Relay-based distributed collaborative spectrum perception method
A distributed cooperation and spectrum sensing technology, applied in the field of distributed cooperative spectrum sensing, can solve the problems of interference with authorized user information transmission, separation of authorized user information and cognitive user information, low spectrum utilization, etc., so as to improve spectrum efficiency and improve The effect of detection probability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
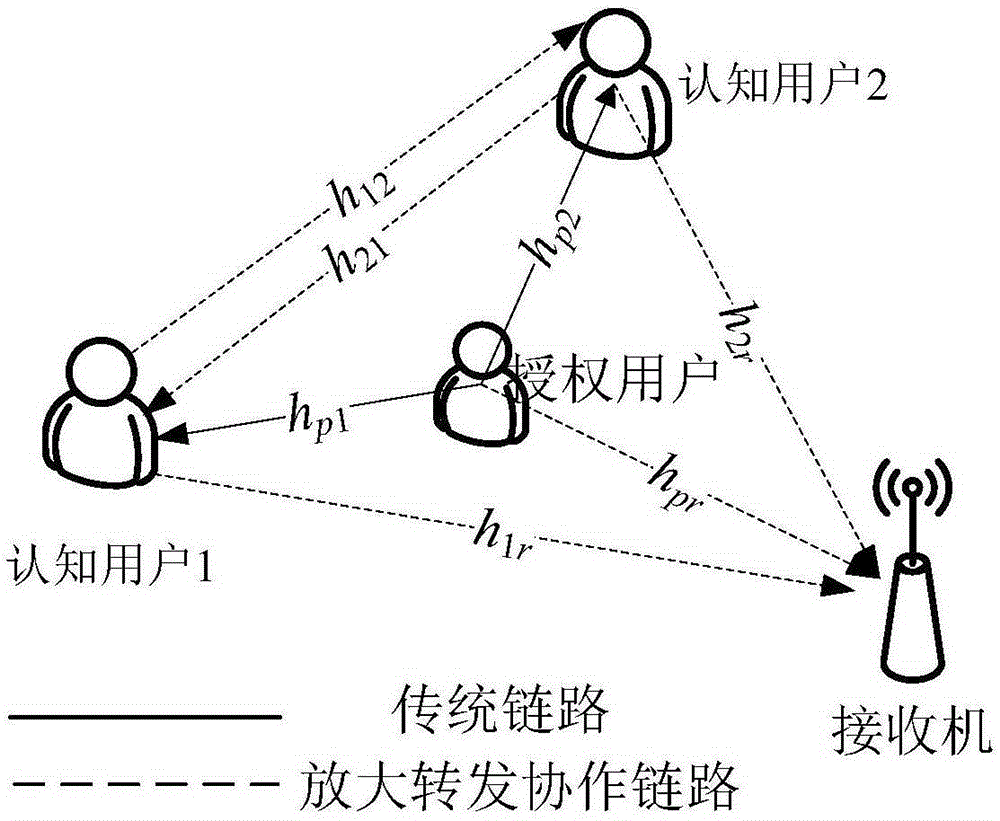
[0023] The relay-based distributed cooperative spectrum sensing method in this embodiment combines Figure 6 As shown, the method is realized through the following steps:
[0024] Step 1. The authorized user obtains and sends the signal, and then estimates the signal power received by the two cognitive users from the authorized user, and the cognitive user with the estimated larger signal power is recorded as the cognitive user U 1 , another cognitive user is denoted as cognitive user U 2 ;
[0025] Step 2. In the first transmission time slot T 1 Time is the first time period, cognitive user U 2 To cognitive user U 1 Send a signal to the cognitive receiver Cognitive user U 1 Using Spectrum Sensing Signals Carry out energy detection, if an authorized user is detected, go to step 7, otherwise, go to step 3;
[0026] Step 3. In the first transmission time slot T 1 After the second transmission slot T 2 Time is the second time period, the cognitive user U 1 will recei...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0036] The difference from Embodiment 1 is that, in the relay-based distributed cooperative spectrum sensing method of this embodiment, the process for authorized users to obtain signals in Step 1 is as follows:
[0037] Step 11. In the cognitive user radio system, let the sinusoidal signal represent the sinusoidal signal sent by the authorized user, and let the Chirp signal represent the cognitive user U with different order 1 and cognitive user U 2 The transmitted signal; in the fractional domain, the Chirp signal is expressed as a pulse signal with a fairly narrow bandwidth, while the sinusoidal signal is expressed as a broadband signal with a wider bandwidth; it shows that the Chirp signal has the characteristics of energy accumulation in the fractional domain, while the sinusoidal Signal does not;
[0038] Step 12: Through the narrowband fractional domain filter, the cognitive user U 1 and cognitive user U 2 The signal of the authorized user is separated from the signa...
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0040] The difference from the specific embodiment 1 or 2 is that, in the relay-based distributed cooperative spectrum sensing method in this embodiment, the cognitive user U described in step 2 2 To cognitive user U 1 Send a signal to the cognitive receiver Cognitive user U 1 Using Spectrum Sensing Signals to the received signal During the energy detection process, the spectrum sensing signal Expressed as the following formula:
[0041] y 1 d ( 1 ) = θh p 1 ( 1 ) s p ( 1 ) + w ( 1 ) - - - ( ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com