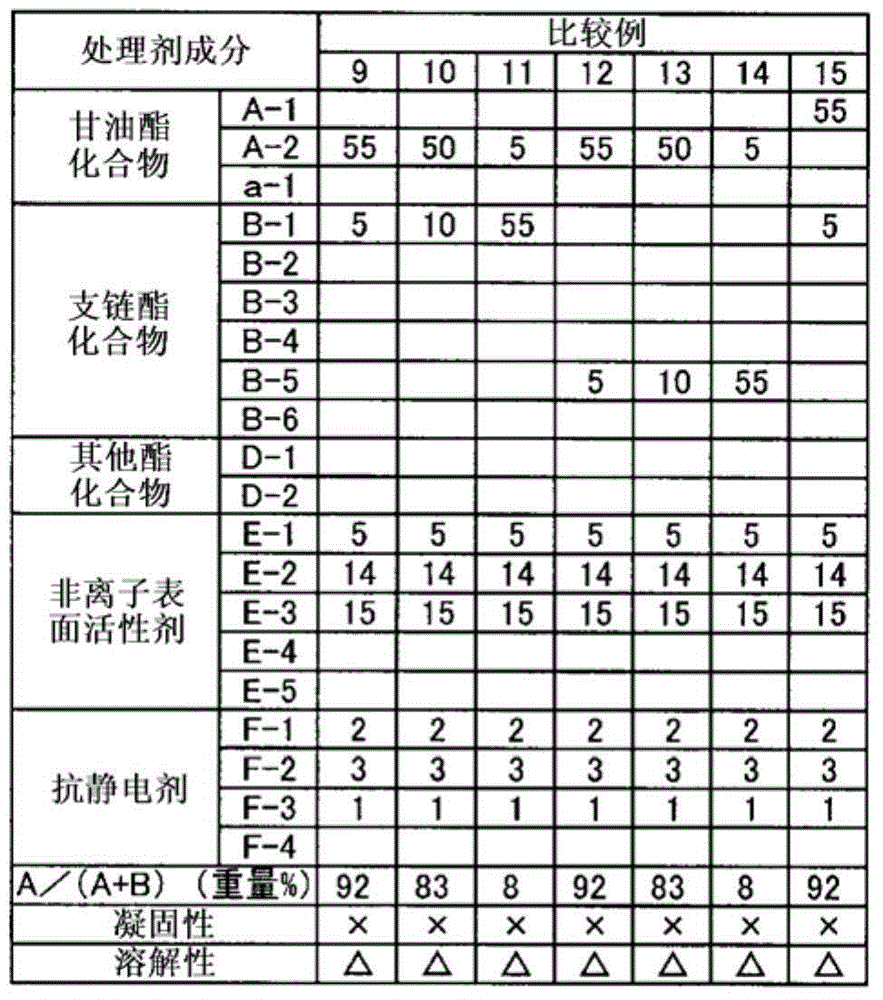
Embodiment 9~24、 comparative example 9~15
[0168] Mix the ingredients listed in Tables 2 and 3 and stir until uniform to prepare treatment agent I. Using each of the prepared treatment agents I, coagulability and solubility were evaluated in the same manner as above. In addition, the figure of the processing agent component of Table 2, 3 shows the weight part of the non-volatile content of a processing agent. In addition, the details of the processing agent components of Tables 2 and 3 are as above.
[0169] Table 2
[0170]
[0171] table 3
[0172]
[0173] It can be seen from Tables 2 and 3 that the treatment agents of Examples are not easy to solidify and have excellent solubility. On the other hand, the treating agent of the comparative example was poor in solubility, needed to be warmed before use, and had poor handling properties. From the results of Examples 1 to 7 and Comparative Examples 1 to 6, it was determined that the solubility was related to the migration stability. Therefore, it can be predic...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to view more
Login to view more - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap