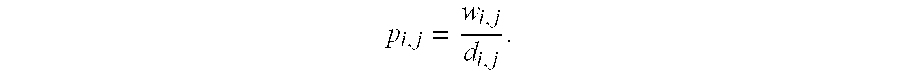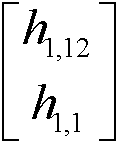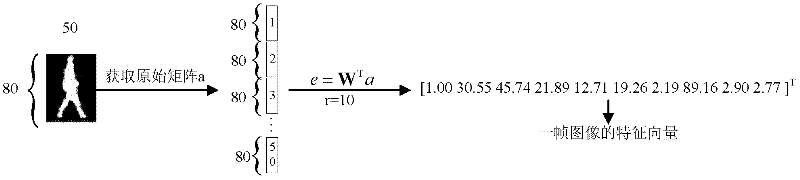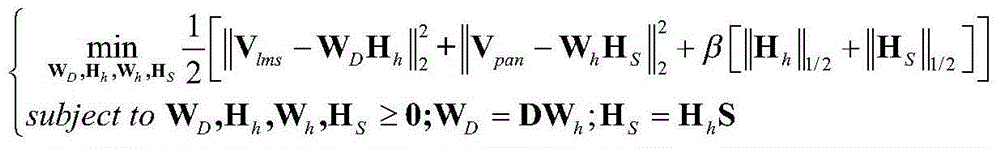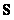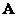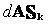Patents
Literature
303 results about "Non-negative matrix factorization" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
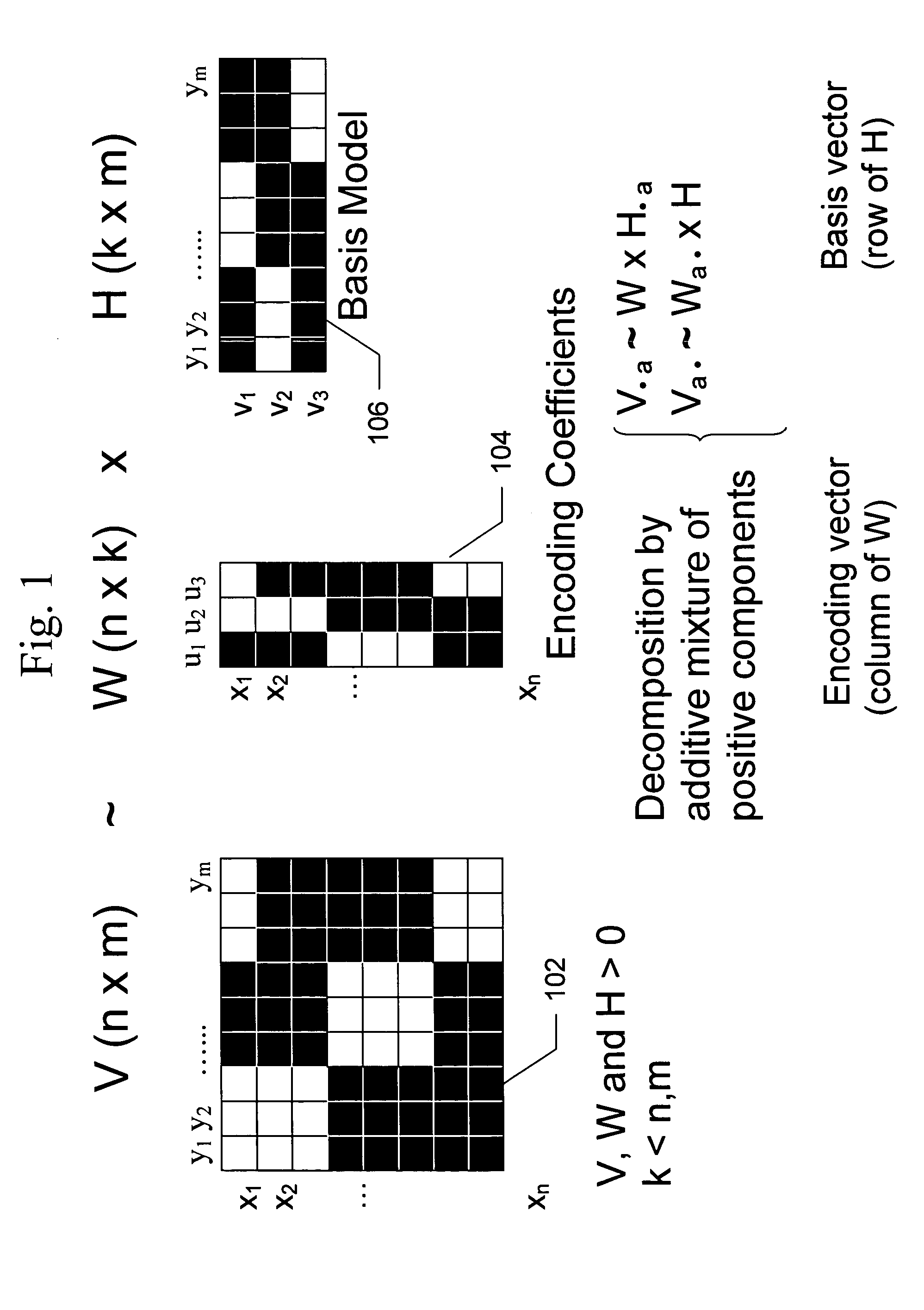
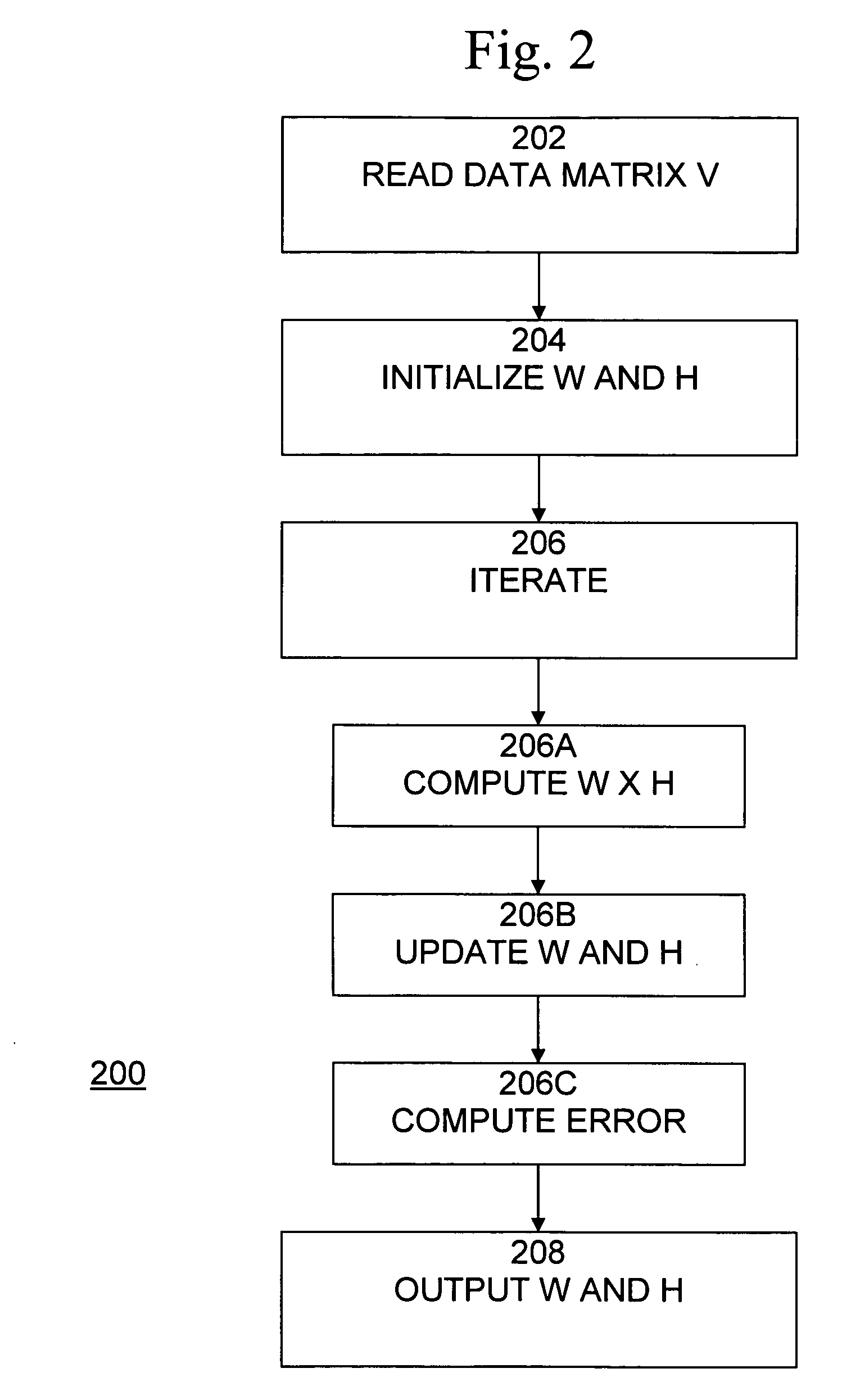
Non-negative matrix factorization (NMF or NNMF), also non-negative matrix approximation is a group of algorithms in multivariate analysis and linear algebra where a matrix V is factorized into (usually) two matrices W and H, with the property that all three matrices have no negative elements. This non-negativity makes the resulting matrices easier to inspect. Also, in applications such as processing of audio spectrograms or muscular activity, non-negativity is inherent to the data being considered. Since the problem is not exactly solvable in general, it is commonly approximated numerically.
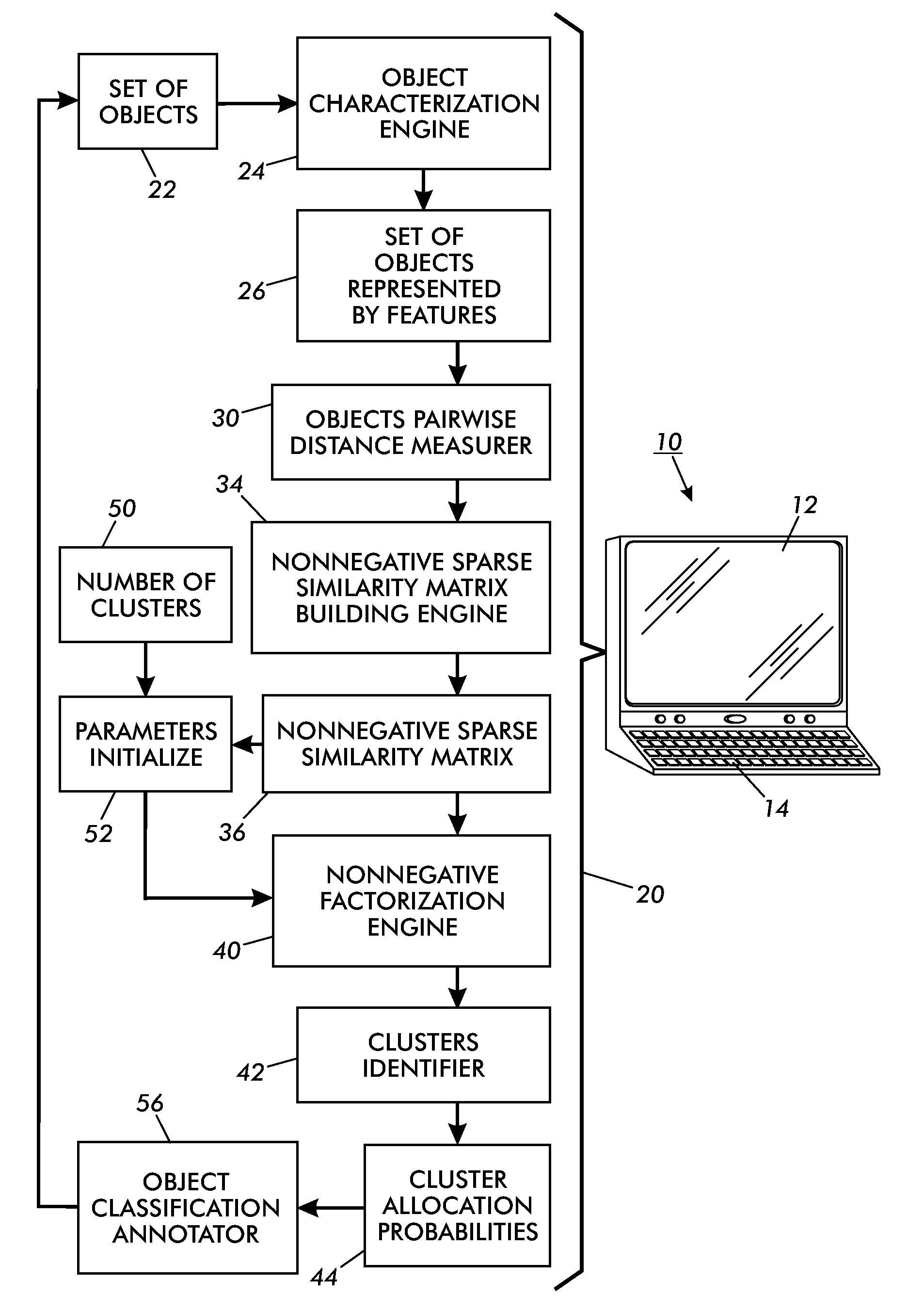
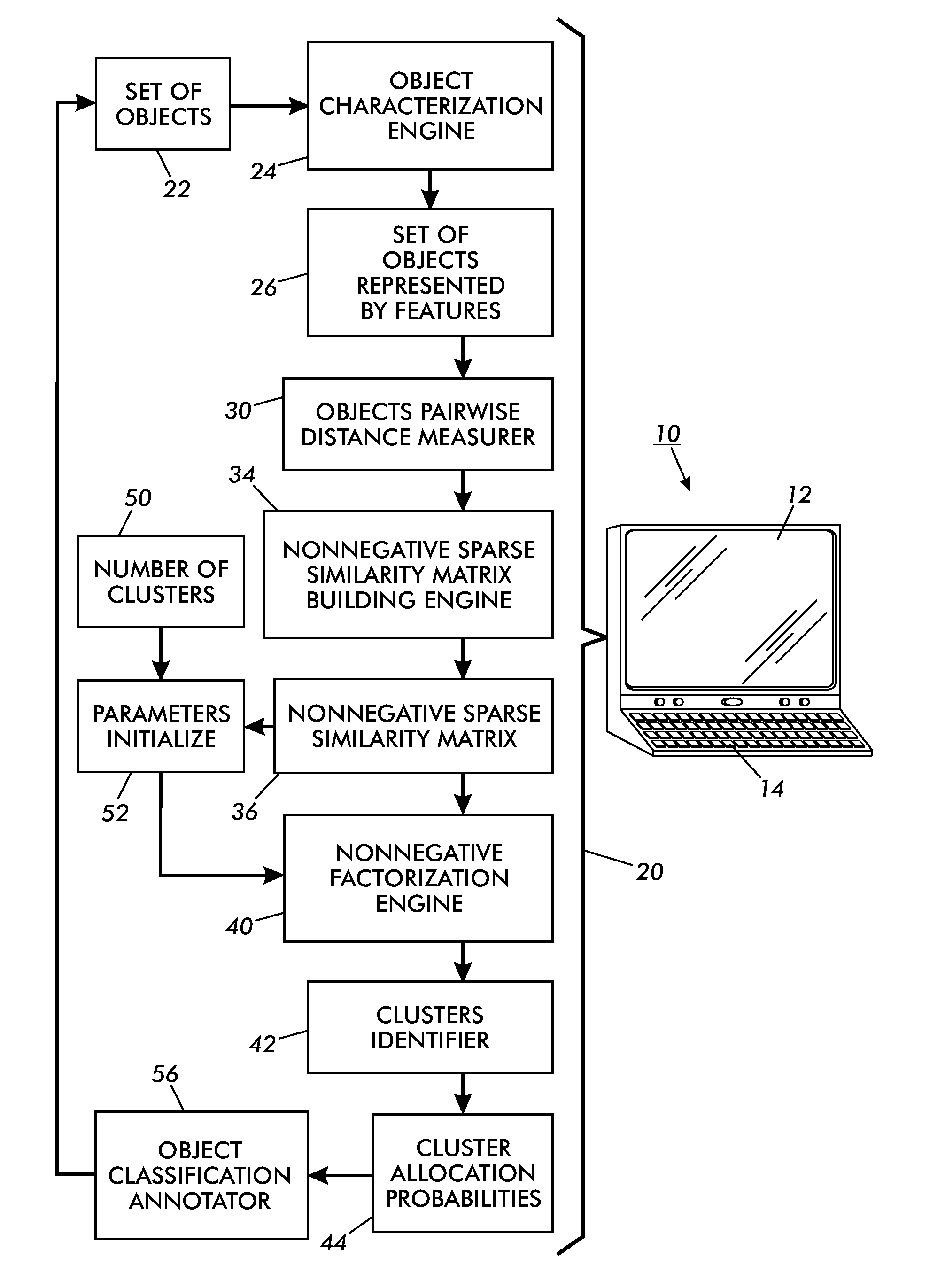
Clustering using non-negative matrix factorization on sparse graphs
InactiveUS20090271433A1Character and pattern recognitionComplex mathematical operationsPattern recognitionNonnegative matrix
Object clustering techniques are disclosed. A nonnegative sparse similarity matrix is constructed for a set of objects. Nonnegative factorization of the nonnegative sparse similarity matrix is performed. Objects of the set of objects are allocated to clusters based on factor matrices generated by the nonnegative factorization of the nonnegative sparse similarity matrix.
