Detection method for determining abnormality of chromosome number in biological samples
A detection method and chromosome technology, applied in the field of nucleic acid detection, can solve the problems of abnormal, non-invasive detection of fetal chromosome number and lack of accurate quantitative ability of gene copy number, etc., and achieve the effect of broad application prospects.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0018] Example 1: Detecting whether the number of chromosomes in a biological sample is abnormal based on droplet digital PCR
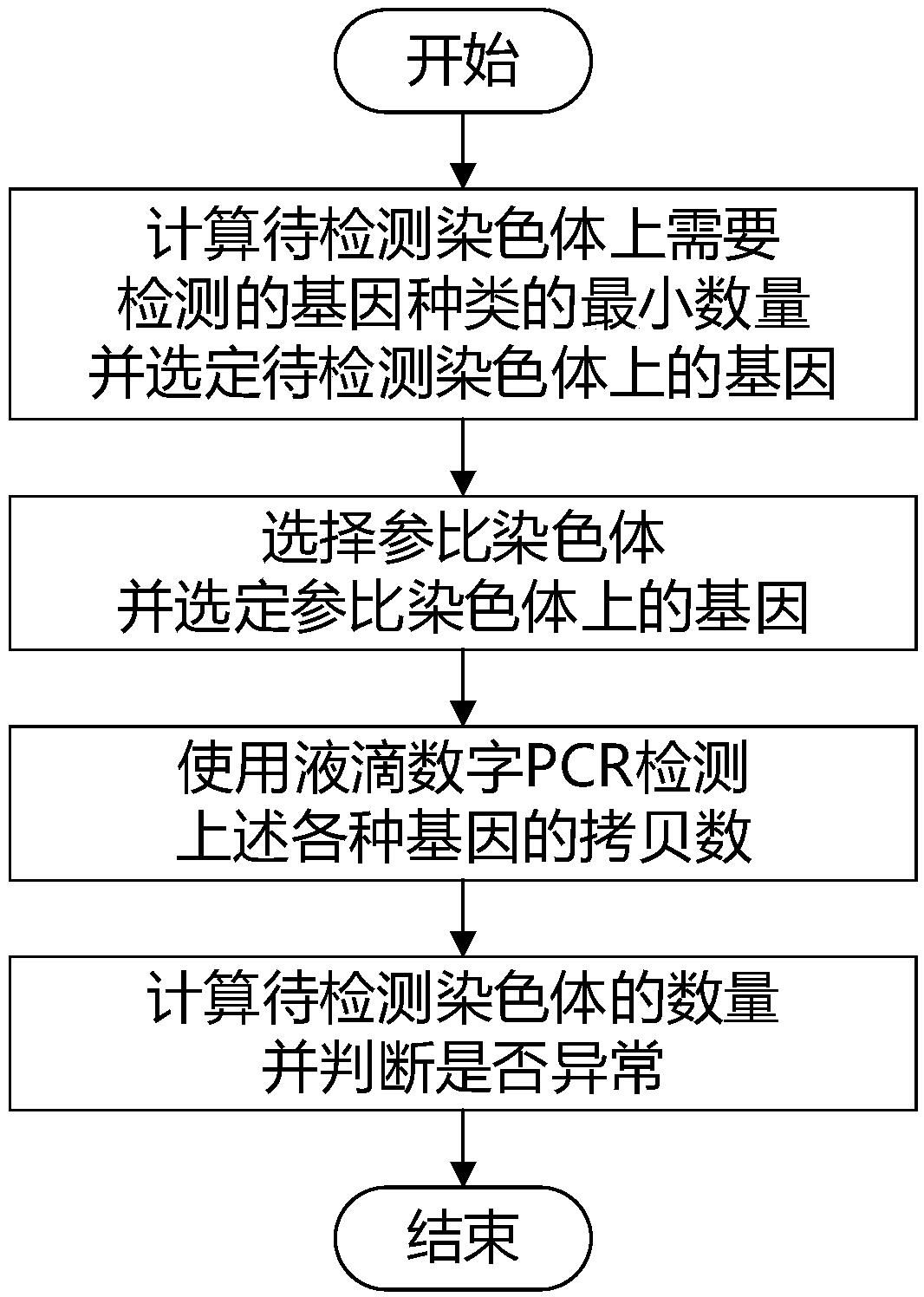
[0019] figure 1 It is a flow chart of detection of chromosome quantity change based on droplet digital PCR. In the figure, the detection process is divided into four steps.
