Steady-state visual evoked potential brain-computer interface method based on cross-modulation frequency
A steady-state visual induction and cross-modulation technology, applied in the field of brain-computer interface, to achieve the effect of increasing the number of targets, easy implementation, and overcoming the limitation of flicker frequency points
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0025] Embodiments of the present invention are described in further detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings:
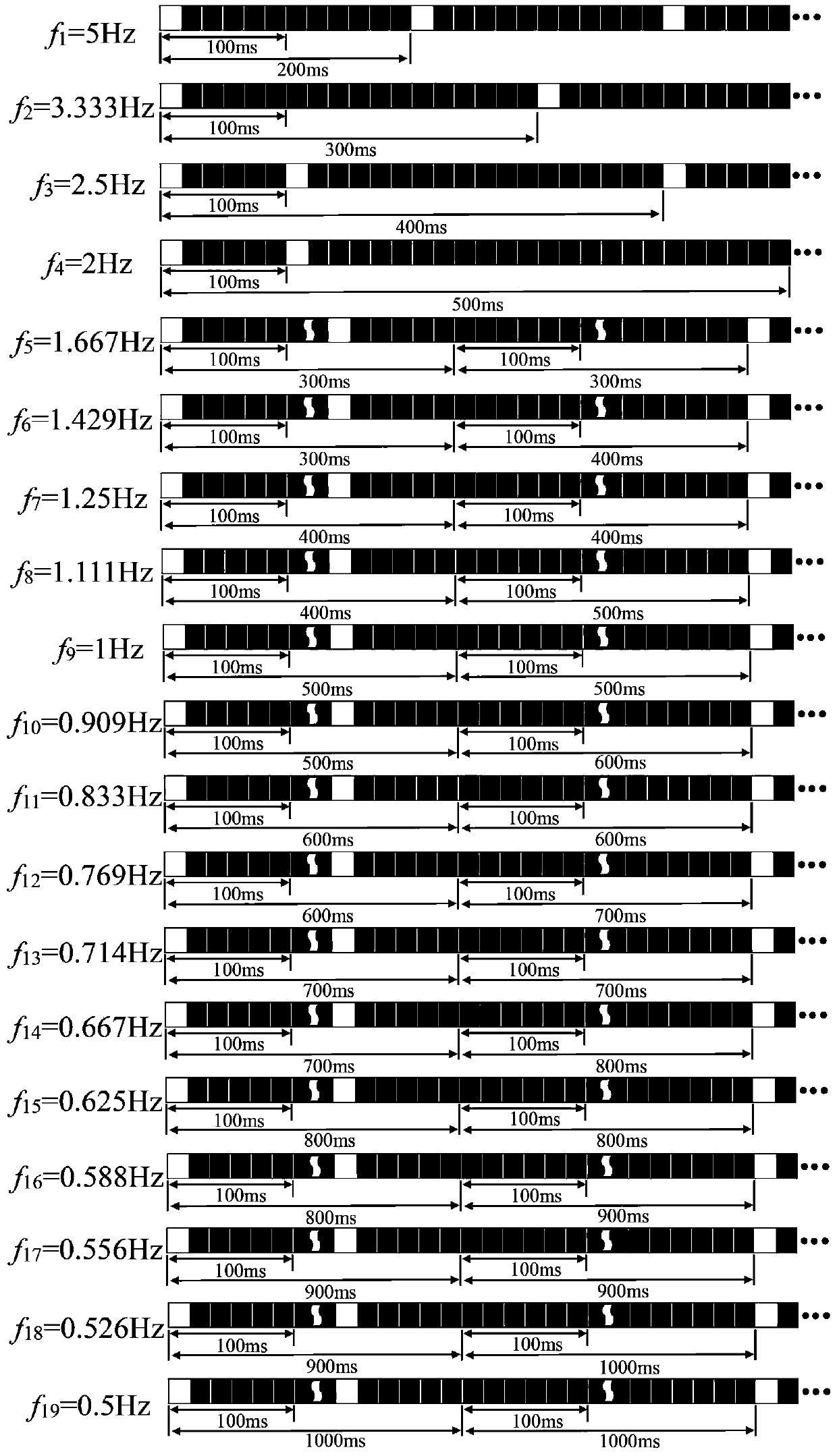
[0026] A steady-state visually evoked potential brain-computer interface method based on cross-modulation frequency, which adopts the cross-modulation frequency encoding method as the