Owner:XEROX CORP
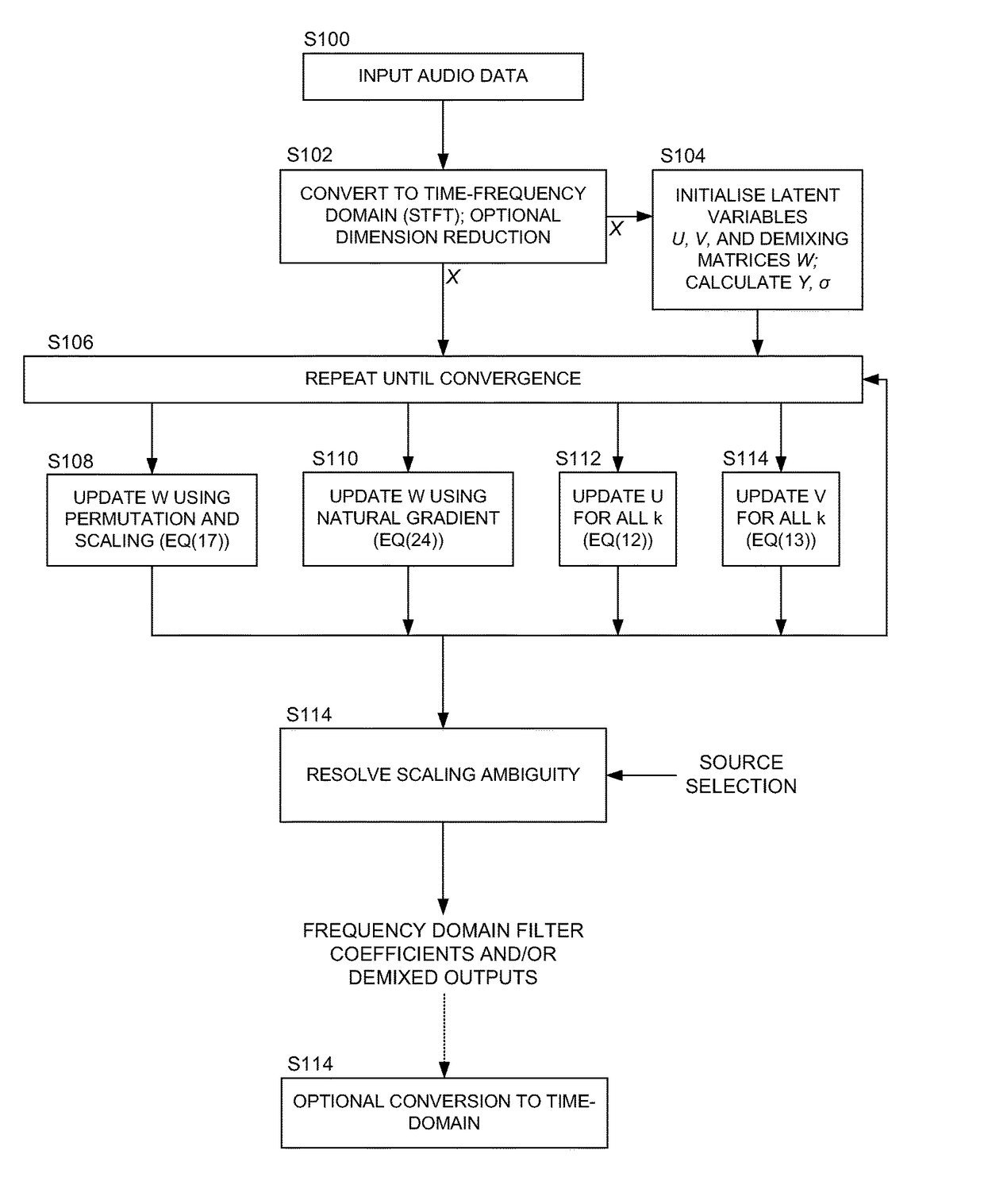
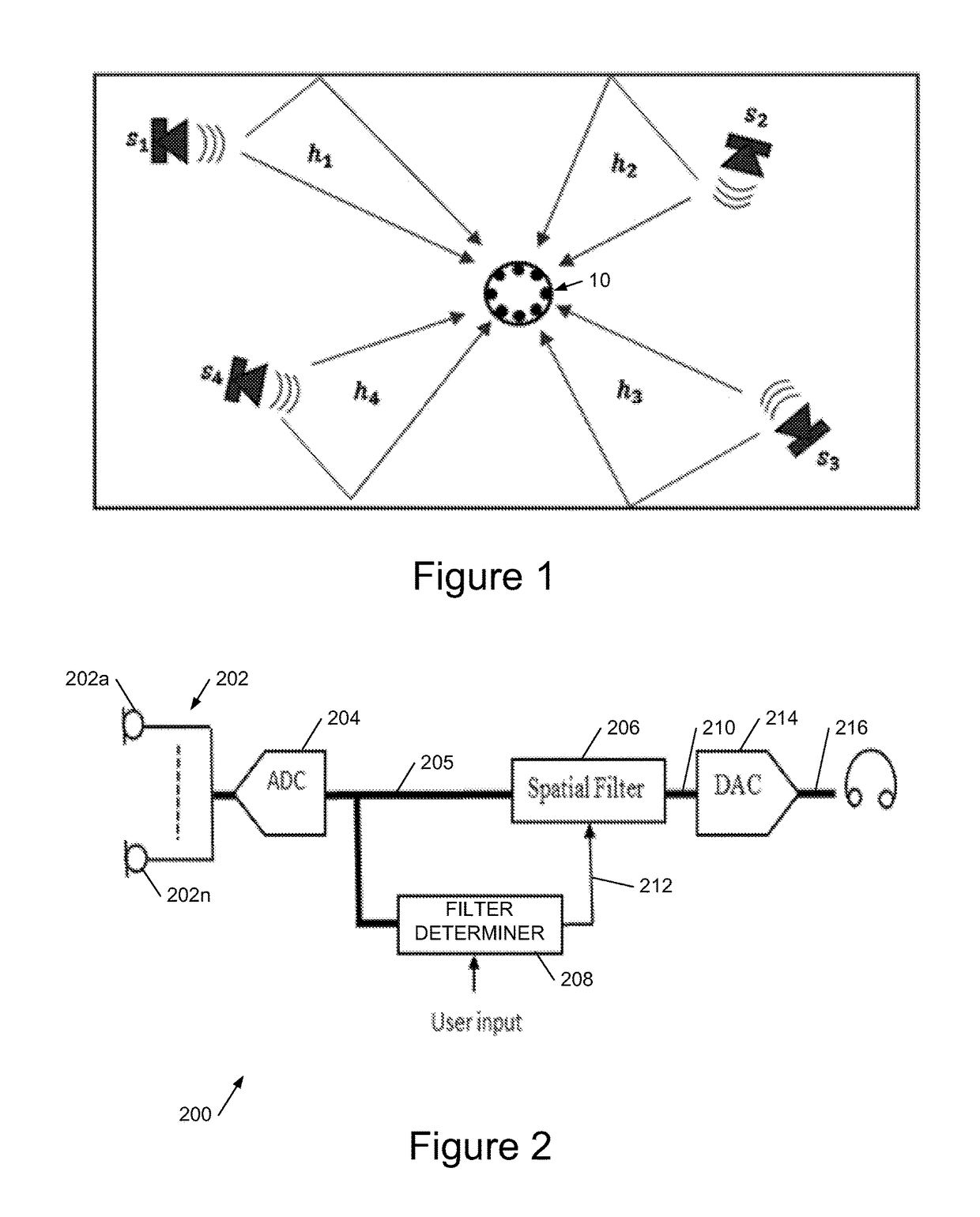
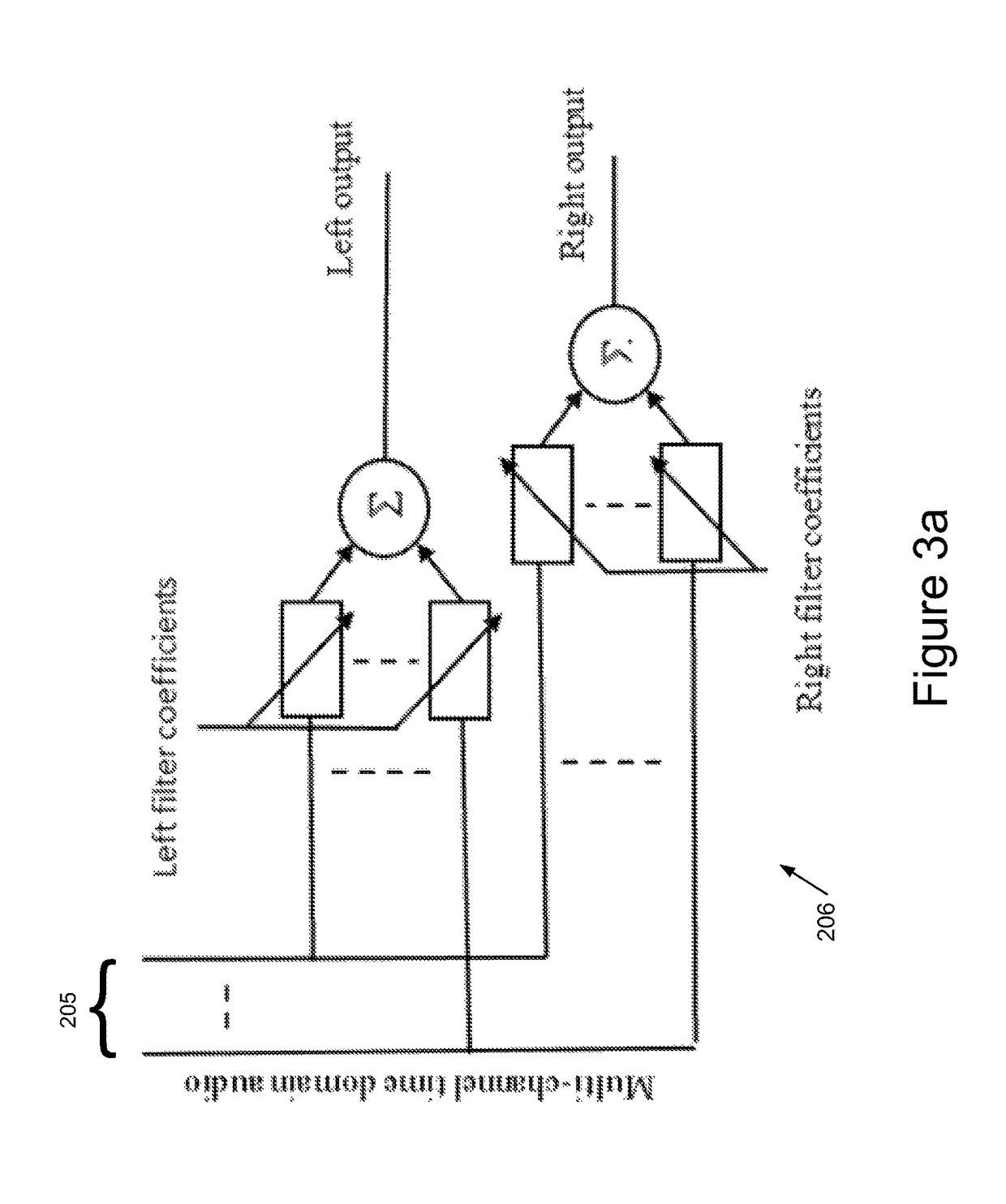
Blind source separation systems
ActiveUS9668066B1Cost for rotationSave spaceSignal processingSets with desired directivityFrequency spectrumHearing aid
We describe a method of blind source separation for use, for example, in a listening or hearing aid. The method processes input data from multiple microphones each receiving a mixed signal from multiple audio sources, performing independent component analysis (ICA) on the data in the time-frequency domain based on an estimation of a spectrogram of each acoustic source. The spectrograms of the sources are determined from non-negative matrix factorization (NMF) models of each source, the NMF model representing time-frequency variations in the output of an acoustic source in the time-frequency domain. The NMF and ICA models are jointly optimized, thus automatically resolving an inter-frequency permutation ambiguity.
Owner:AUDIOTELLIGENCE LTD
Query construction for semantic topic indexes derived by non-negative matrix factorization
InactiveUS20070050356A1Digital data information retrievalSpecial data processing applicationsSubject matterPaper document
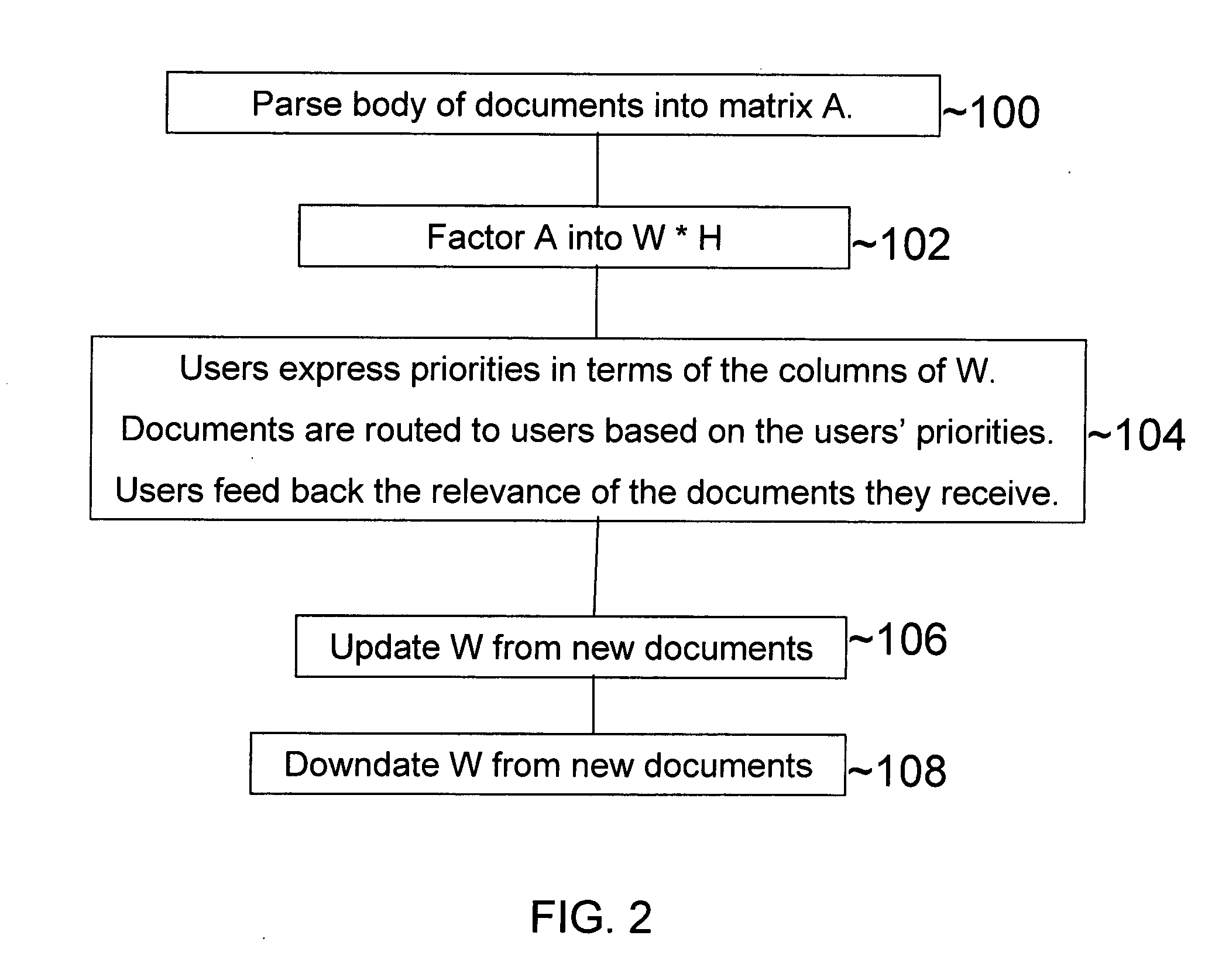
A method, apparatus and machine-readable medium analyze documents processed by non-negative matrix factorization in accordance with semantic topics. Users construct queries by assigning weights to semantic topics to order documents within a set. The query may be refined in accordance with the user's evaluation of the efficacy of the query. Any document that does not result in data indicative of significant correlation with at least one semantic topic is flagged so that a user may make a manual review. The collection of semantic topics may be continually or periodically updated in response to new documents. Additionally, the collection may also be “downdated” to drop semantic factors no longer appearing in new documents received after an initial set has been analyzed. Different sets of semantic topics may be generated and each document evaluated using each set. Reports may be prepared showing results for a body of documents for each of a plurality of sets of semantic topics.
Owner:AMADIO WILLIAM J
Systems and methods for media summarization
InactiveUS20050123053A1Maximizing similarityImage analysisPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesDecompositionAlgorithm
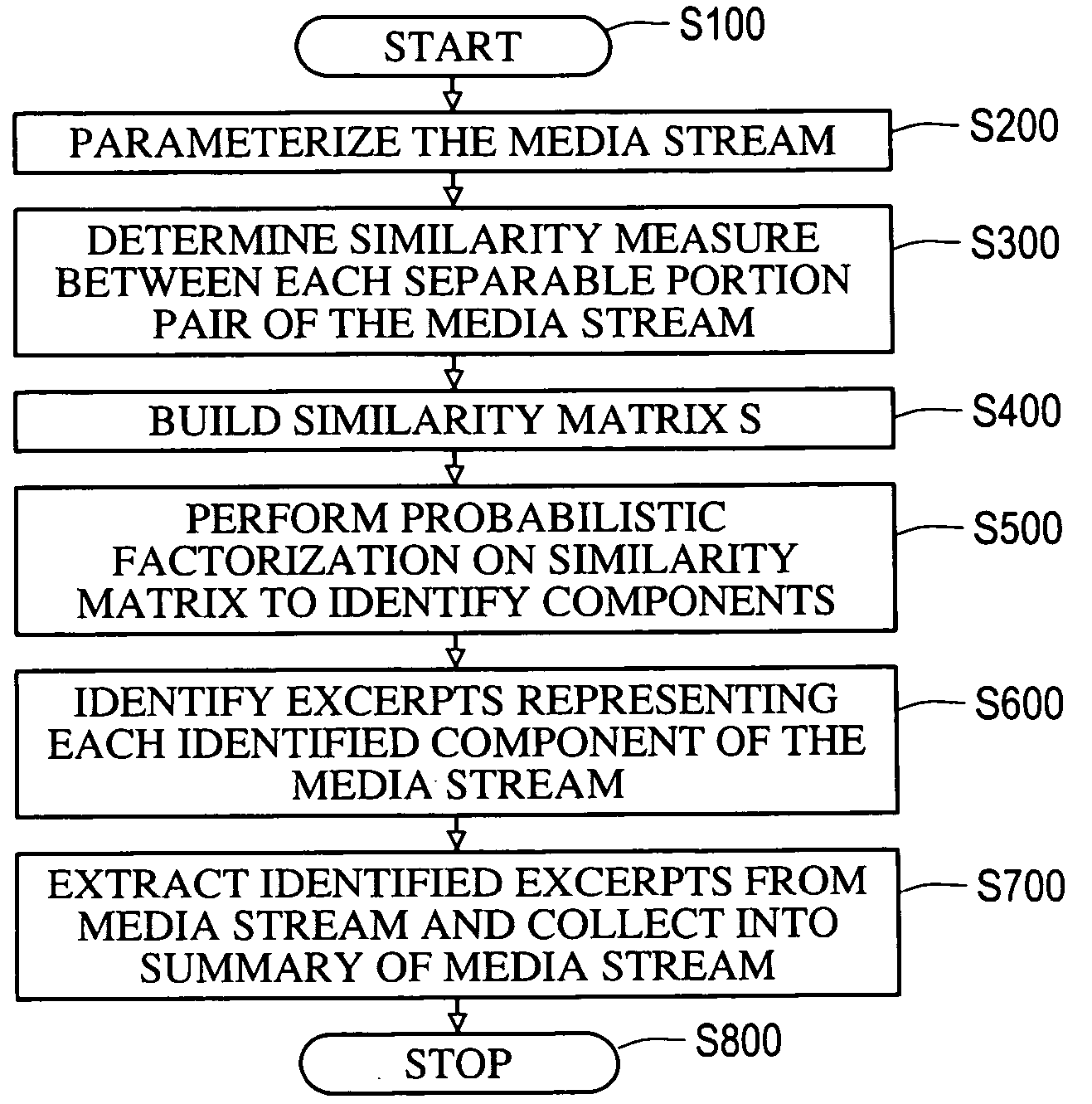
A stream of ordered information, such as, for example, audio, video and / or text data, can be windowed and parameterized. A similarity between the parameterized and windowed stream of ordered information can be determined, and a probabilistic decomposition or probabilistic matrix factorization, such as non-negative matrix factorization, can be applied to the similarity matrix. The component matrices resulting from the decomposition indicate major components or segments of the ordered information. Excerpts can then be extracted from the stream of ordered information based on the component matrices to generate a summary of the stream of ordered information.