[0020] Step 1: Calculate the minimum number of gene types that need to be detected on each chromosome.
[0021]The variation value of the number of chromosomes refers to the minimum absolute difference that may occur between the number of the chromosomes to be detected under abnormal conditions and the number of chromosomes to be detected under normal conditions in a single genome of the organism. Taking the number of human chromosome 21 on a single genome as an example, the number of this chromosome may be 3 under abnormal conditions, and the number of this chromosome is 2 under normal conditions, so the minimum absolute difference between the two that may appear before is δ= ...
Embodiment 2
[0041] Example 2: Detecting whether the number of fetal chromosome 21 in cervical smear samples is abnormal based on droplet digital PCR
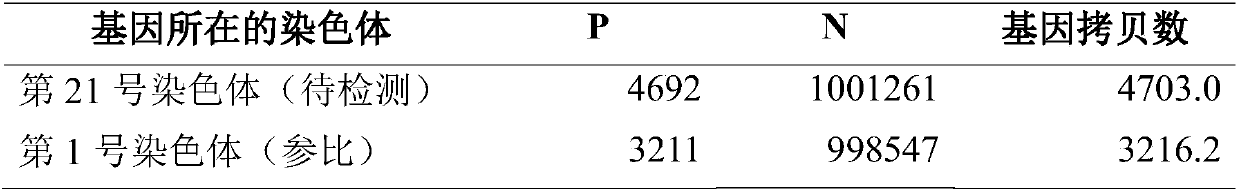
[0042] Based on the procedure described in Example 1, in this example, human chromosome 1 is used as a reference chromosome to detect changes in the number of human chromosome 21.
[0043] Step 1: For human chromosome No. 21, the change value of the number of chromosomes to be detected is |3-2|=1; the quality of the nucleic acid measured by an ultraviolet spectrophotometer is 10ng (10000pg), and calculated: sample The nucleic acid equivalent in is 10000 / 6.4×2=3125.0; the confidence level is 95%.
[0044] If it is to realize the detection that the change value of chromosome number is δ=1 (S>R), then U is required - (P S ,N S ) / kU + (P R ,N R )-2>δ, the calculation can get p*=1.1E-3, then -10 6 ×ln(1-p*)=1100.6. Divide the calculation result of 1100.6 by the nucleic acid equivalent of 3125.0 to get: 1100.6 / 3125.0<1, that is, the minim...
Embodiment 3
[0050] Example 3: Based on digital PCR to detect whether the number of chromosomes 13, 18, 21, X and Y in the fetal cell-free nucleic acid of the maternal peripheral blood sample is abnormal
[0051] Based on the process described in Example 1, in this example, human chromosome No. 1 is used as a reference chromosome to detect changes in the number of five human chromosomes No. 13, No. 18, No. 21, X and Y.
[0052] Step 1: For chromosomes No. 13, No. 18 and No. 21, the change value of the number of chromosomes to be detected is δ=|3-2|=1, and for X and Y chromosomes, the change value of the number of chromosomes to be detected Also δ=1, but divided into the following four different situations: δ=|3-2|=1 (only X chromosome will appear), δ=|2-1|=1 (only X chromosome will appear), δ=|1-2|=1 (only Y chromosome will appear) or δ=|1-0|=1 (only Y chromosome will appear), so it is necessary to use different S>R and S<R two cases Formula; the quality of the nucleic acid measured by th...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com