induction method of steady-state visually evoked potential, and the EEG acquisition equipment collects the user's EEG signal, stores it and performs pre-processing. Processing (segmentation, down-sampling and band-pass filtering of the EEG signals recorded by the electrodes according to the synchronous signal); frequency features are extracted from the preprocessed steady-state visual evoked potentials, and the extracted frequency features are classified and identified , and finally output the control command. Specifically include the following steps:
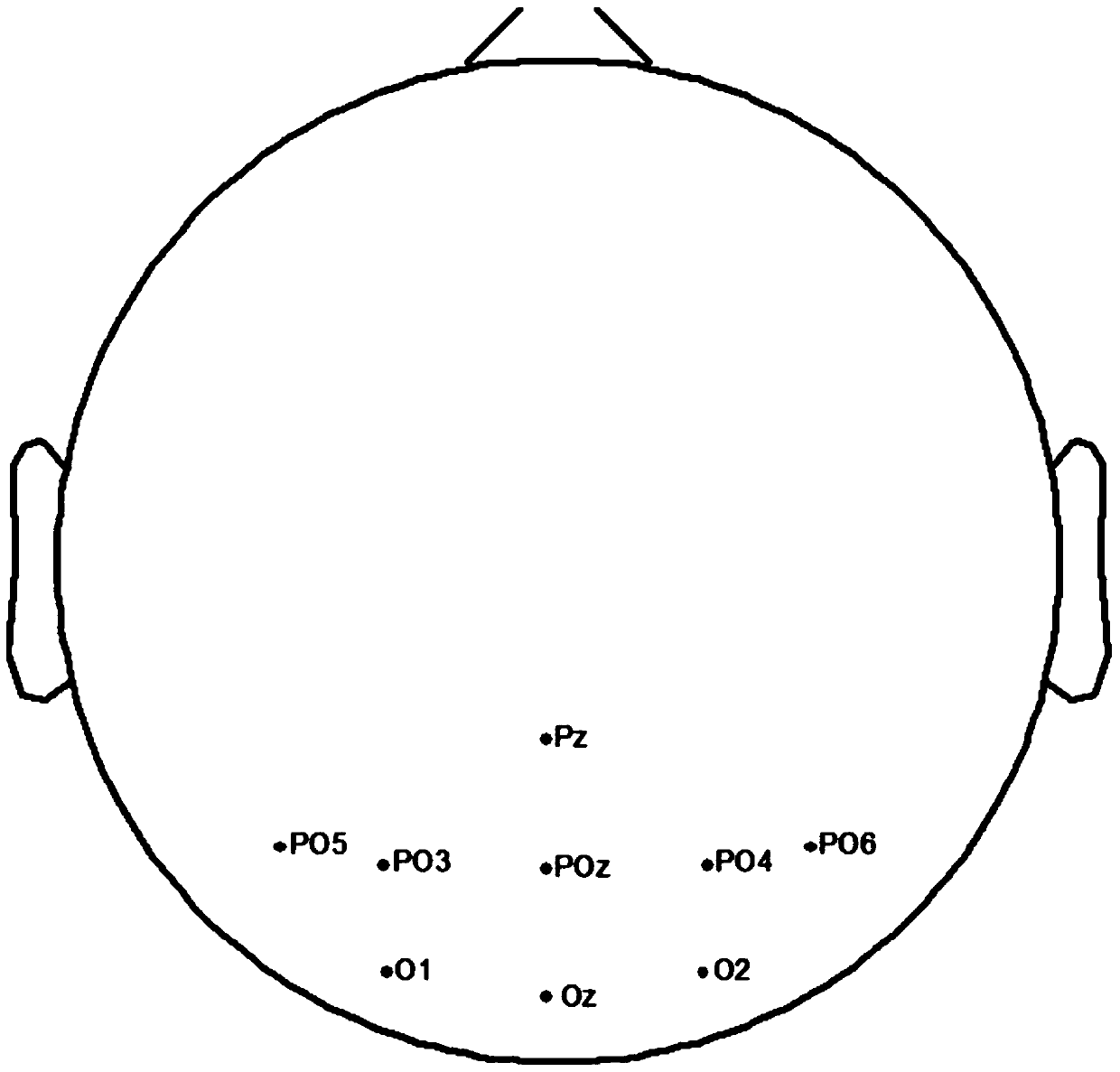
[0027] Step 1. Place measurement electrodes at Pz, PO5, PO3, POz, PO4, PO6, O1, Oz, and O2 in the occipital area of...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com