Owner:FUJIFILM BUSINESS INNOVATION CORP
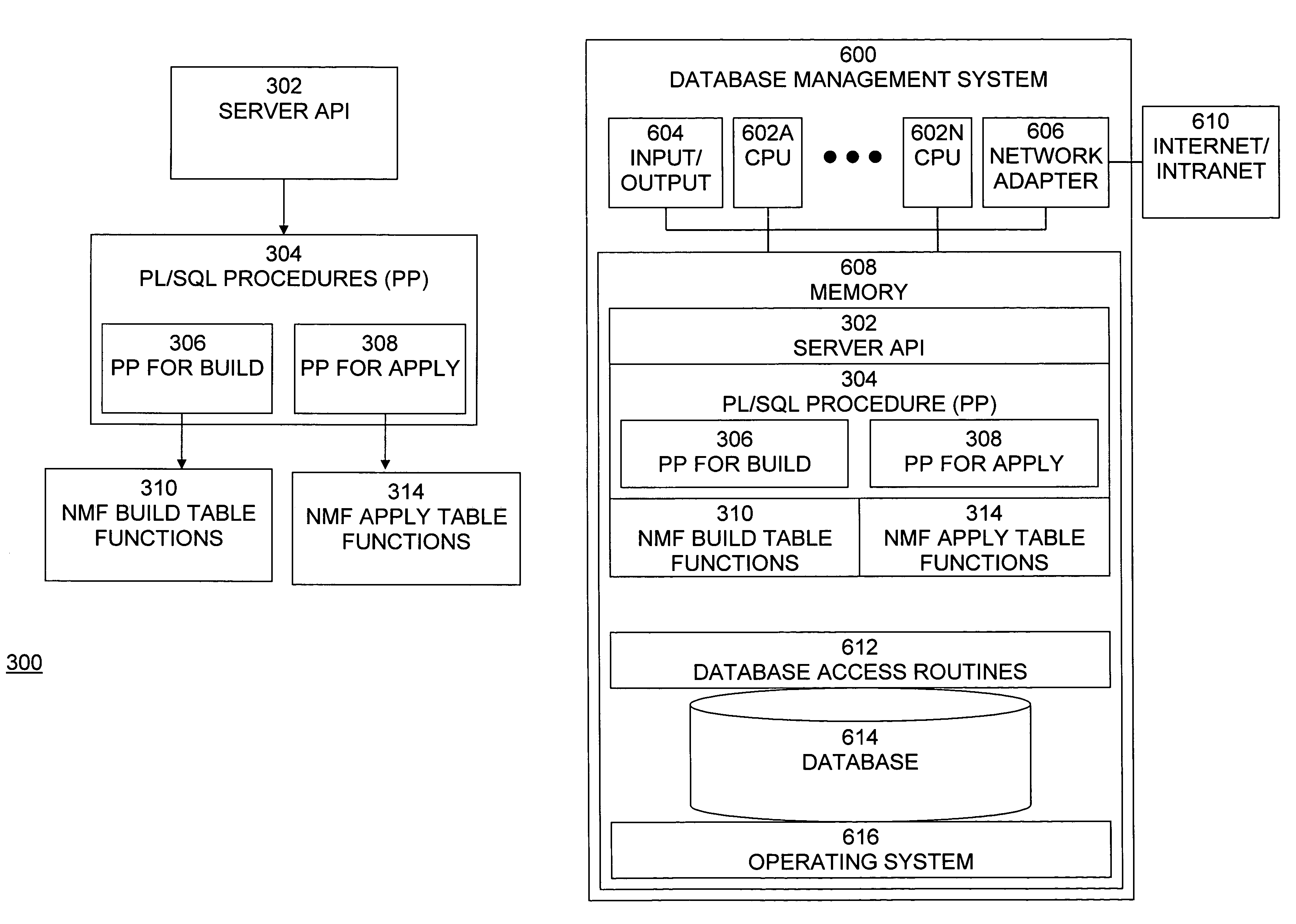
Non-negative matrix factorization from the data in the multi-dimensional data table using the specification and to store metadata representing the built relational database management system
ActiveUS7734652B2High indexDigital data processing detailsMulti-dimensional databasesRelational database management systemMultidimensional data
An implementation of NMF functionality integrated into a relational database management system provides the capability to apply NMF to relational datasets and to sparse datasets. A database management system comprises a multi-dimensional data table operable to store data and a processing unit operable to perform non-negative matrix factorization on data stored in the multi-dimensional data table and to generate a plurality of data tables, each data table being smaller than the multi-dimensional data table and having reduced dimensionality relative to the multi-dimensional data table. The multi-dimensional data table may be a relational data table.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
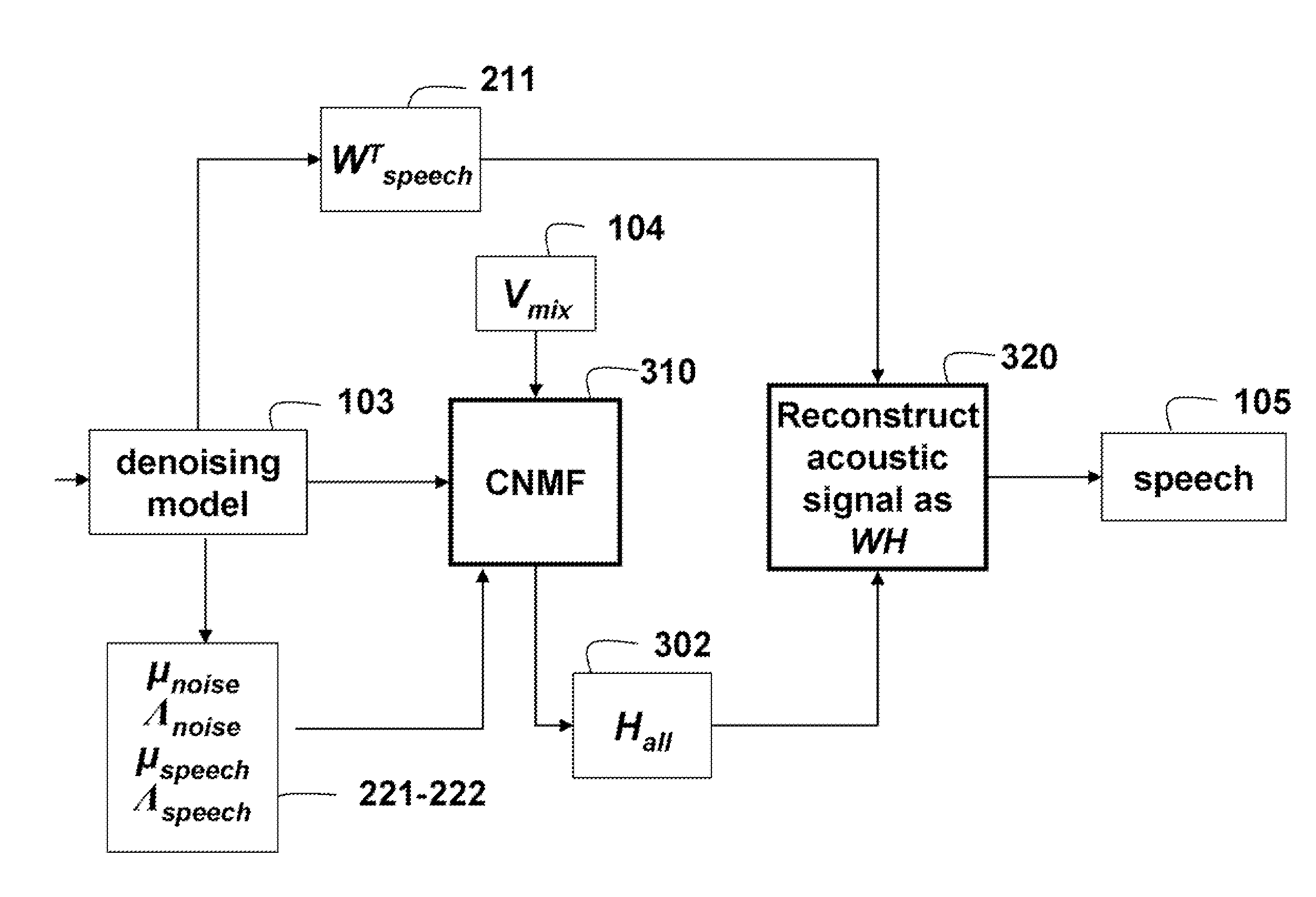
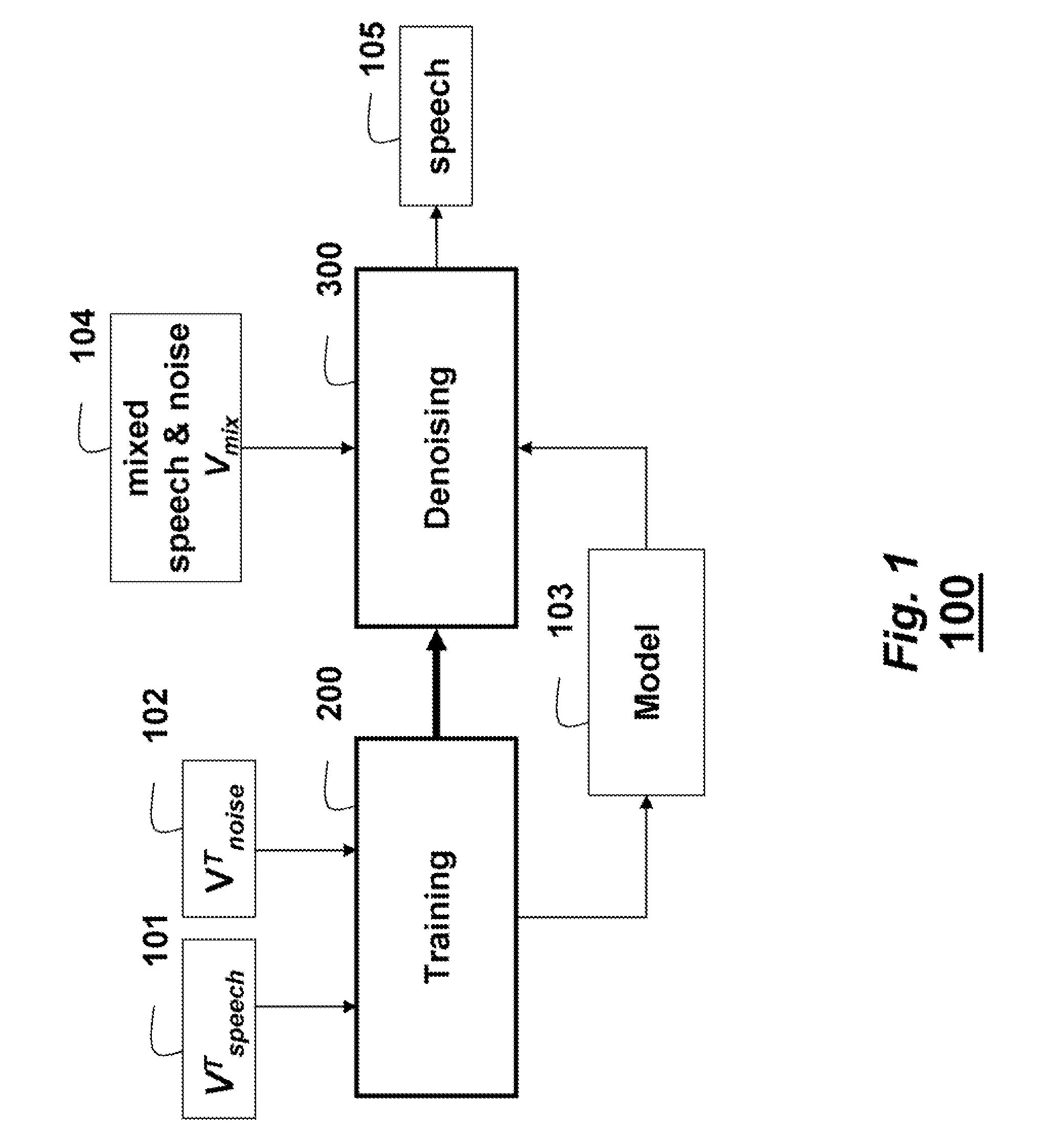
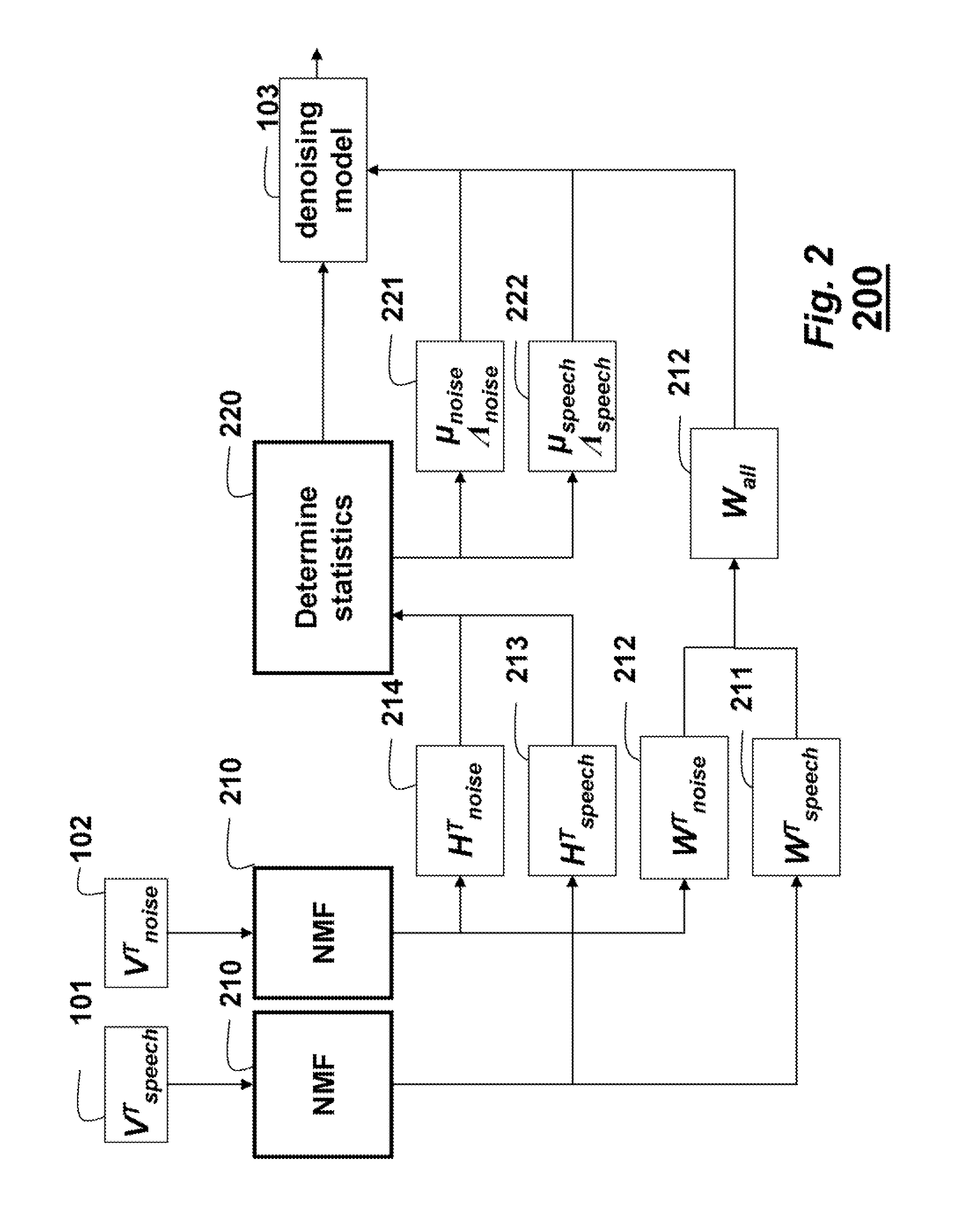
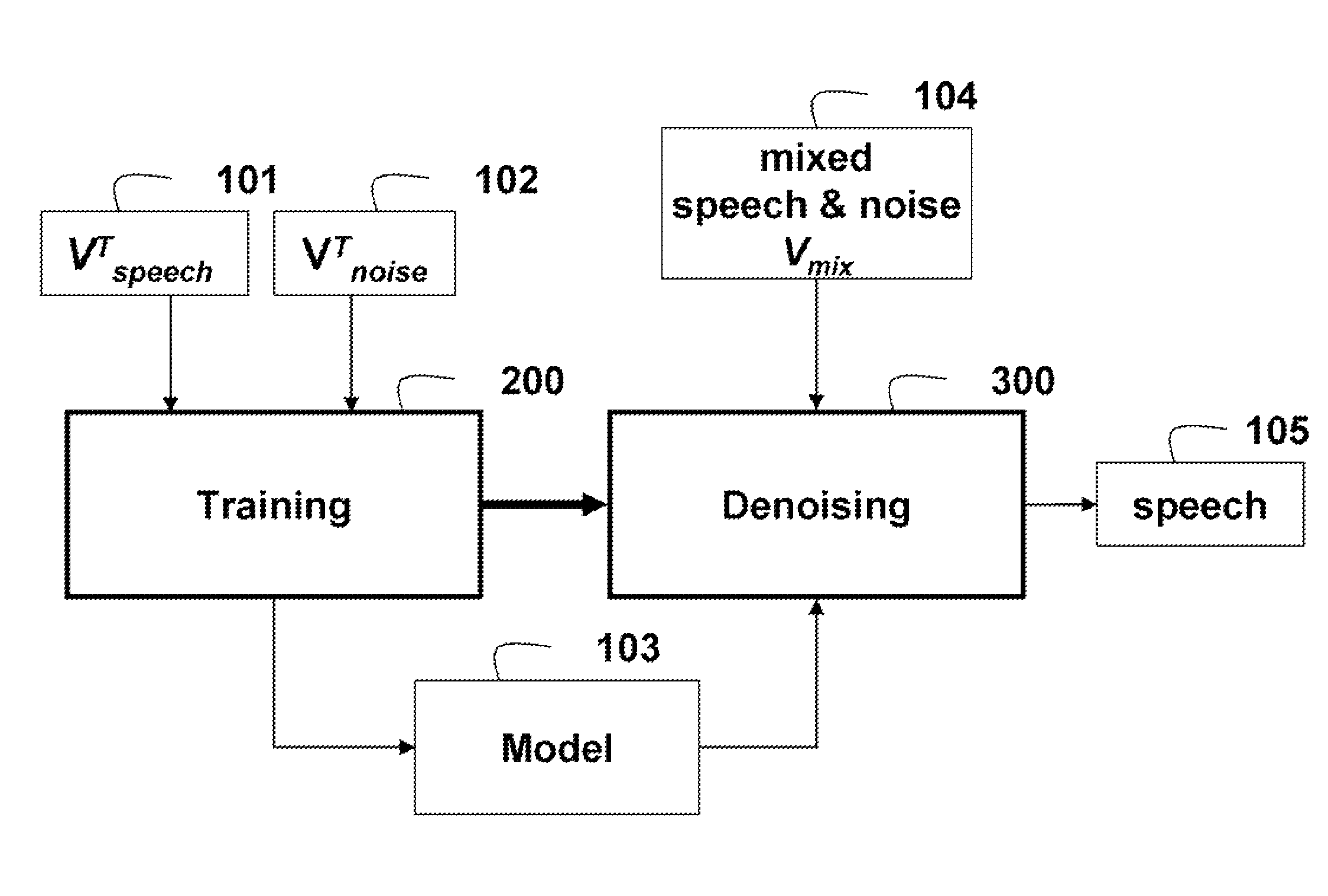
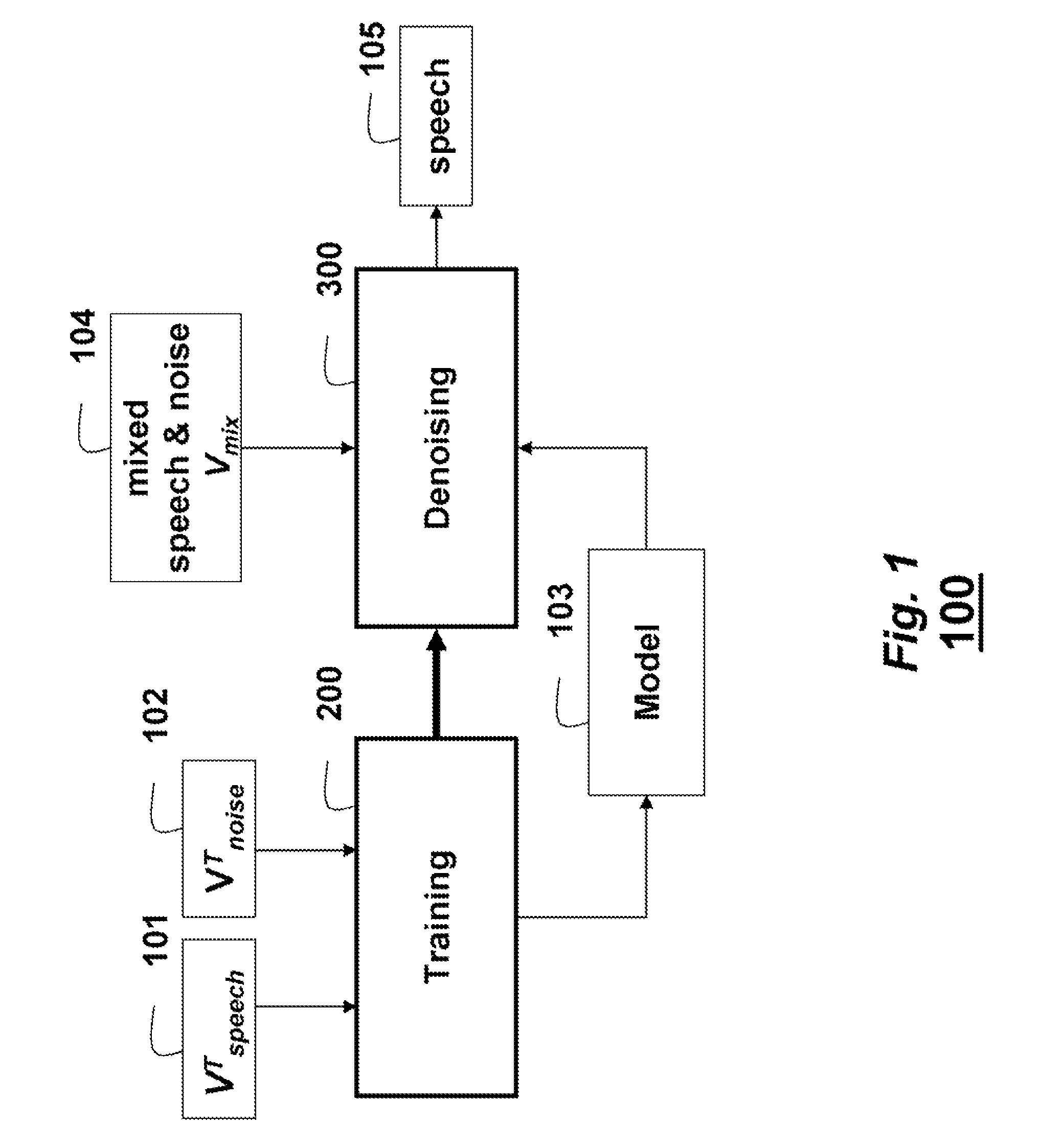
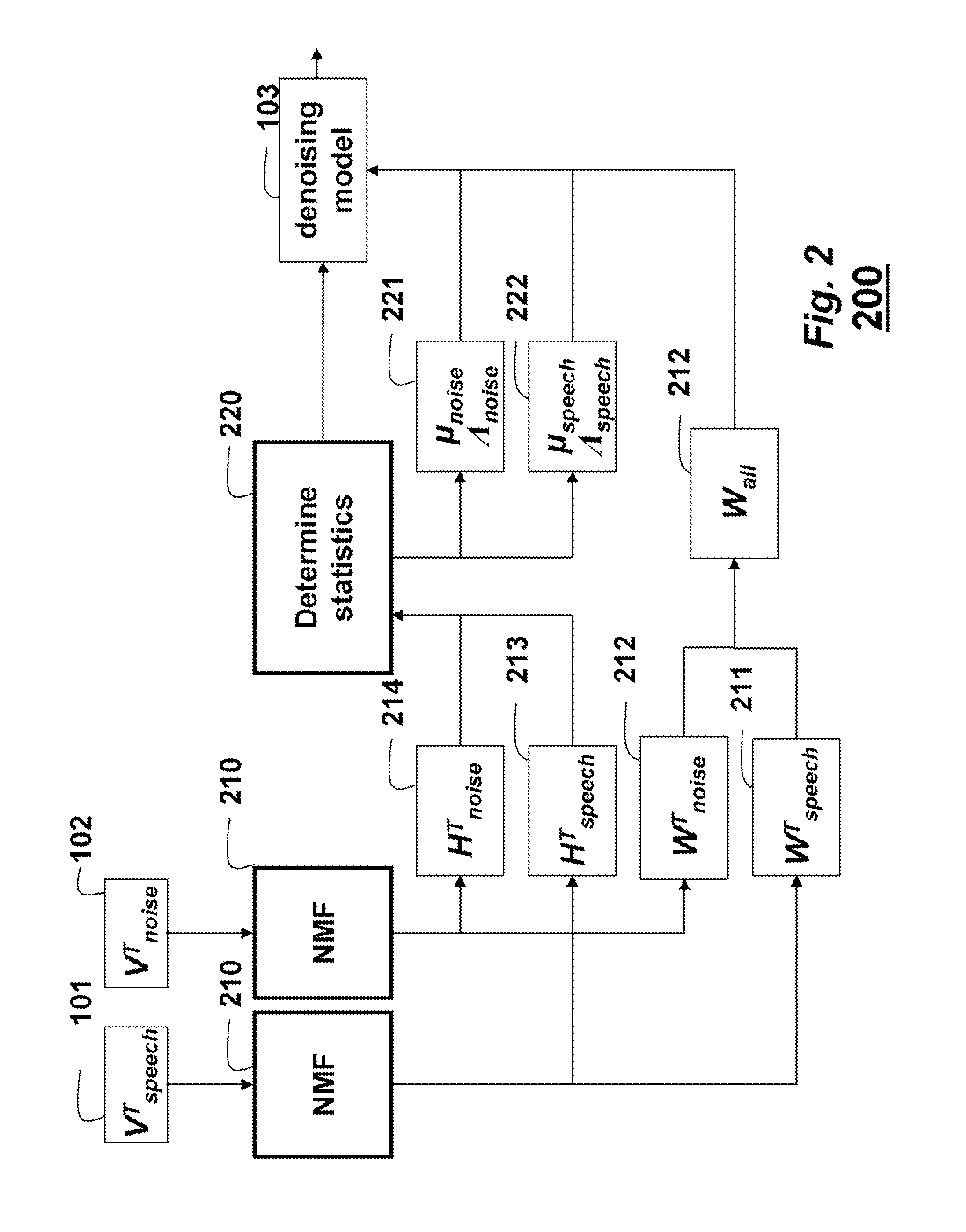
Denoising Acoustic Signals using Constrained Non-Negative Matrix Factorization
A method and system denoises a mixed signal. A constrained non-negative matrix factorization (NMF) is applied to the mixed signal. The NMF is constrained by a denoising model, in which the denoising model includes training basis matrices of a training acoustic signal and a training noise signal and statistics of weights of the training basis matrices. The applying produces weight of a basis matrix of the acoustic signal, of the mixed signal. A product of the weights of the basis matrix of the acoustic signal and the training basis matrices of the training acoustic signal and the training noise signal is taken to reconstruct the acoustic signal. The mixed signal can be speech and noise.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC RES LAB INC
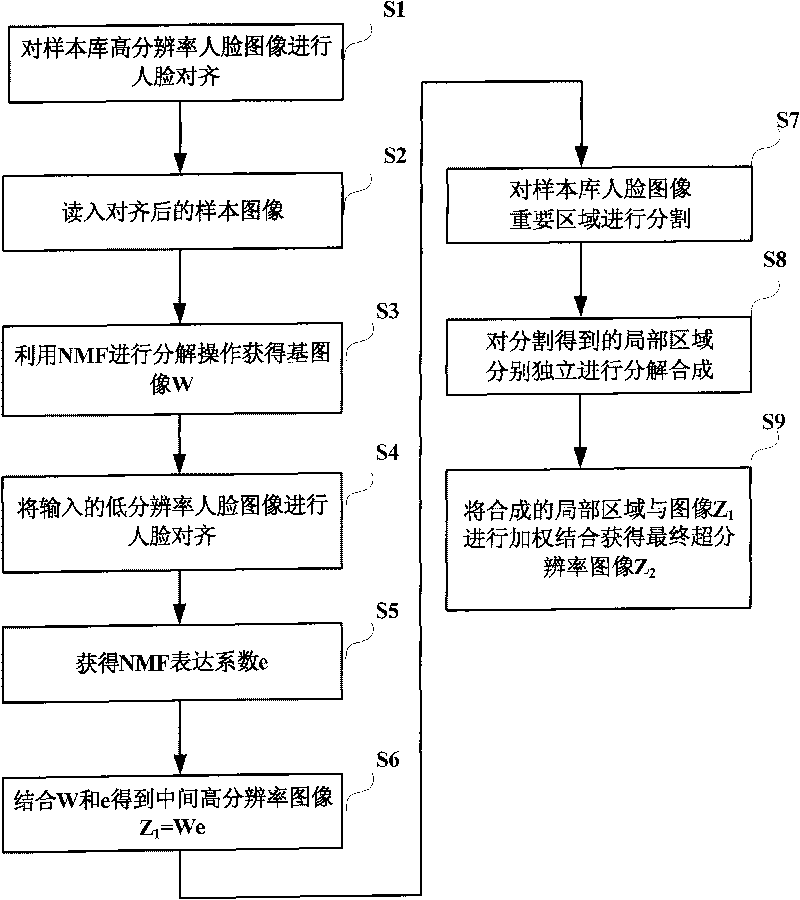
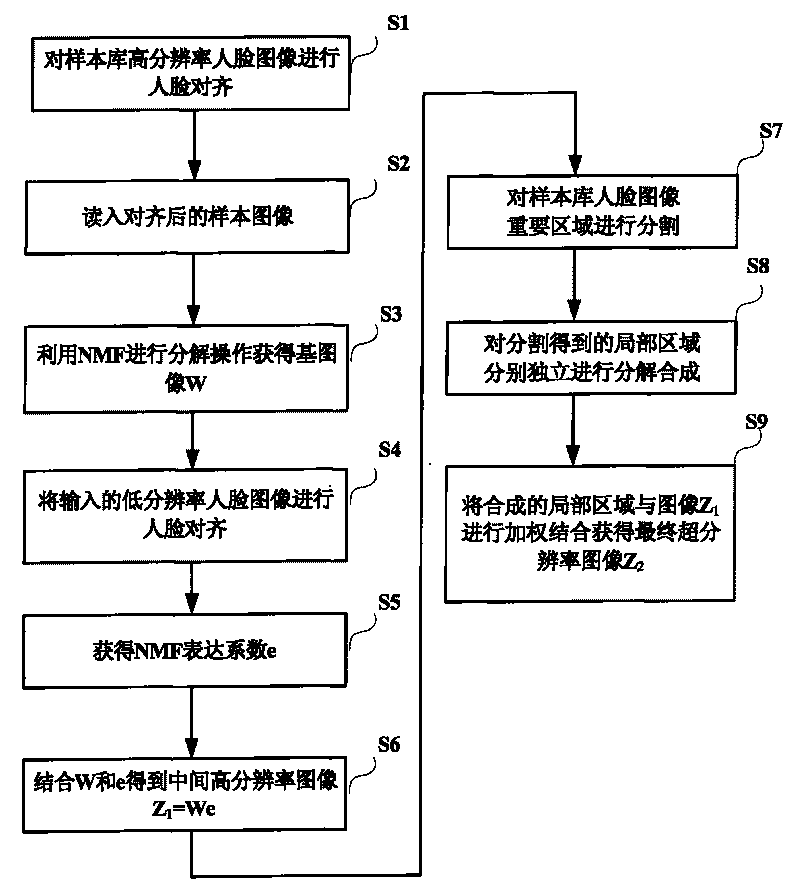
Non-negative matrix factorization-based face super-resolution processing method
InactiveCN101719270AIncreasing grayscale is non-negativeEnhance expressive abilityImage enhancementGeometric image transformationImage resolutionSample image
