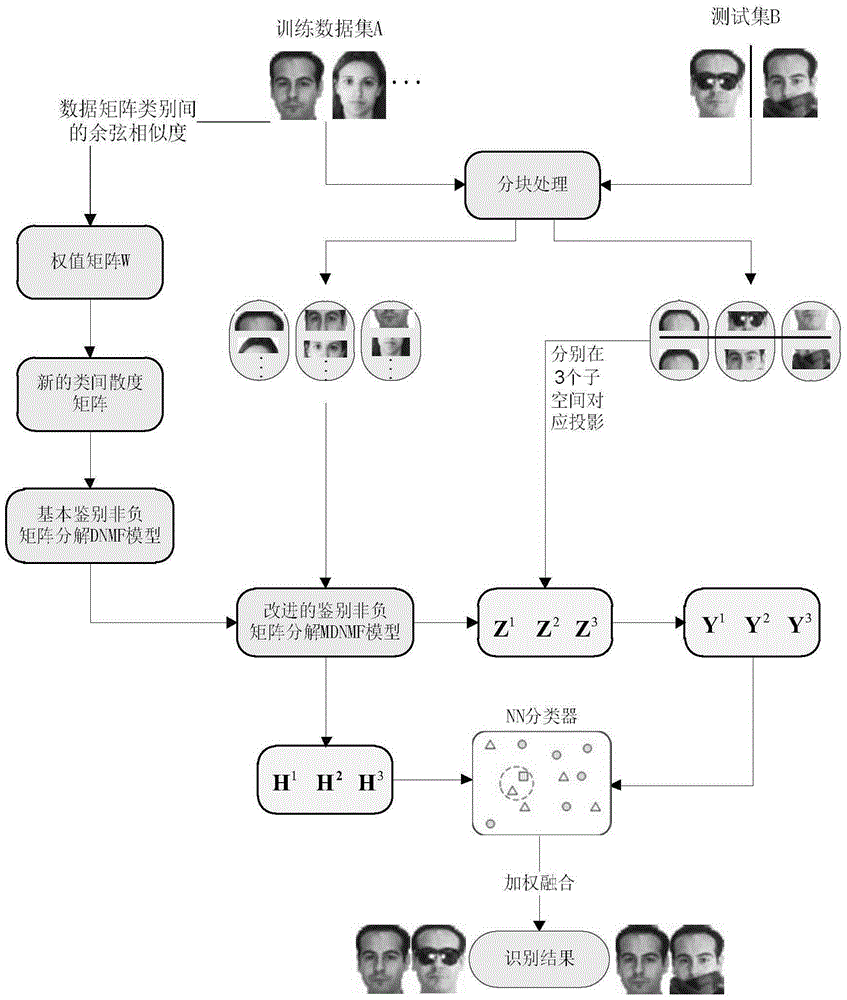
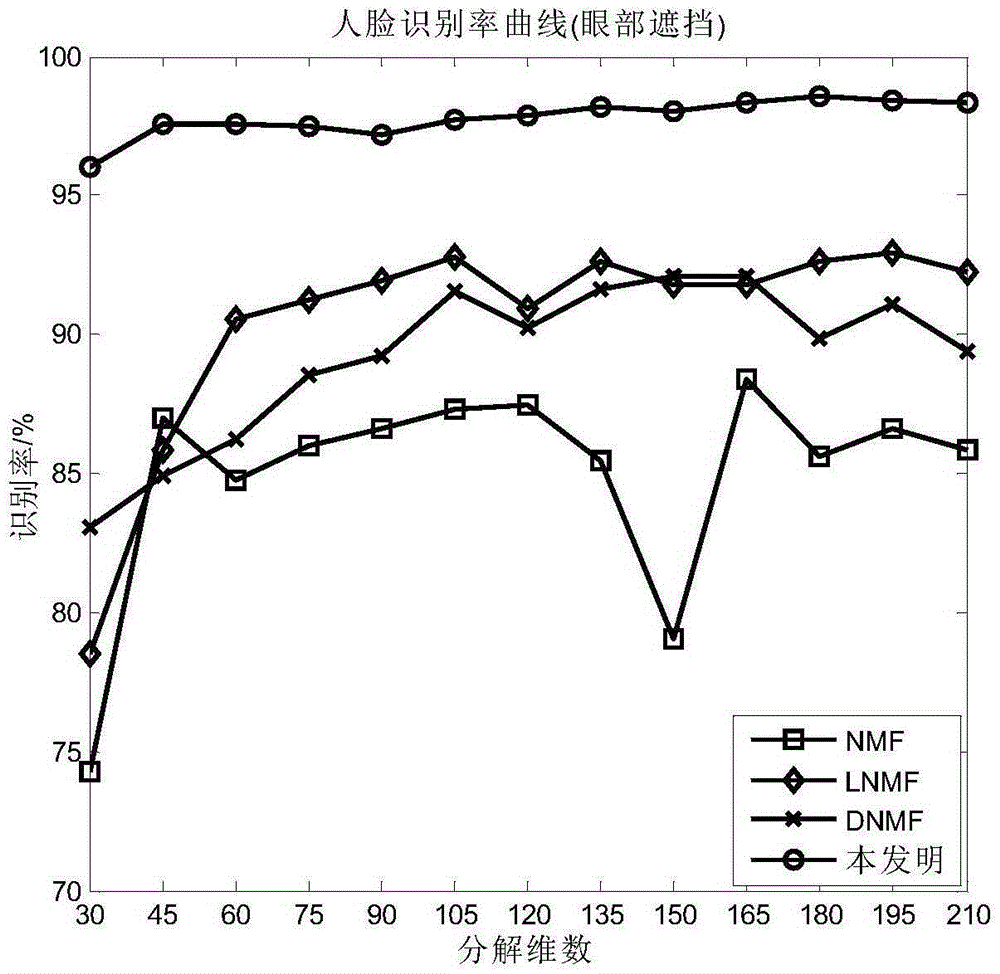
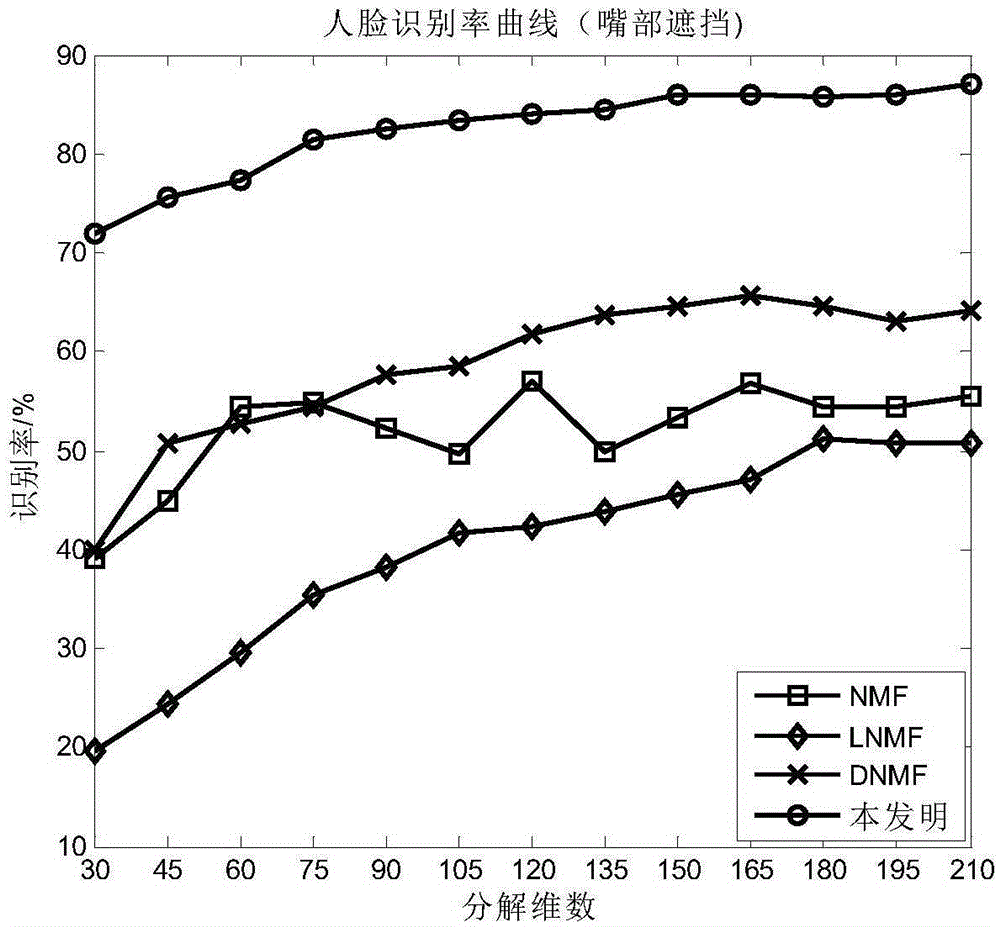
Method for identifying shielded face on basis of blocks and identification of non-negative matrix factorization
A non-negative matrix decomposition and non-negative matrix technology, applied in the field of face image recognition, can solve the problems of insufficient robustness of recognition, poor robustness and adaptability of non-negative matrix decomposition DNMF, etc., to improve the recognition rate and overcome the problem of face recognition The effect of less expressive features
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0029] 1. Introduction to basic theory.
[0030]How to deal with massive data, how to extract features and make effective use of them has attracted extensive attention from the business community and academia. Non-negative matrix factorization (NMF) is an effective feature extraction and data dimensionality reduction method. When dealing with high-dimensional massive data, this method can extract potential local features of data, greatly reduce the dimensionality of data features, and save a lot of storage space. The non-negativity constraint makes the decomposition results have a certain degree of sparsity, which can suppress the impact of external environment changes on the feature extraction to a certain extent. In addition, the non-negative matrix factorization NMF has the intelligent feature of local perception of the whole.
[0031] 1. Basic non-negative matrix factorization NMF model.
[0032] There are n m-dimensional non-negative sample vectors to form an m×n-dimensi...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com