The invention relates to the technical field of image super-resolution processing, in particular to a non-negative matrix factorization-based face super-resolution processing method. The method comprises the following steps: performing face alignment on high-resolution face images in a sample library, reading the aligned sample image library, utilizing a non-negative matrix factorization algorithm to perform a factorization operation to obtain a basic image W, performing alignment on input low-resolution face images to obtain the non-negative matrix factorization expression coefficient e of a target high-resolution face image, obtaining the target high-resolution image Z1=We in combination with the basic image W and the expression coefficient e and dividing the important areas of the face images in the sample library; performing factorization synthesis on the divided local areas; and weighting and combining the synthesized local area and the image Z1 to obtain a super-resolution image Z2. The method has the advantages of increasing semantic constraint like that the grayscale of the image is non-negative, improving the expression capacity of the characteristic basic image and finally improving the quality of the super-resolution image.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Sound Detection Method for Recognizing Hazard Situation
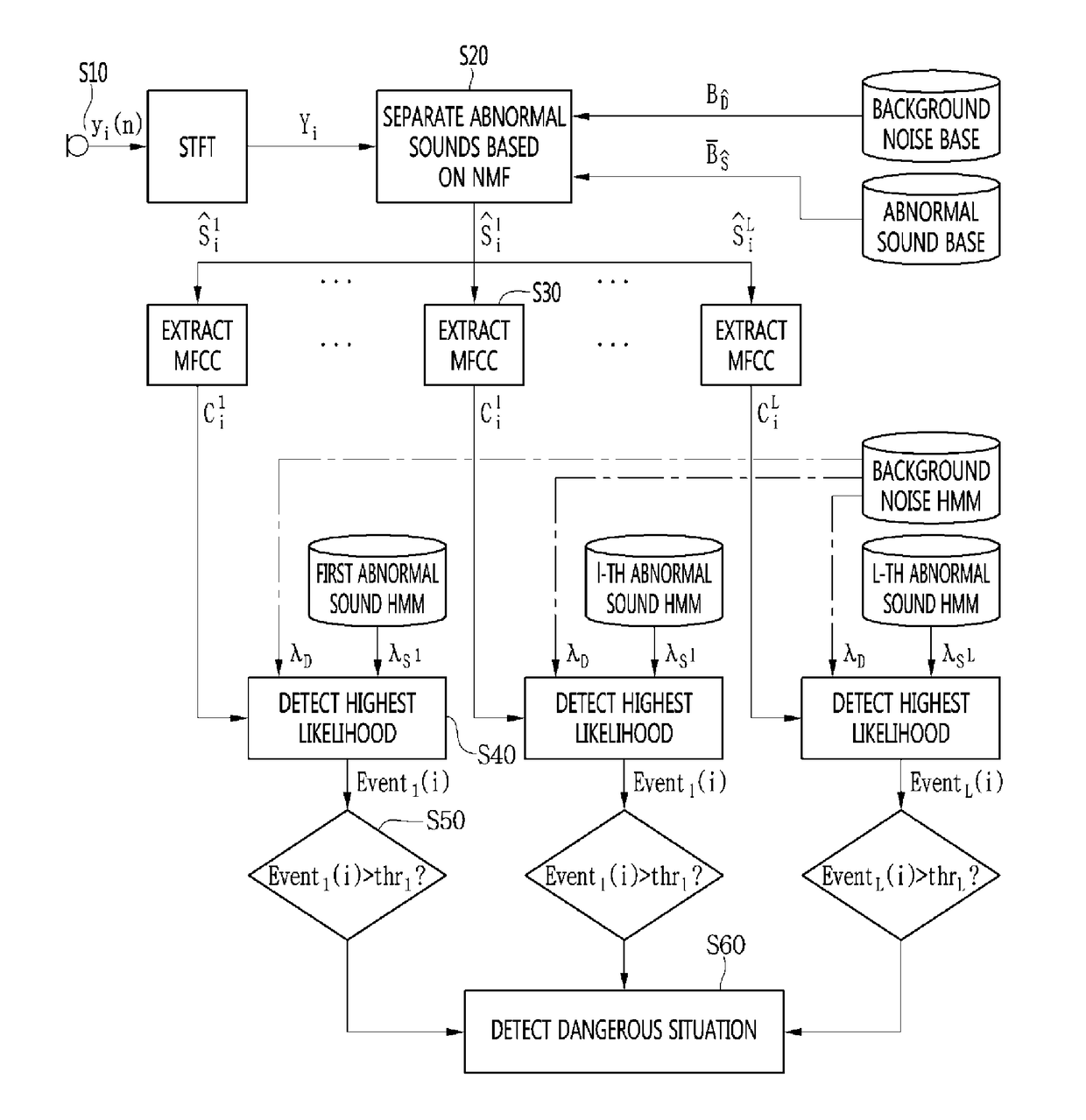
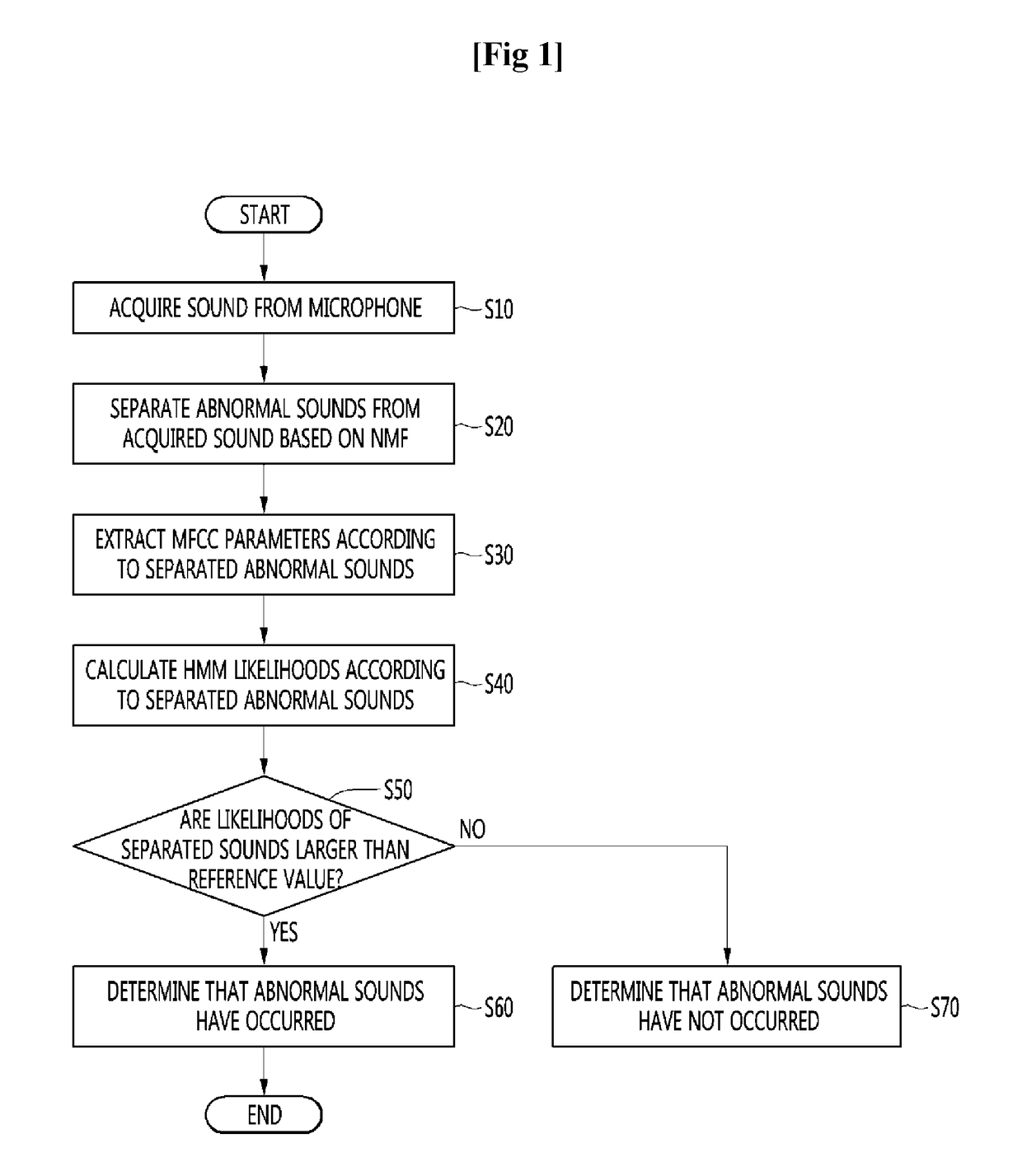
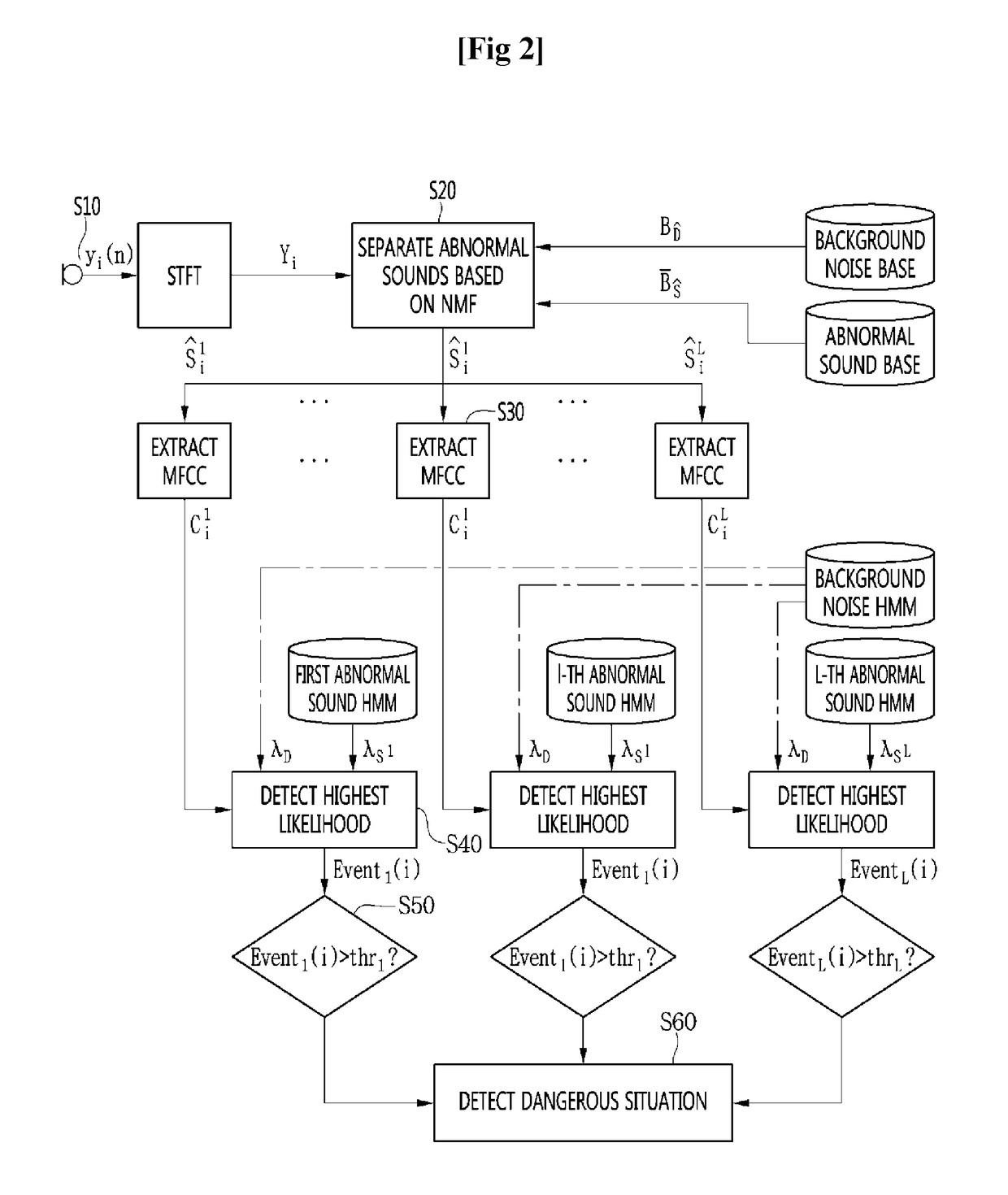
InactiveUS20170103776A1Quick identificationEasy to handleSpeech recognitionBurglar alarm mechanical vibrations actuationSound detectionEnvironmental noise
A method of detecting a particular abnormal sound in an environment with background noise is provided. The method includes acquiring a sound from a microphone, separating abnormal sounds from the input sound based on non-negative matrix factorization (NMF), extracting Mel-frequency cepstral coefficient (MFCC) parameters according to the separated abnormal sounds, calculating hidden Markov model (HMM) likelihoods according to the separated abnormal sounds, and comparing the likelihoods of the separated abnormal sounds with a reference value to determine whether or not an abnormal sound has occurred. According to the method, based on NMF, a sound to be detected is compared with ambient noise in a one-to-one basis and classified so that the sound may be stably detected even in an actual environment with multiple noises.
Owner:GWANGJU INST OF SCI & TECH
Denoising acoustic signals using constrained non-negative matrix factorization
A method and system denoises a mixed signal. A constrained non-negative matrix factorization (NMF) is applied to the mixed signal. The NMF is constrained by a denoising model, in which the denoising model includes training basis matrices of a training acoustic signal and a training noise signal, and statistics of weights of the training basis matrices. The applying produces weight of a basis matrix of the acoustic signal of the mixed signal. A product of the weights of the basis matrix of the acoustic signal and the training basis matrices of the training acoustic signal and the training noise signal is taken to reconstruct the acoustic signal. The mixed signal can be speech and noise.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC RES LAB INC
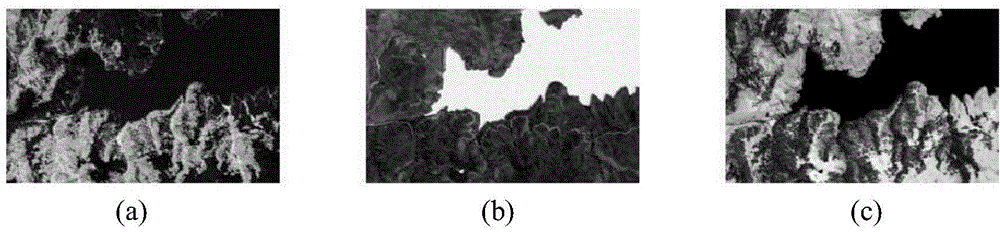
Mixed pixel decomposition method for remote sensing images
InactiveCN102193090AEnsure stabilityOvercome the shortcoming of easy to fall into local minimumImage analysisWave based measurement systemsSensing dataObject based
The invention belongs to the technical field of remote sensing image processing, and particularly relates to a new mixed pixel decomposition method based on an NMF (non-negative matrix factorization) algorithm. The method comprises the following steps: introducing constraint conditions for abundance separability and smoothness into the target functions of the NMF algorithm according to the spectrum and abundance characteristics of hyperspectral images; and removing the constraint conditions at the right time, and continuing to carry out iteration, thereby overcoming the defects that the NMF algorithm is easily sunk into local minimum, so that the mixed pixel decomposition method for high mixed remote sensing data can be implemented effectively. The method disclosed by the invention has especially important application value in the aspects of detecting and identifying ground targets and classifying topographical objects based on the high accuracies of multispectral and hyperspectral remote sensing images.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
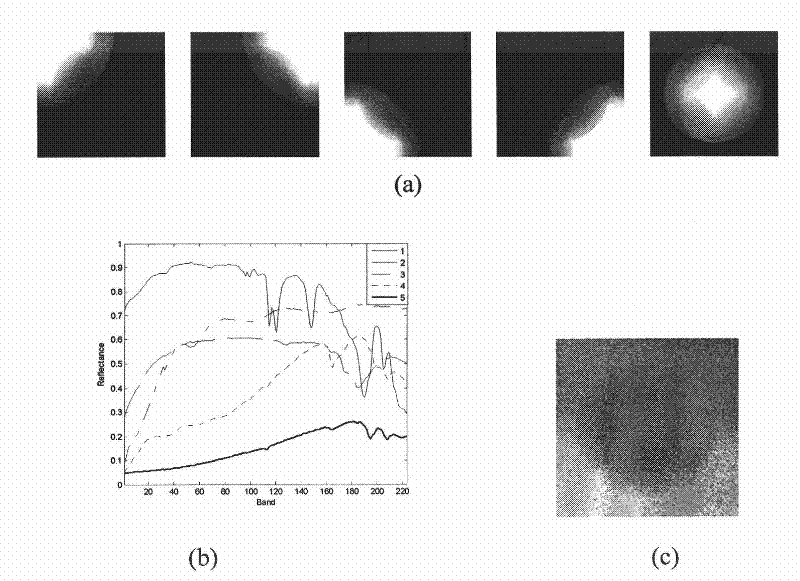
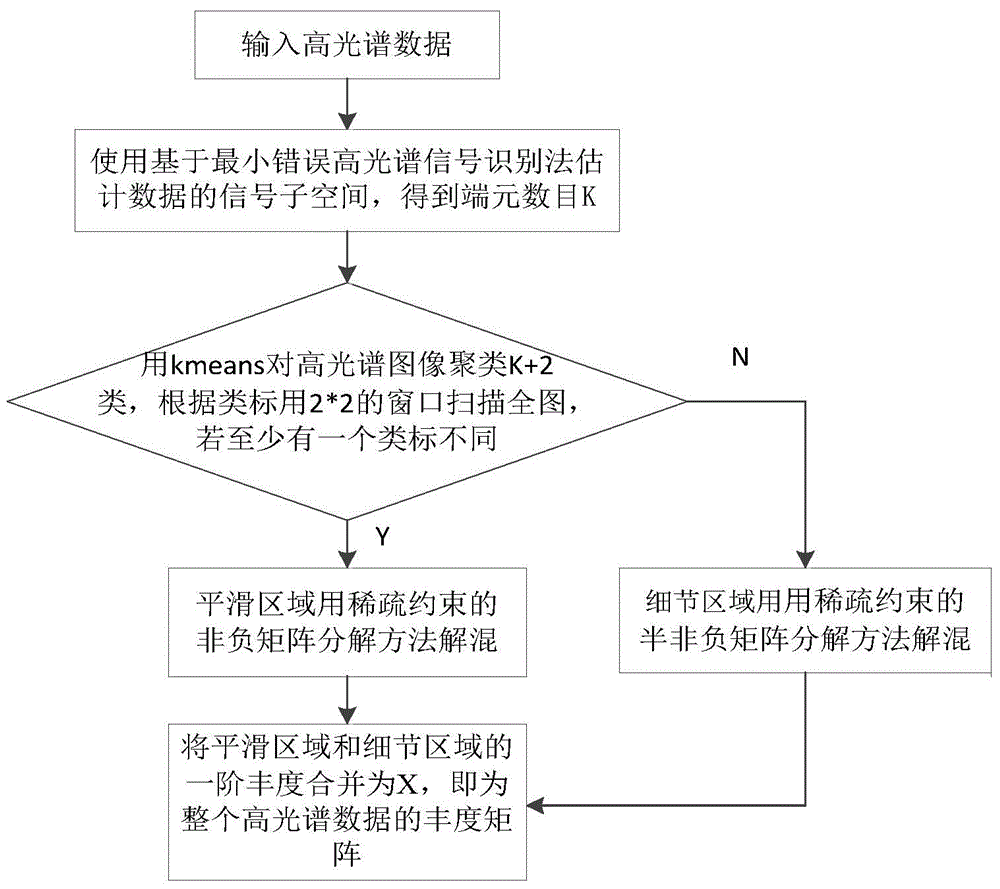
Self-adaptive hyperspectral image unmixing method based on region segmentation
ActiveCN104952050AUnmixing AccurateAccurate representationImage enhancementImage analysisImage segmentationNonnegative matrix
The invention discloses a self-adaptive hyperspectral image unmixing method based on region segmentation. In consideration of coexistence of linear mixing and bilinear mixing, the method is implemented by adopting the following steps: inputting a hyperspectral image; estimating the number of end elements with a minimum error based hyperspectral signal recognition method; extracting end element matrixes with a vertex component analysis algorithm; clustering hyperspectral data with a K-means clustering method, and segmenting the image into a homogeneous region and a detail region; adopting a linear model for the homogeneous region and performing unmixing with a sparse-constrained non-negative matrix factorization method, and adopting a generalized bilinear model for the detail region and performing unmixing with a sparse-constrained semi-non-negative matrix factorization method. According to the method, characteristics of the hyperspectral data and abundance are combined, the hyperspectral image is represented more accurately, and the unmixing accuracy rate is increased. The sparse constraint condition is added to the abundance, the defect of high probability of local minimum limitation of the semi-non-negative matrix factorization method is overcome, more accurate abundance is obtained, and the method is applied to ground-object recognition for the hyperspectral image.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
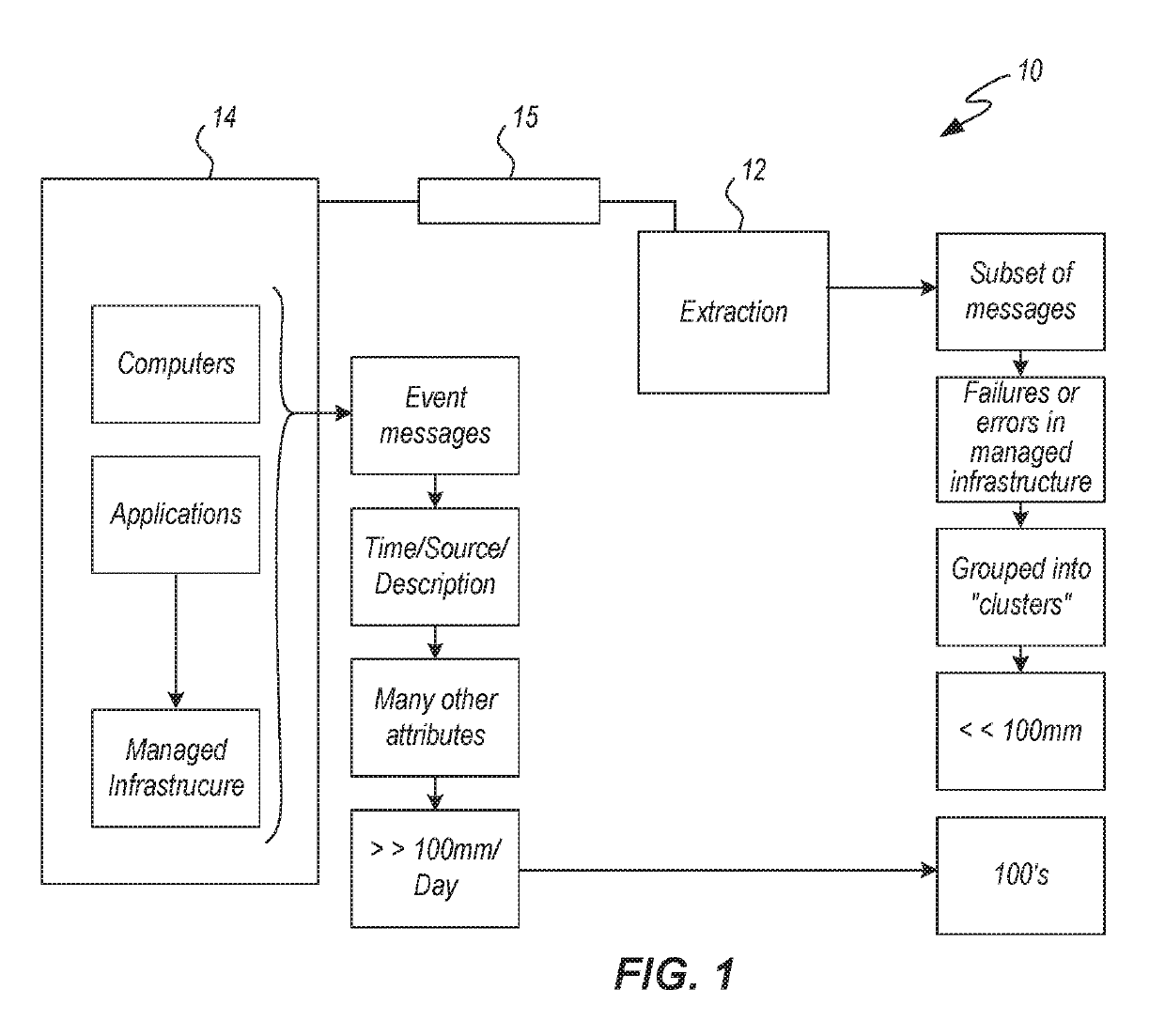
System for managing an instructure with security
PendingUS20190138372A1Maintain securityInterprogram communicationCharacter and pattern recognitionGraphicsDisplay device
A system is provided for managing an infrastructure. An extraction engine is in communication with a managed infrastructure that includes physical hardware. A signalizer engine includes one or more of an NMF engine (Non-negative matrix factorization), a k-means clustering engine (a method of vector quantization), and a topology proximity engine. The signalizer engine determines one or more common characteristics of events and produces clusters of events relating to the failure or errors in the infrastructure. The signalizer engine uses graph coordinates and optionally a subset of attributes assigned to each event to generate one or more clusters to bring together events whose characteristics are similar. One or more interactive displays provide a collaborative interface coupled to the extraction and the signalizer engine with a collaborative interface (UI) for decomposing events from the infrastructure. The events are converted into words and subsets to group the events into clusters that relate to security of the managed infrastructure. In response to grouping the events physical changes are made to at least a portion of the physical hardware. In response to production of the clusters security of the managed infrastructure is maintained.
Owner:MOOGSOFT
Image Retrieval Method Based on Sparse Nonnegative Matrix Factorization
InactiveCN102270241AImproving Image Retrieval PerformanceImplement transfer learningSpecial data processing applicationsImage retrievalSource image
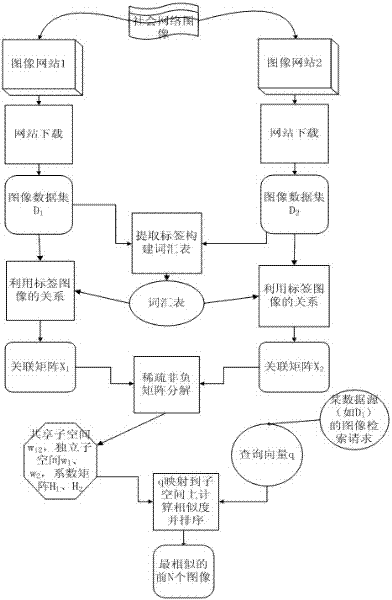
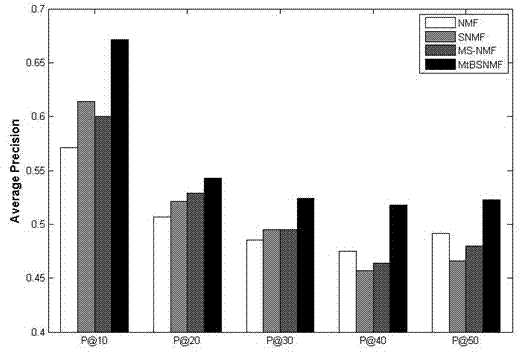
The invention discloses an image retrieval method based on sparse non-negative matrix decomposition. It includes the following steps: 1) Query and extract the image and accompanying text of the retrieval results under two different image data sources; 2) Extract the tags in the accompanying text, and filter the results according to word frequency to form a vocabulary; 3) For each Image set, using the association relationship between labels and images to form an association matrix between labels and images; 4) Using sparse non-negative matrix decomposition to analyze the association matrix obtained in step 3), to obtain the shared subspaces of different sources of data and their corresponding independent subspaces Subspace; 5) The user sends a retrieval request for images on a data source, forms a query vector and maps it to the corresponding subspace of the data source, calculates the similarity with all images and sorts them, and returns the top N most similar images. The present invention makes full use of the associated knowledge of tags and images under multiple data sources, performs migration learning through sparse non-negative matrix decomposition, and improves the accuracy of image retrieval on target data sources.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Method for extracting time-frequency domain spectrum of mixed signals of rotating machinery
InactiveCN102519578AAccurate extractionReduce distractionsSubsonic/sonic/ultrasonic wave measurementPattern recognitionFrequency spectrum
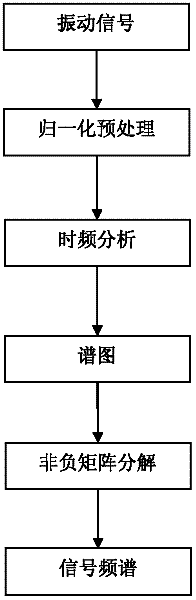
The invention provides a method for extracting a time-frequency domain spectrum of mixed signals of rotating machinery. The method comprises the following steps of: carrying out normalization pre-processing on collected vibration signals at first, and carrying out time-frequency analysis to obtain instantaneous parameters representing non-steady signal characteristics, namely short-time Fourier transform coefficients; then, calculating a spectrogram, and carrying out non-negative matrix factorization on the spectrogram with the order number r of 1; and finally, obtaining a characteristic spectrum of original vibration signals from a factorized basis matrix. The method disclosed by the invention is capable of extracting the characteristic spectrum rapidly and accurately and effectively reducing interference of outside noise at the same time.
Owner:GUANGDONG UNIV OF PETROCHEMICAL TECH
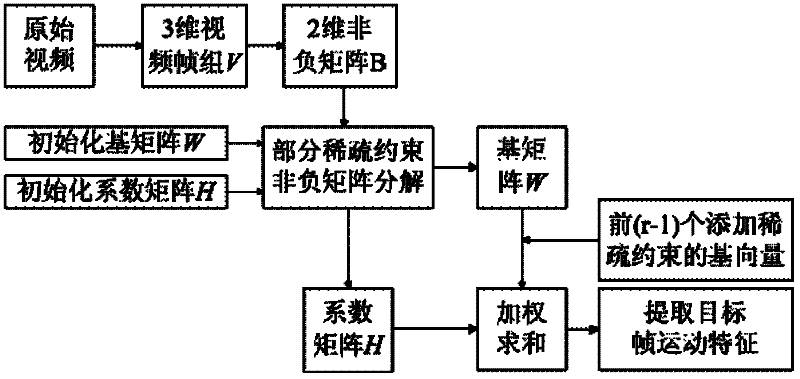
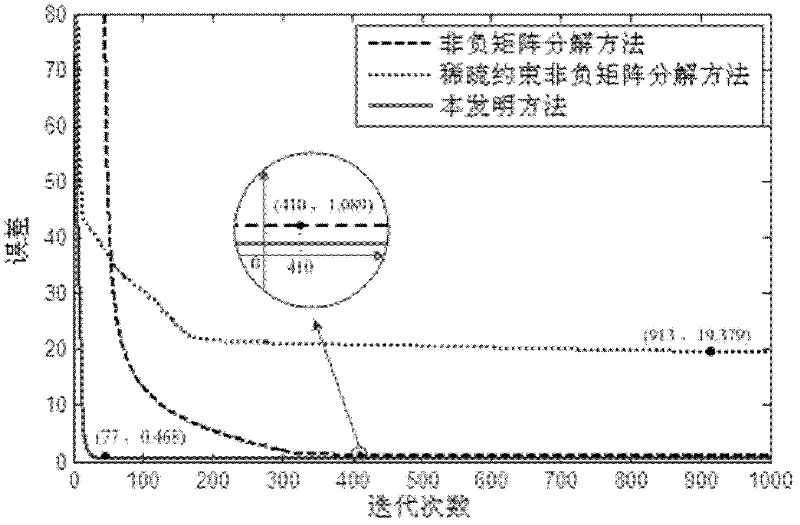
Video motion characteristic extracting method based on local sparse constraint non-negative matrix factorization
InactiveCN102254328AAccurate extractionNot affected by flash pointsImage analysisPattern recognitionVideo monitoring
The invention discloses a video motion characteristic extracting method based on local sparse constraint non-negative matrix factorization. The video motion characteristic extracting method mainly solves the problems that static background interference and flash points of a video cannot be filtrated, the convergence rate is low, and the factorization error is over-serious in the prior art. The video motion characteristic extracting method comprises the steps of: firstly converting a video into a video frame group by taking a target frame as the center, and converting the video frame group into a non-negative matrix; next, factorizing the non-negative matrix by a local sparse constraint non-negative matrix factorization method, carrying out sparse constraint on part of base matrix column vectors, and calculating a motion vector of the target frame through weighted summarization of the part of the base matrix column vectors undergoing sparse constraint and the corresponding coefficient matrixes; and finally converting the motion vector of the target frame into the motion characteristic of the target frame. The video motion characteristic extracting method disclosed by the invention is applicable to target tracking and video monitoring, and can be used for extracting the video motion characteristic quickly, accurately and effectively.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
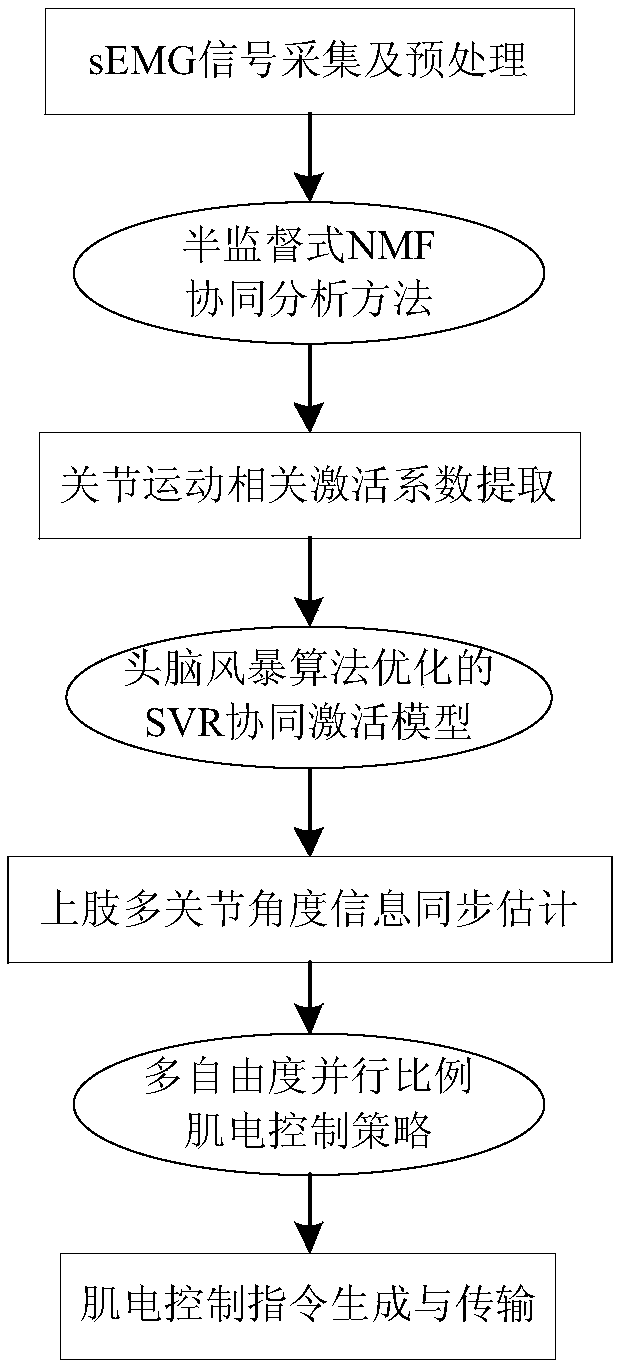
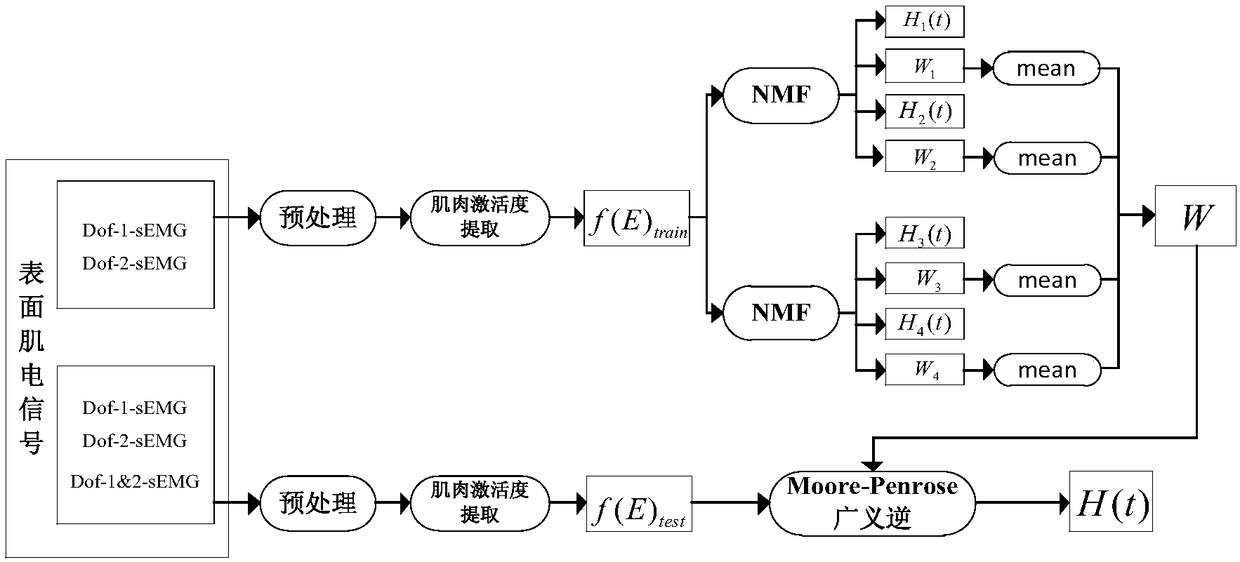
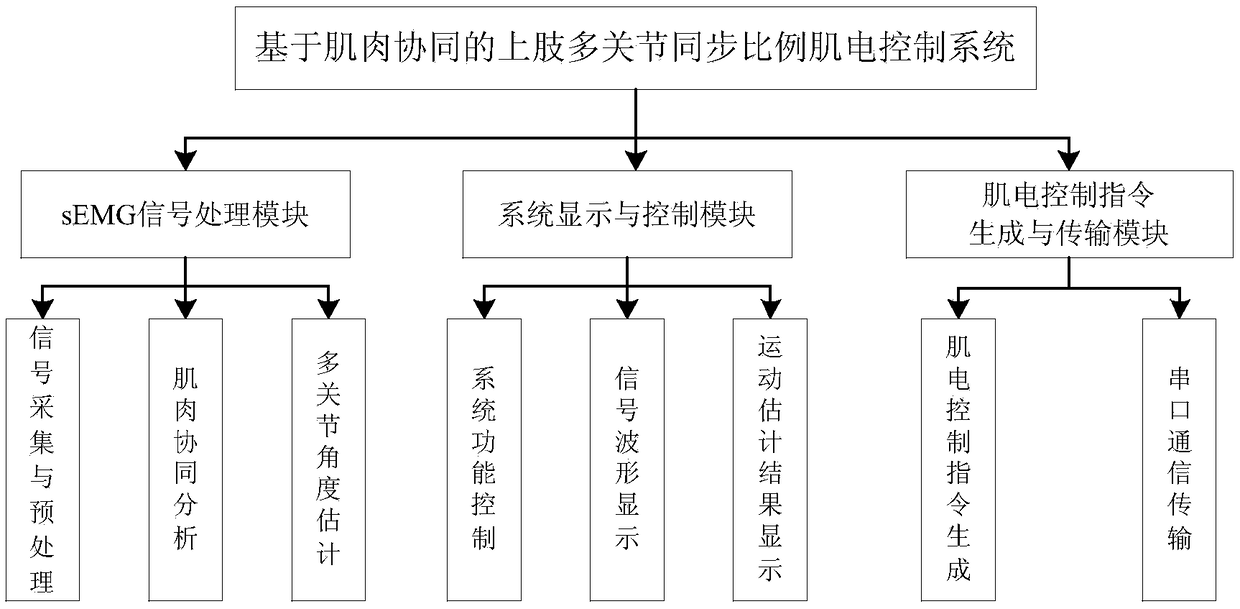
Upper limb multi-joint synchronous proportional electromyography control method and system based on muscle synergy
ActiveCN109262618AImprove interactivityEffective decouplingProgramme-controlled manipulatorMuscle synergyModel parameters
The invention discloses an upper limb multi-joint synchronous proportional electromyography control method and system based on muscle synergy. The method includes first collecting and preprocessing asurface electromyography signal of joint motion related muscles, providing a semi-supervised non-negative matrix factorization synergic analysis method according to a muscle synergic contraction modelto decouple the electromyography signal and effectively extract joint motion related muscle synergy elements and activation coefficient sequences; second constructing a synergic activation model of activation coefficients and joint angles through support vector regression and adopting a brainstorming algorithm to optimize model parameters to achieve synchronous estimation of multiple joint motionangle information of upper limbs; finally constructing an upper limb multi-joint synchronous proportional electromyography control system based on muscle synergy by combining the multi-degree-of-freedom parallel proportional electromyography control strategy to convert the estimated multi-joint motion angle information into multi-degree-of-freedom operation displacement of a rehabilitation aid device and provide a smooth stable motion control instruction for the rehabilitation aid device.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF TECH
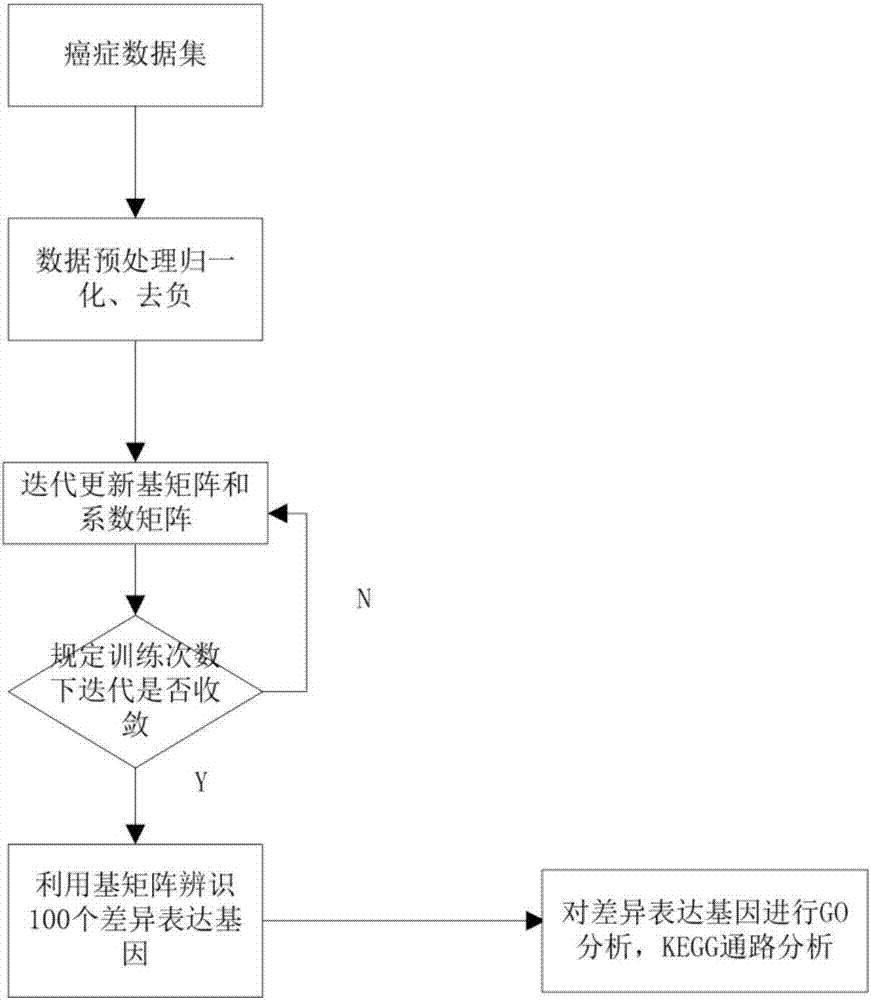
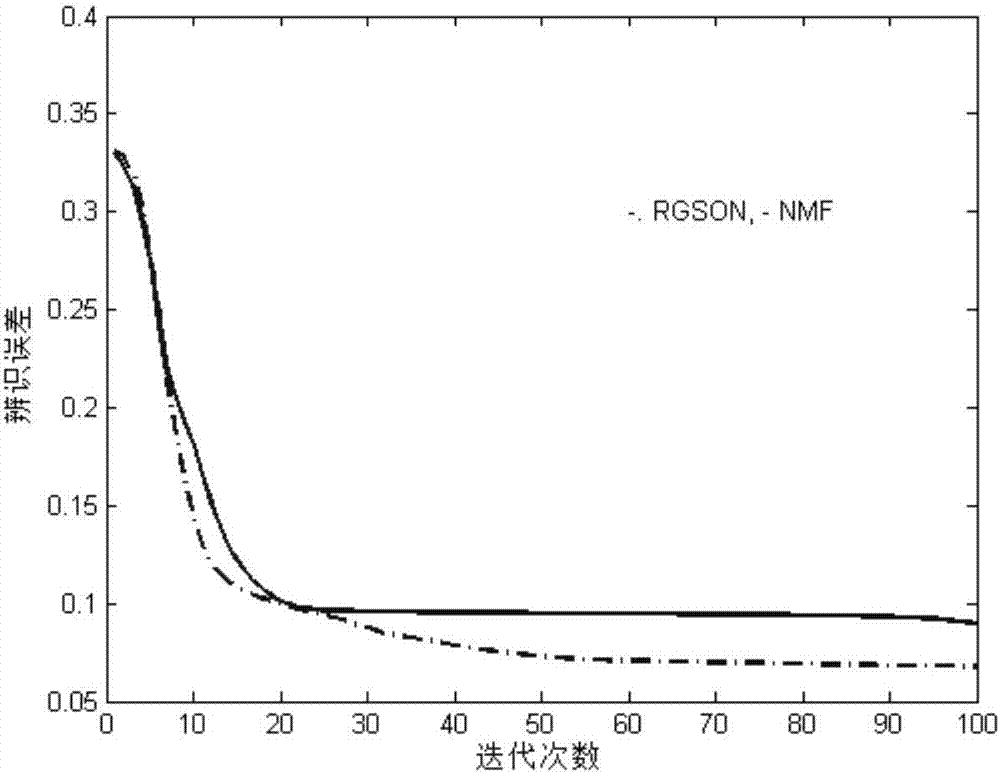
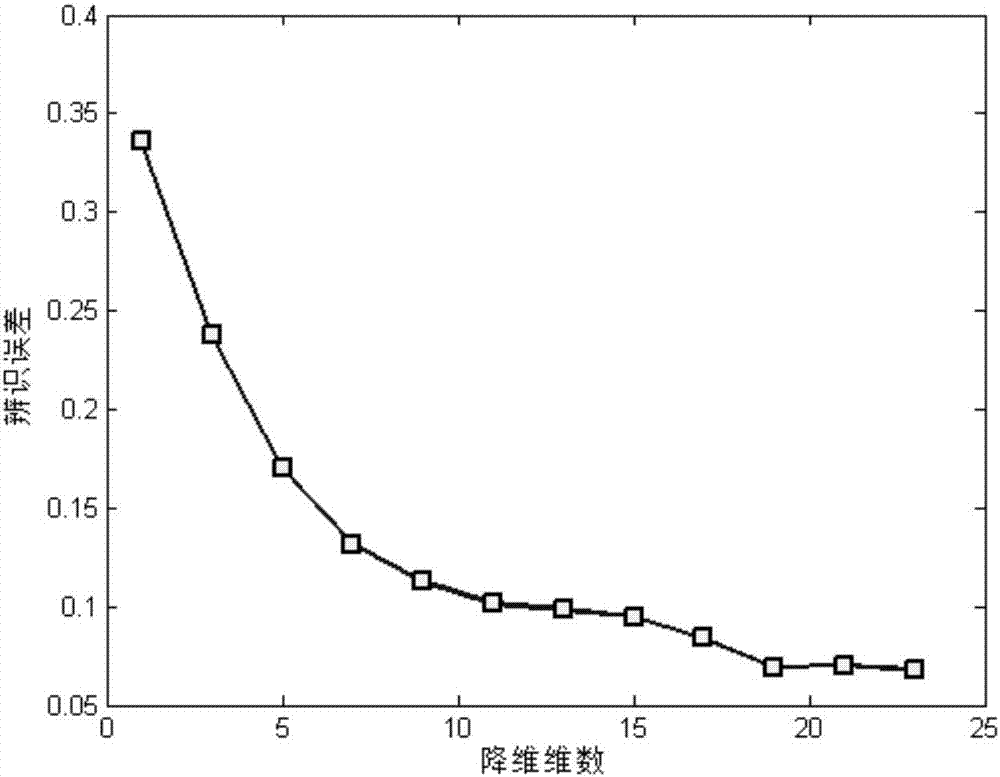
Differentially expressed gene identification method based on combined constraint non-negative matrix factorization
ActiveCN107016261AEffective decomposition resultsEfficient Sparse Decomposition ResultsSpecial data processing applicationsData setAlgorithm
The invention discloses a differentially expressed gene identification method based on combined constraint non-negative matrix factorization. The method comprises the following steps of 1, representing a cancer-gene expression data set with a non-negative matrix X, 2, constructing a diagonal matrix Q and an element-full matrix E, 3, introducing manifold learning in the classical non-negative matrix factorization method, conducting orthogonal-constraint sparseness and constraint on a coefficient matrix G, and obtaining a combined constraint non-negative matrix factorization target function, 4, calculating the target function, and obtaining iterative formulas of a basis matrix F and the coefficient matrix G, 5, conducting semi-supervision non-negative matrix factorization on the non-negative data set X, and obtaining the basis matrix F and the coefficient matrix G after iteration convergence, 6, obtaining an evaluation vector (the formula is shown in the description), sorting elements in the evaluation vector (the formula is shown in the description) from large to small according to the basis matrix F, and obtaining differentially expressed genes, 7, testing and analyzing the identified differentially expressed genes through a GO tool. The identification method can effectively extract the differentially expressed genes where cancer data is concentrated, and be applied in discovering differential features in a human disease gene database. The identification method has important clinical significance for early diagnosis and target treatment of diseases.
Owner:HANGZHOU HANGENE BIOTECH CO LTD
Non-negative matrix factorization method applied to hyperspectral image processing
The present invention discloses a Non-negative Matrix Factorization (NMF) based on sparse and correlation constraints and the method is applied to processing of decomposition of mixed pixels of a hyper-spectral remote sensing image. According to the method, finally, a given non-negative matrix Vm*n is factorized into a product of a basis matrix Wm*r and a coefficient matrix Hr*n, i.e. Vm*n is approximately equal to Wm*r Hr*n ; firstly, the non-negative matrix V is selected, W and H are randomly initialized, then the minimum correlation constraint is applied to the coefficient matrix H in a target function, the sparse constraint is applied to the basis matrix W and the coefficient matrix H and then iteration is carried out according to an iteration formula until the matrices W and H are converged.
Owner:南京博曼环保设备有限公司
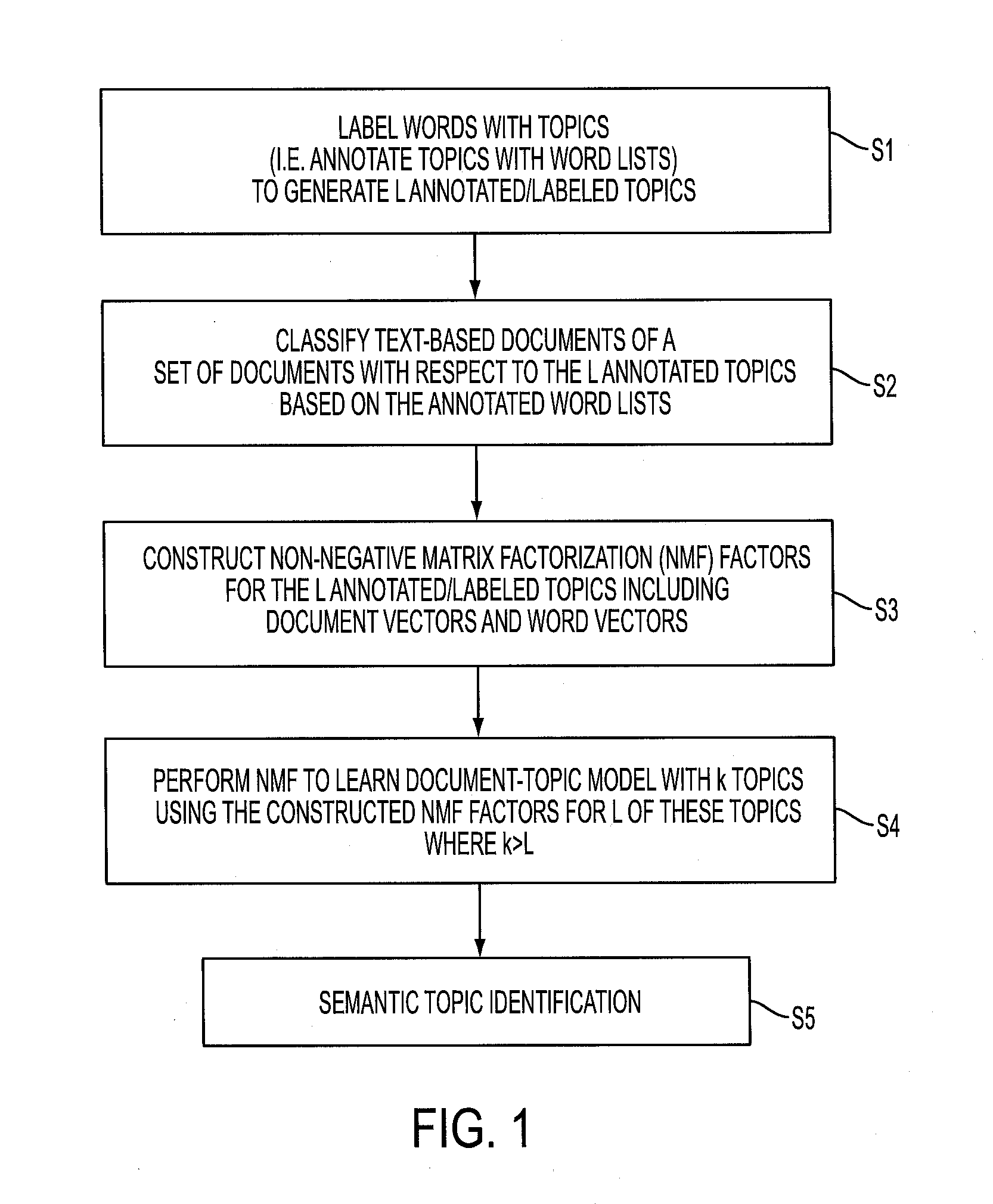
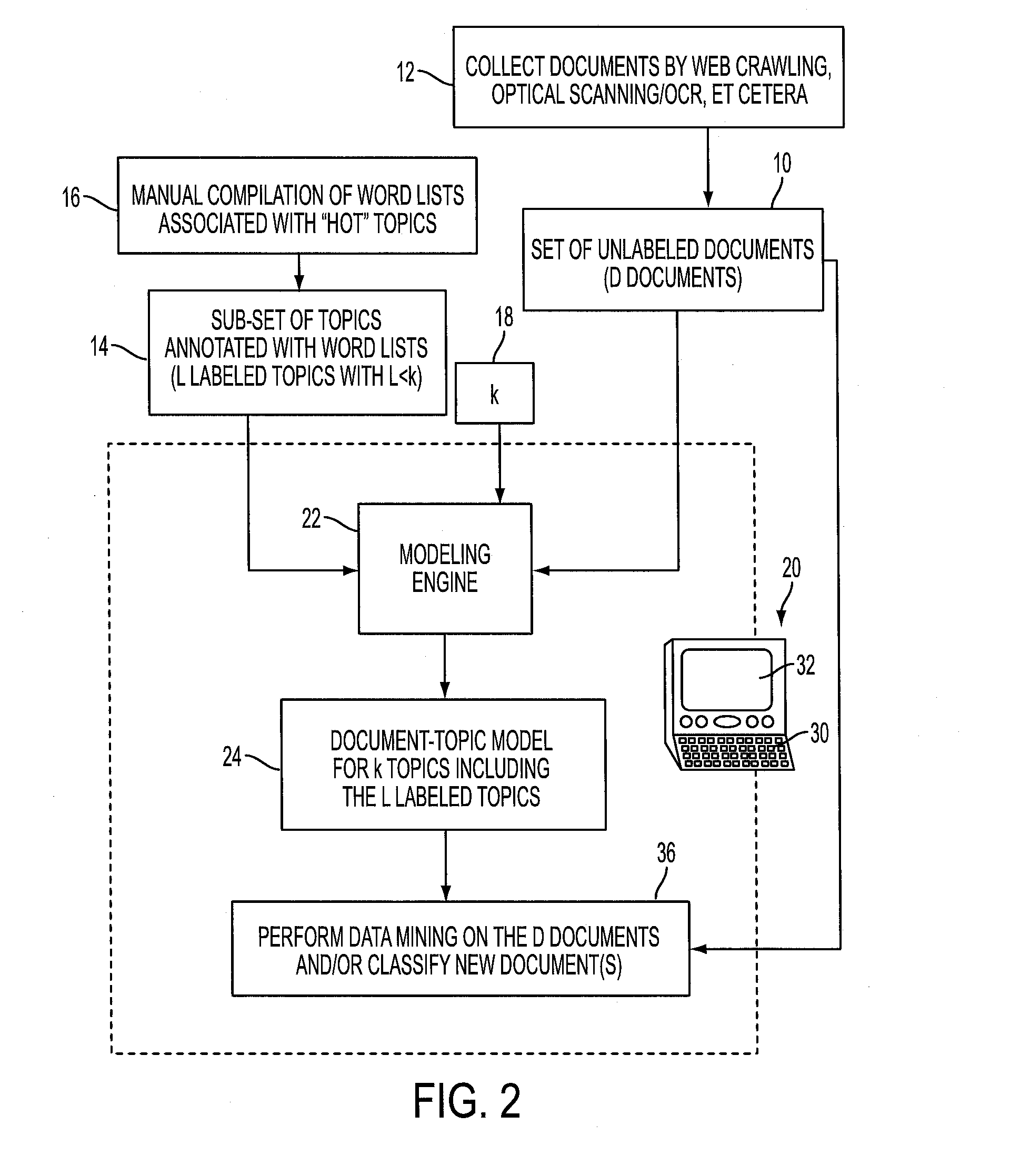
Joint approach to feature and document labeling
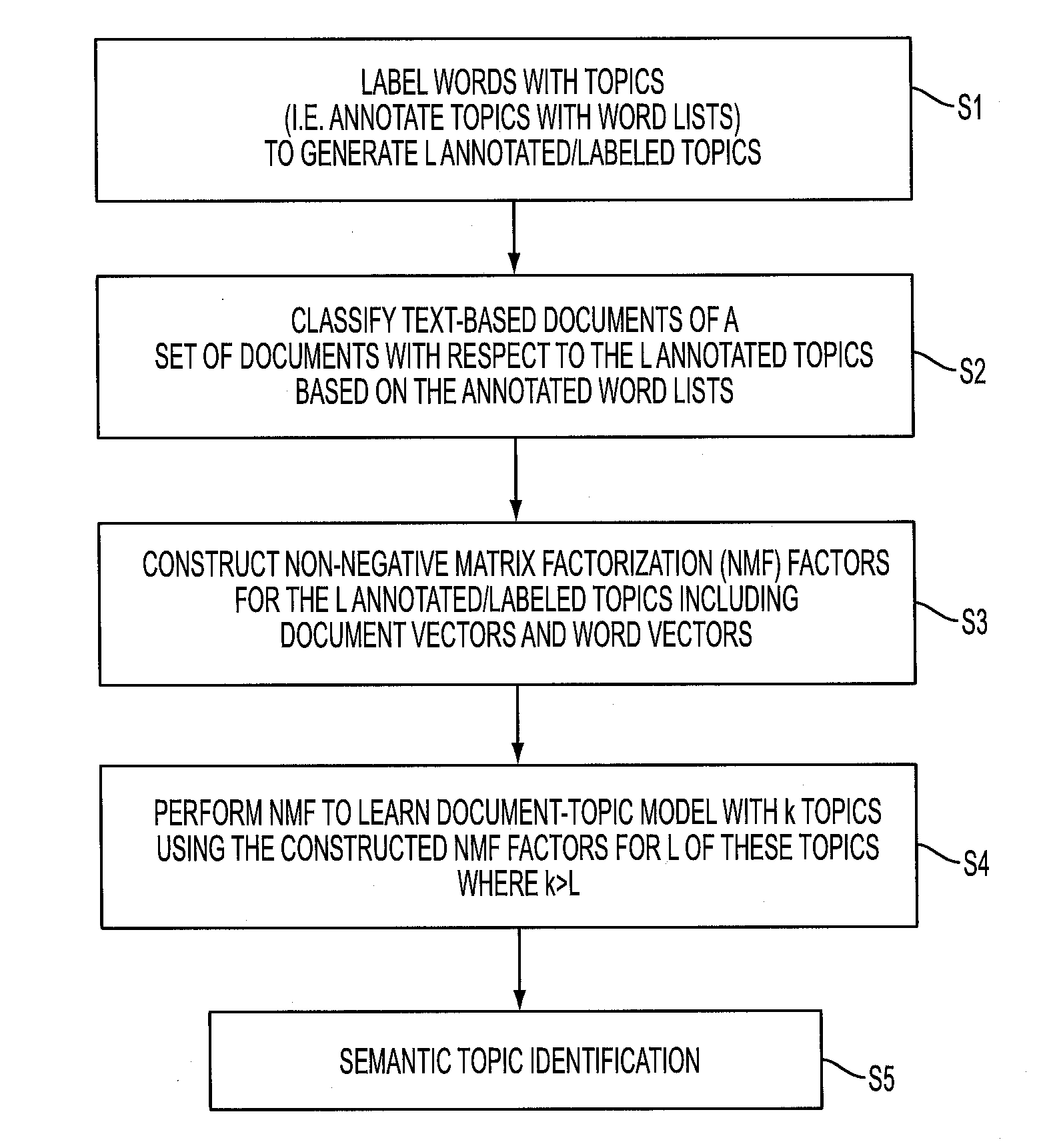
InactiveUS20160203209A1Simple technologyDigital data processing detailsRelational databasesWord listDocumentation
Documents of a set of documents are represented by bag-of-words (BOW) vectors. L labeled topics are provided, each labeled with a word list comprising words of a vocabulary that are representative of the labeled topic and possibly a list of relevant documents. Probabilistic classification of the documents generates for each labeled topic a document vector whose elements store scores of the documents for the labeled topic and a word vector whose elements store scores of the words of the vocabulary for the labeled topic. Non-negative matrix factorization (NMF) is performed to generate a document-topic model that clusters the documents into k topics where k>L. NMF factors representing L topics of the k topics are initialized to the document and word vectors for the L labeled topics. In some embodiments the NMF factors representing the L topics initialized to the document and word vectors are frozen, that is, are not updated by the NMF after the initialization.
Owner:XEROX CORP
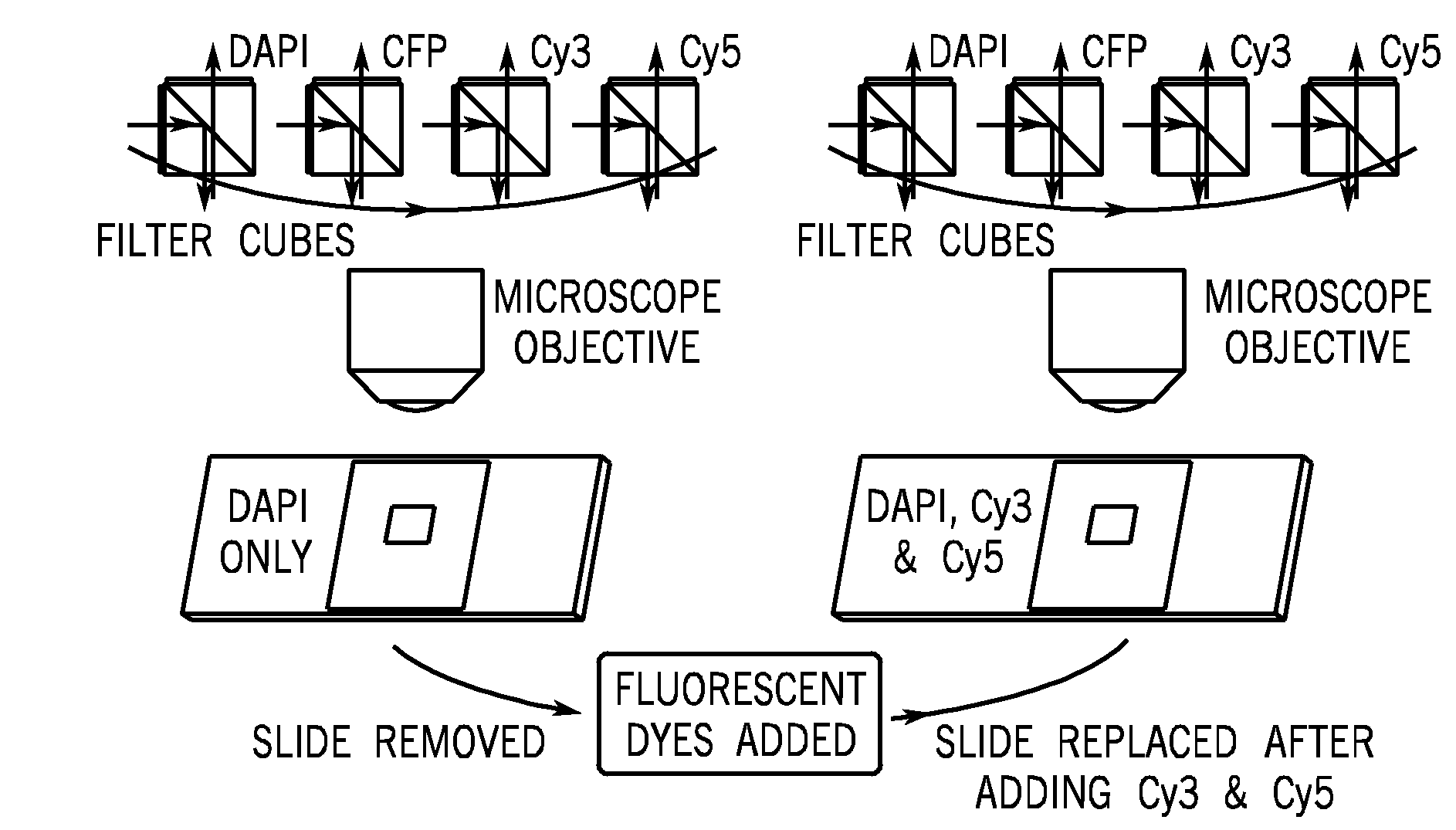
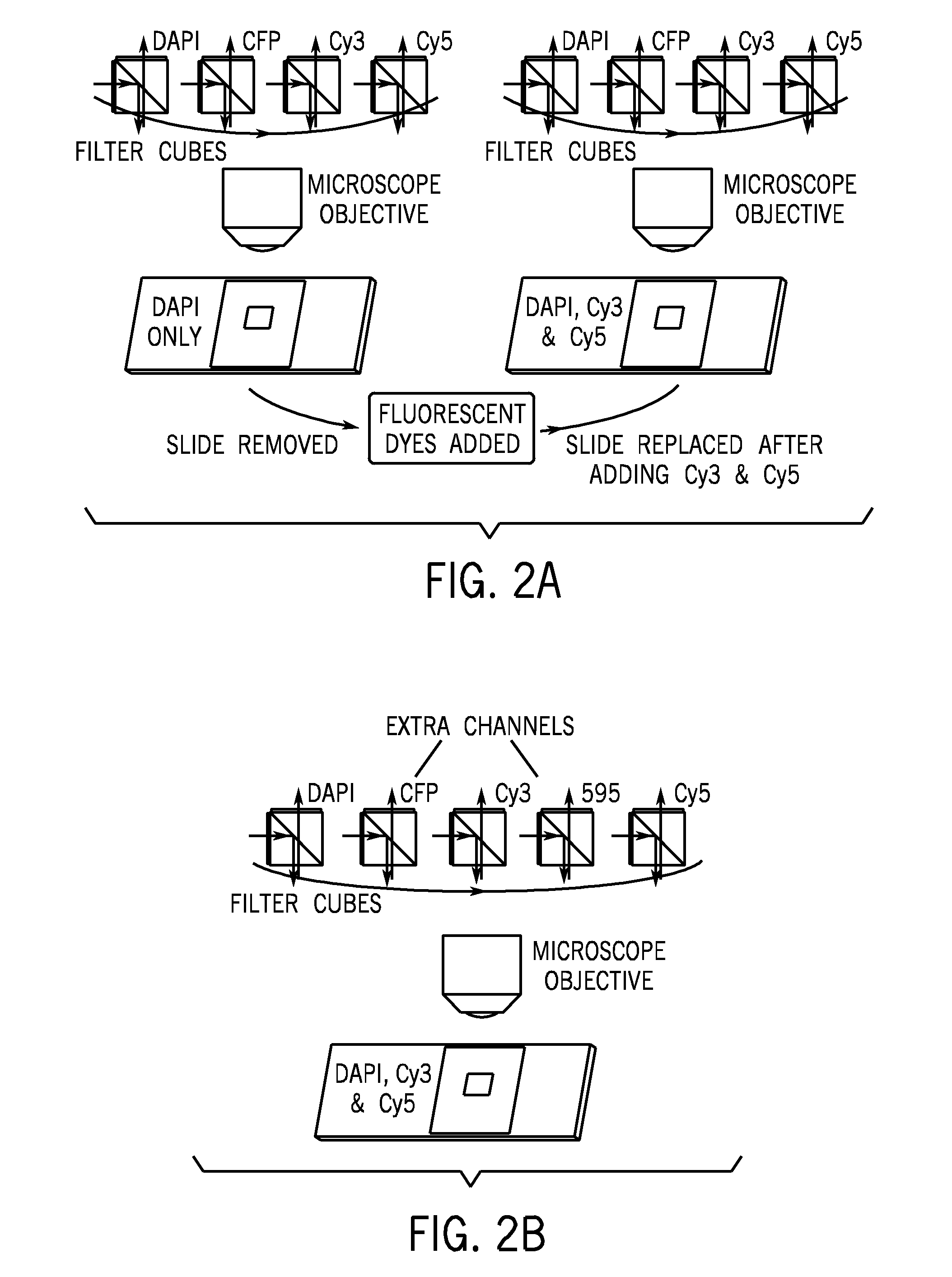
Method and Apparatus for Removing Tissue Autofluorescence
ActiveUS20090245611A1Remove dark current noiseRemove autofluorescenceMicrobiological testing/measurementSurgeryPattern recognitionNonnegative matrix
Techniques for removing image autoflourescence from fluorescently stained biological images are provided herein. The techniques utilize non-negative matrix factorization that may constrain mixing coefficients to be non-negative. The probability of convergence to local minima is reduced by using smoothness constraints. The non-negative matrix factorization algorithm provides the advantage of removing both dark current and autofluorescence.
Owner:LEICA MICROSYSTEMS CMS GMBH
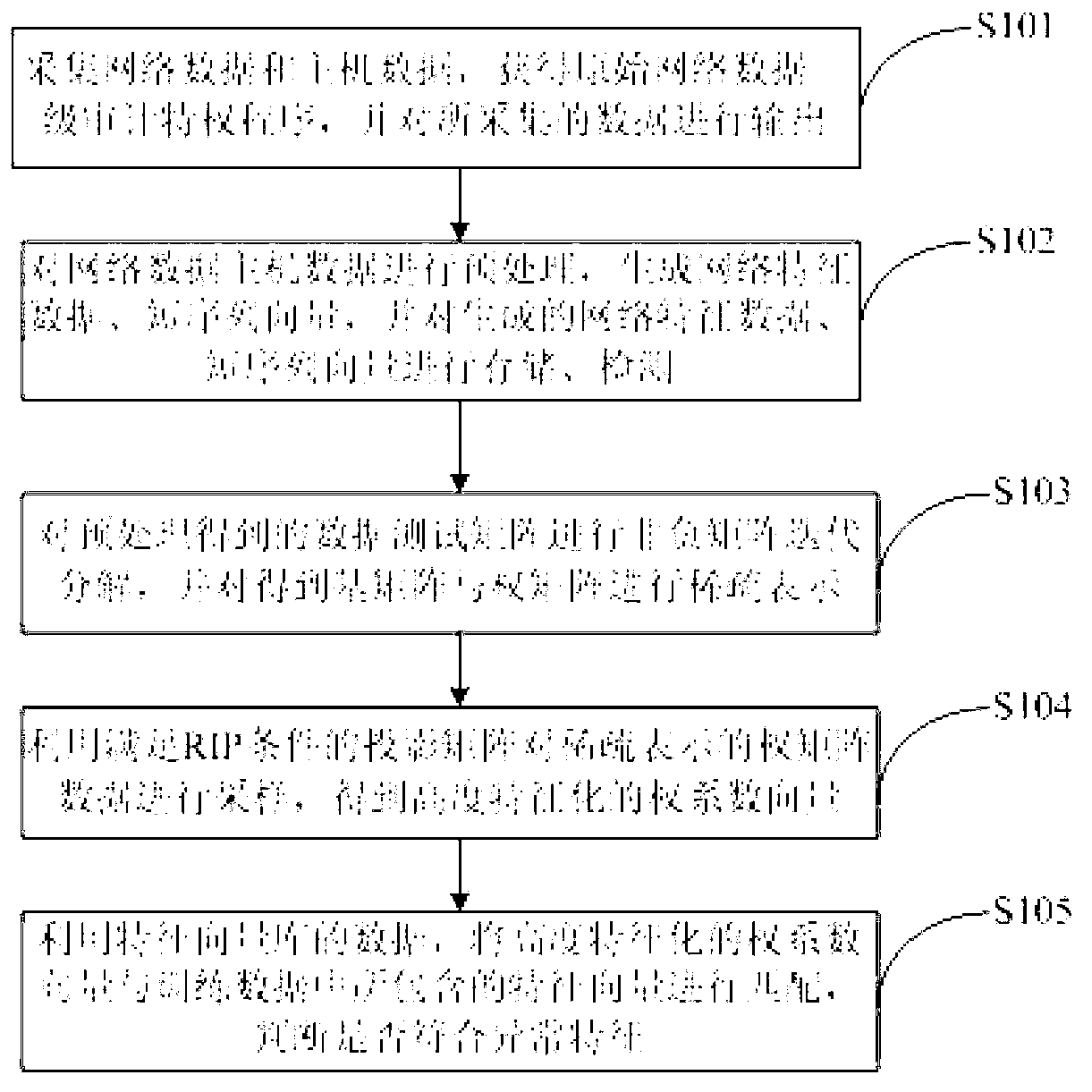
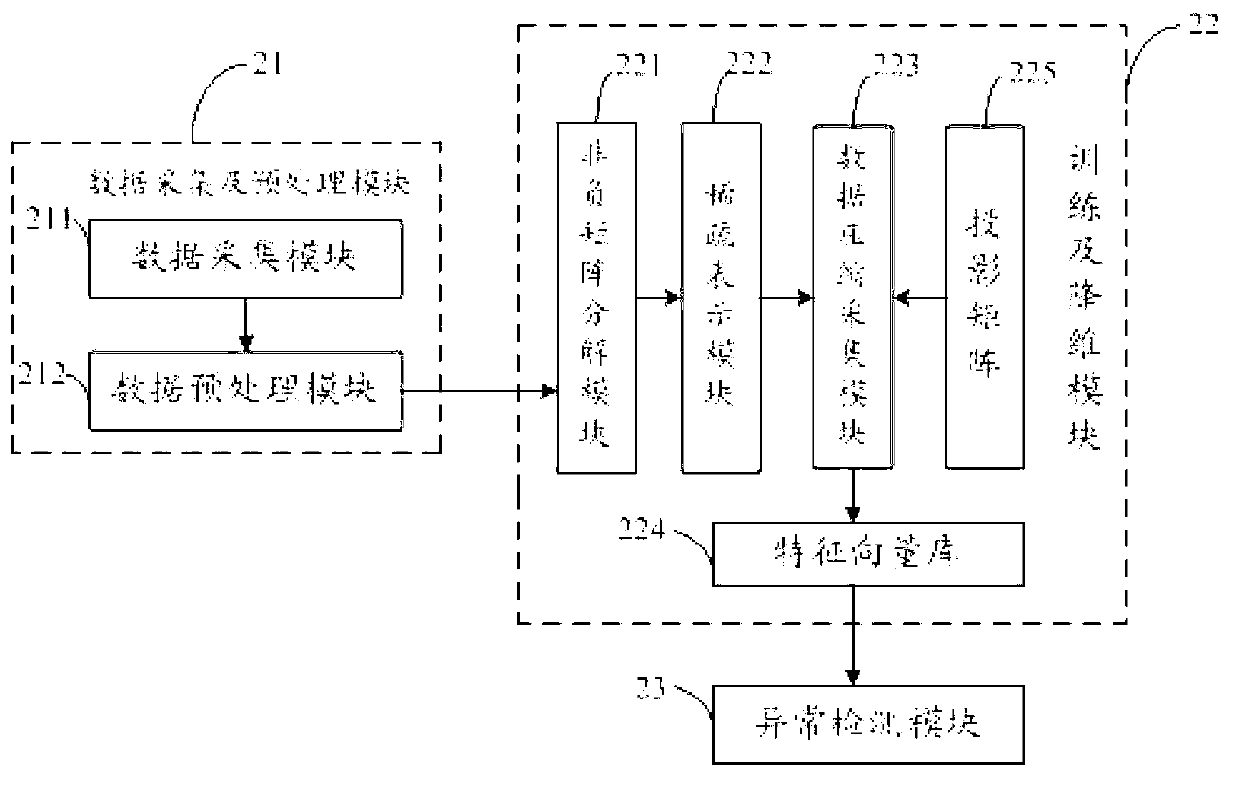
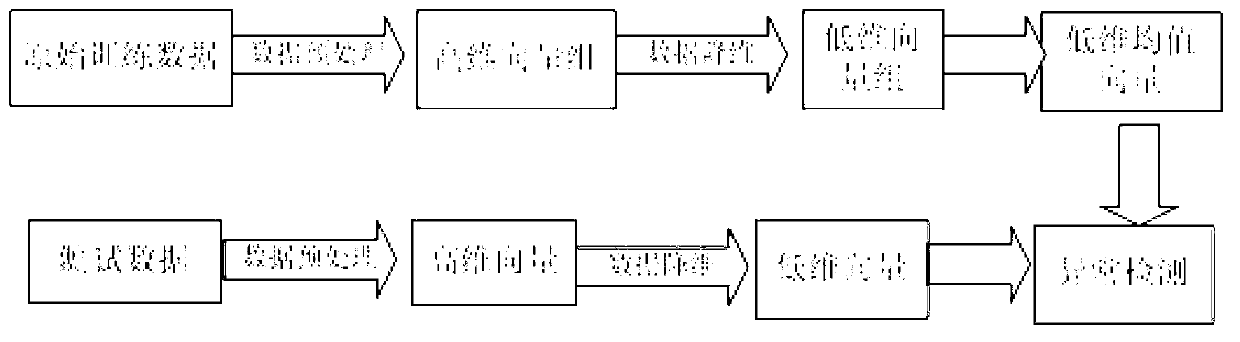
Method and system for intrusion detection based on non-negative matrix factorization under sparse representation
InactiveCN103023927AReduce the detection dimensionConstrained Decomposition Iterative ProcessTransmissionHat matrixWeight coefficient
The invention discloses a method and a system for intrusion detection based on non-negative matrix factorization under sparse representation. The method includes: acquiring network data and host data, and obtaining a level-one audit privilege program of original network data; preprocessing the network data and the host data, and generating network characteristic data and short-sequence vectors; performing non-negative matrix iterative factorization for a data test matrix, and performing sparse representation for a basis matrix and a weight matrix; sampling weight matrix data subjected to sparse representation by the aid of a projection matrix so that highly characteristic weight coefficient vectors are obtained; and matching the highly characteristic weight coefficient vectors with characteristic vectors in training data by the aid of characteristic vector library data, and judging whether abnormal characteristics are conformed to or not. The method and the system for intrusion detection achieve data dimension reduction by non-negative matrix factorization and uses multi-divergence as a measurement level, an RIP (routing information protocol) condition in sparse representation is added into a combined divergence objective function family to restrain a non-negative matrix factorization iterative process, data detection dimensionality is lowered, and high-dimensional mass data processing of the system for intrusion detection is facilitated.
Owner:SOUTHWEST UNIVERSITY
Identifying optimal colors for calibration and color filter array design
InactiveUS20070230774A1Good colorCharacter and pattern recognitionColor television detailsPattern recognitionData set
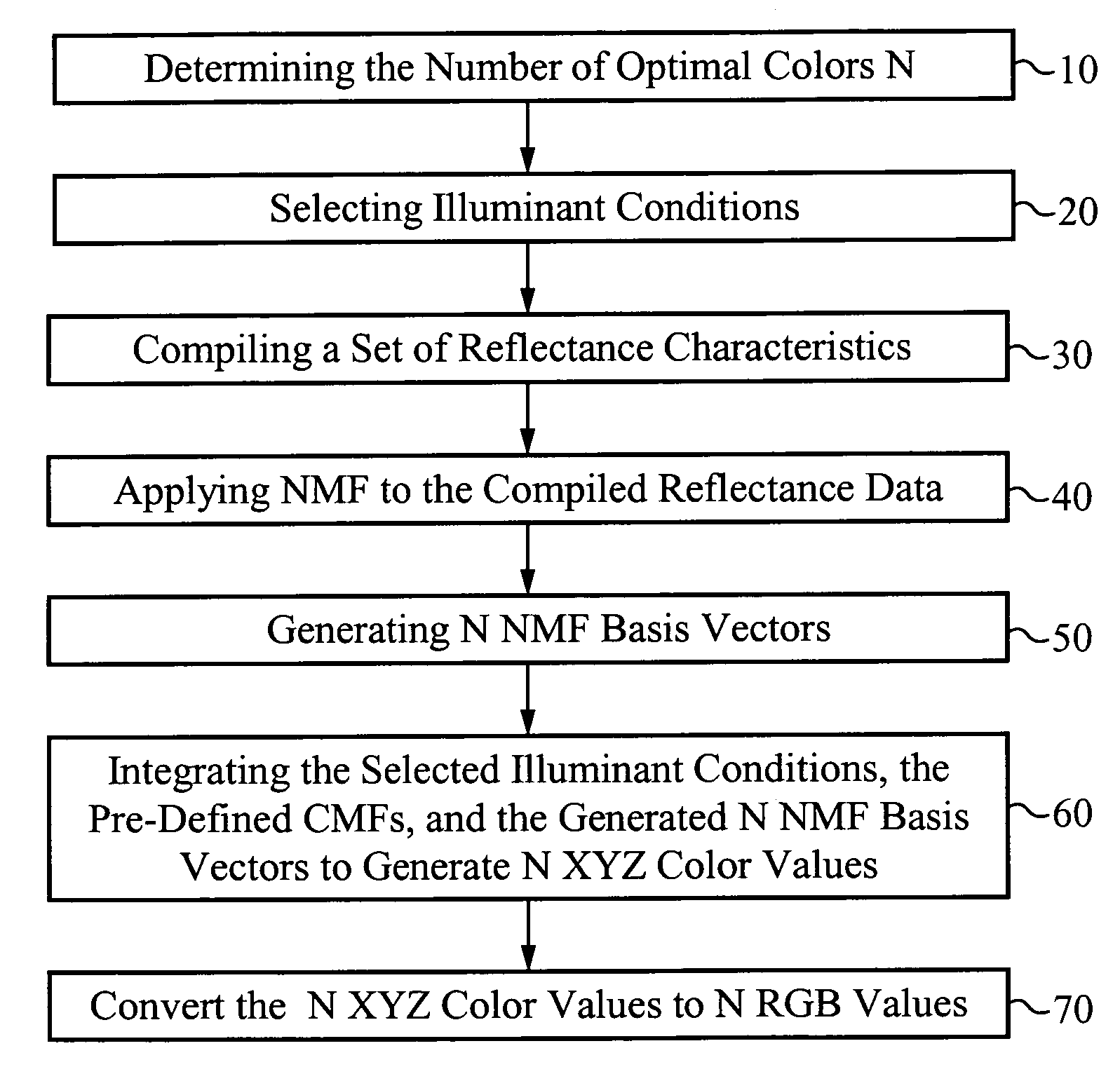
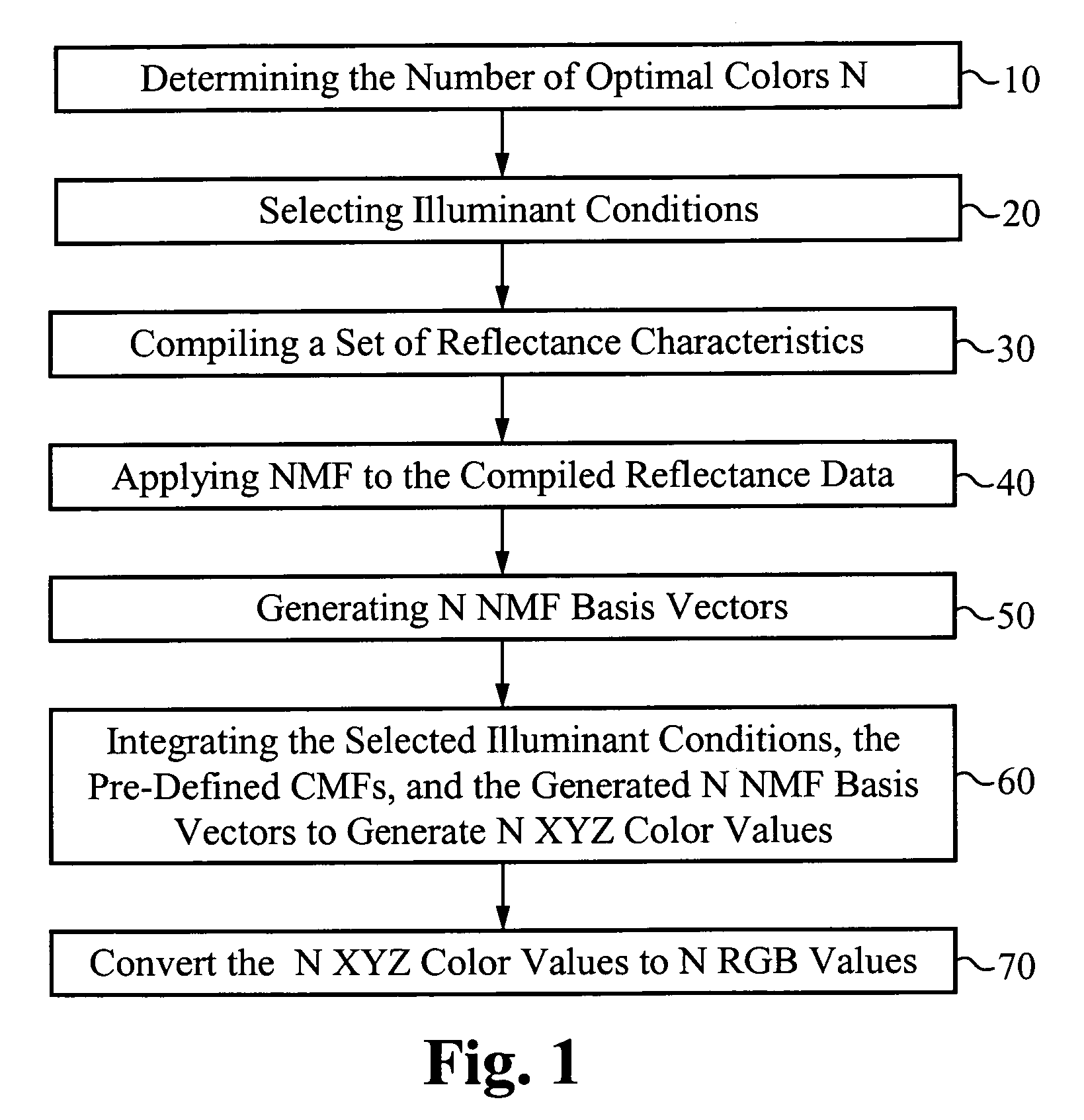
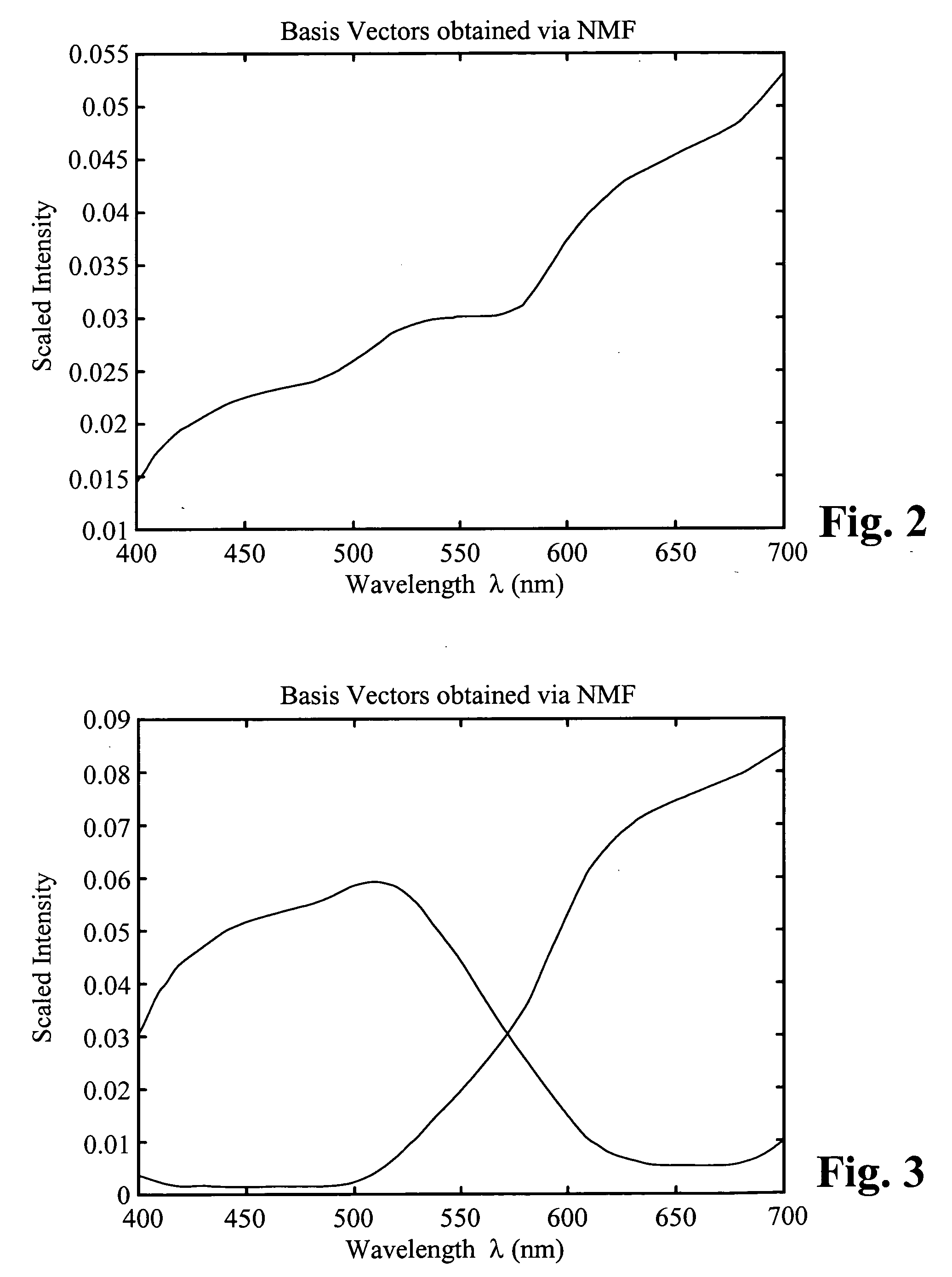
A color determination method utilizes color matching functions to approximate the imaging system's sensitivity characteristics. The illuminant conditions are modeled according to known illuminant intensity versus wavelength functions. Non-negative Matrix Factorization (NMF) is applied to a set of known reflectance data to decompose the known reflectance data set into a defined number of NMF basis vectors. In general, for an N-color based imaging system, N NMF basis functions are determined. Since basis functions provided by NMF are non-negative, the determined N NMF basis functions are related to actual physical colors. The NMF basis vectors are integrated with the illuminate conditions and color matching function(s) that approximate the imaging system's sensitivity to generate XYZ color values. These are converted to RGB values which are used to determine the optimal N colors for the N-color based imaging system.
Owner:SONY CORP +1
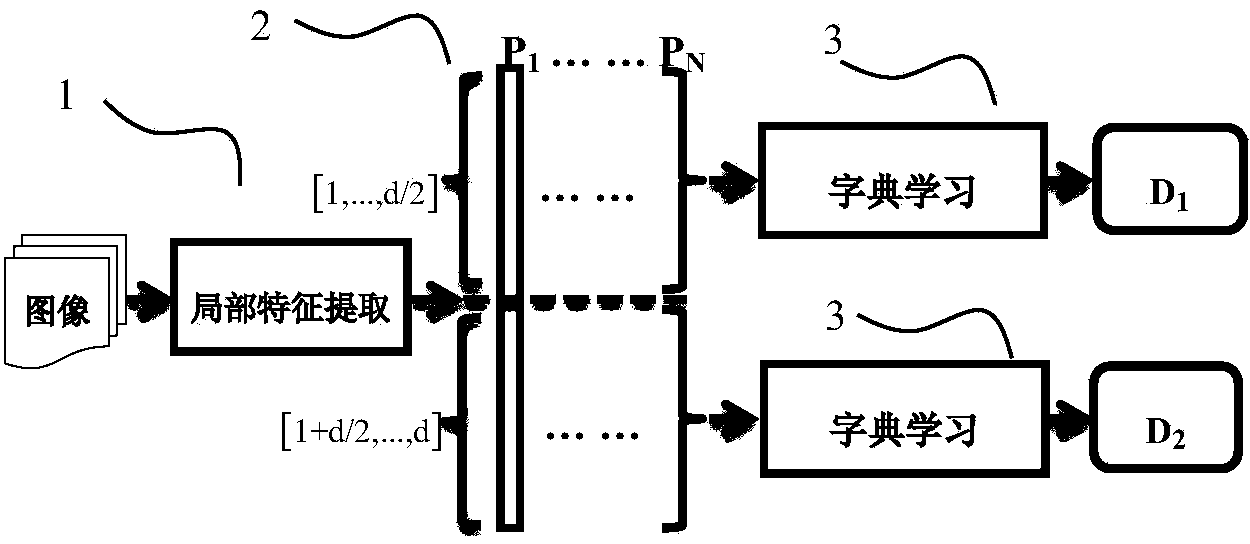
Dictionary learning method, visual word bag characteristic extracting method and retrieval system
ActiveCN104036012AReduce training timeReduce memory usageSpecial data processing applicationsDictionary learningFeature extraction
The invention provides a dictionary learning method. The dictionary learning method includes 1), dividing local characteristic vector of images into first segments and second segments on the basis of dimensionality; 2) establishing a first data matrix by the first segments of a plurality of local characteristic vectors, and establishing a second data matrix by the second segments of a plurality of local characteristic vectors; 3) subjecting the first data matrix to sparse non-negative matrix factorization to obtain a first dictionary sparsely coding the first segments of the local characteristic vectors; subjecting the second data matrix to sparse non-negative matrix factorization to obtain a second dictionary sparsely coding the second segments of the local characteristic vectors. The invention further provides a visual word bag characteristic extracting method for sparsely indicating the local characteristic vectors of the images segment by segment on the basis of the dictionaries and provides a corresponding retrieval system. Memory usage can be greatly reduced, wordlist training time and characteristic extraction time are shortened, and the dictionary learning method is particularly suitable for mobile terminals.
Owner:INST OF COMPUTING TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
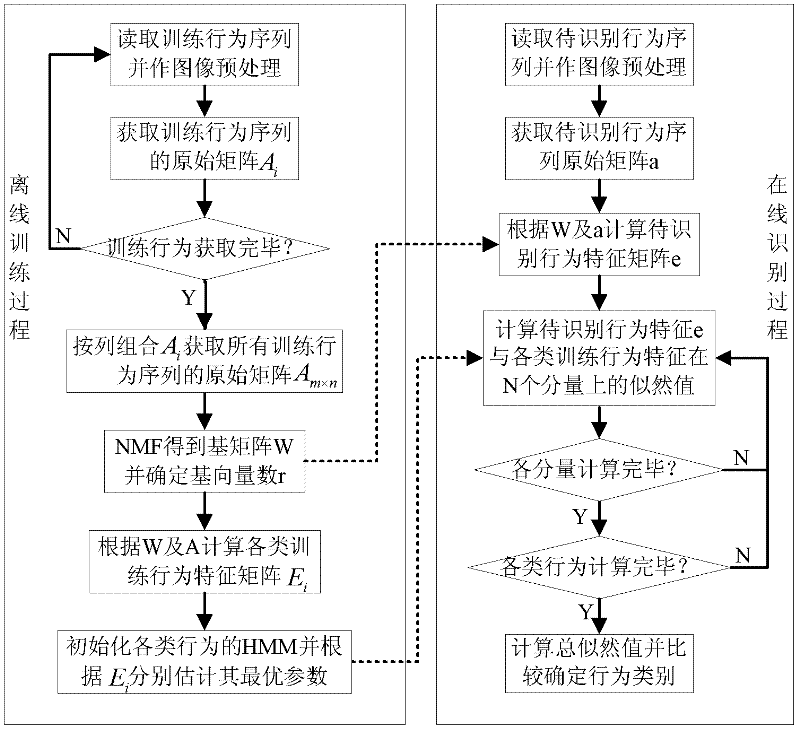
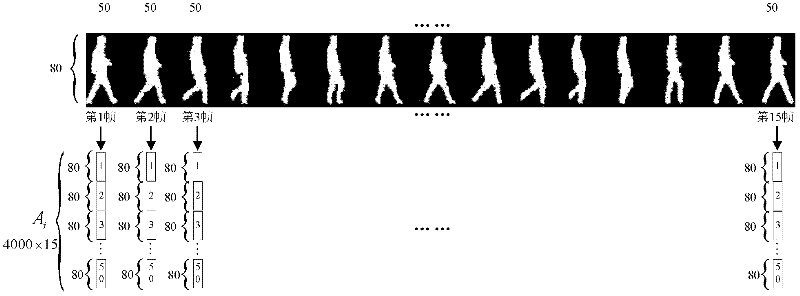
Human behavior identification method based on non-negative matrix decomposition and hidden Markov model
ActiveCN102393910AHigh behavior recognition rateImprove automatic behavior analysis capabilitiesCharacter and pattern recognitionVideo monitoringHuman behavior
A human behavior identification method based on non-negative matrix decomposition and a hidden Markov model comprises an off-line training stage of firstly pre-processing image of each kind of selected behavior sequence training data to obtain a total sample data matrix A of all training data, carrying out non-negative matrix decomposition (NMF) on the A to obtain a basic matrix W and a basic vector number r, and obtaining a characteristic matrix Ei of each kind of training behavior sequence according to the W and the A, and initializing the hidden Markov model (HMM) of each kind of training behavior sequence and respectively estimating an optimal parameter thereof; and an on-line identification stage of firstly pre-processing the image of the input behavior sequence to be identified to obtain an original matrix a of the behavior sequence, obtaining a characteristic matrix e according to the W and the a; and lastly, figuring up a likelihood of the behavior sequence to be identified and each kind of training behavior sequence to determine behavior types. In the invention, the human behavior identification rate is higher, and the automatic analysis ability of the human behavior applied to a real-time intelligent video monitoring system is improved.
Owner:菏泽建数智能科技有限公司
Multi-view clustering method based on non-negative matrix factorization and diversity-consistency
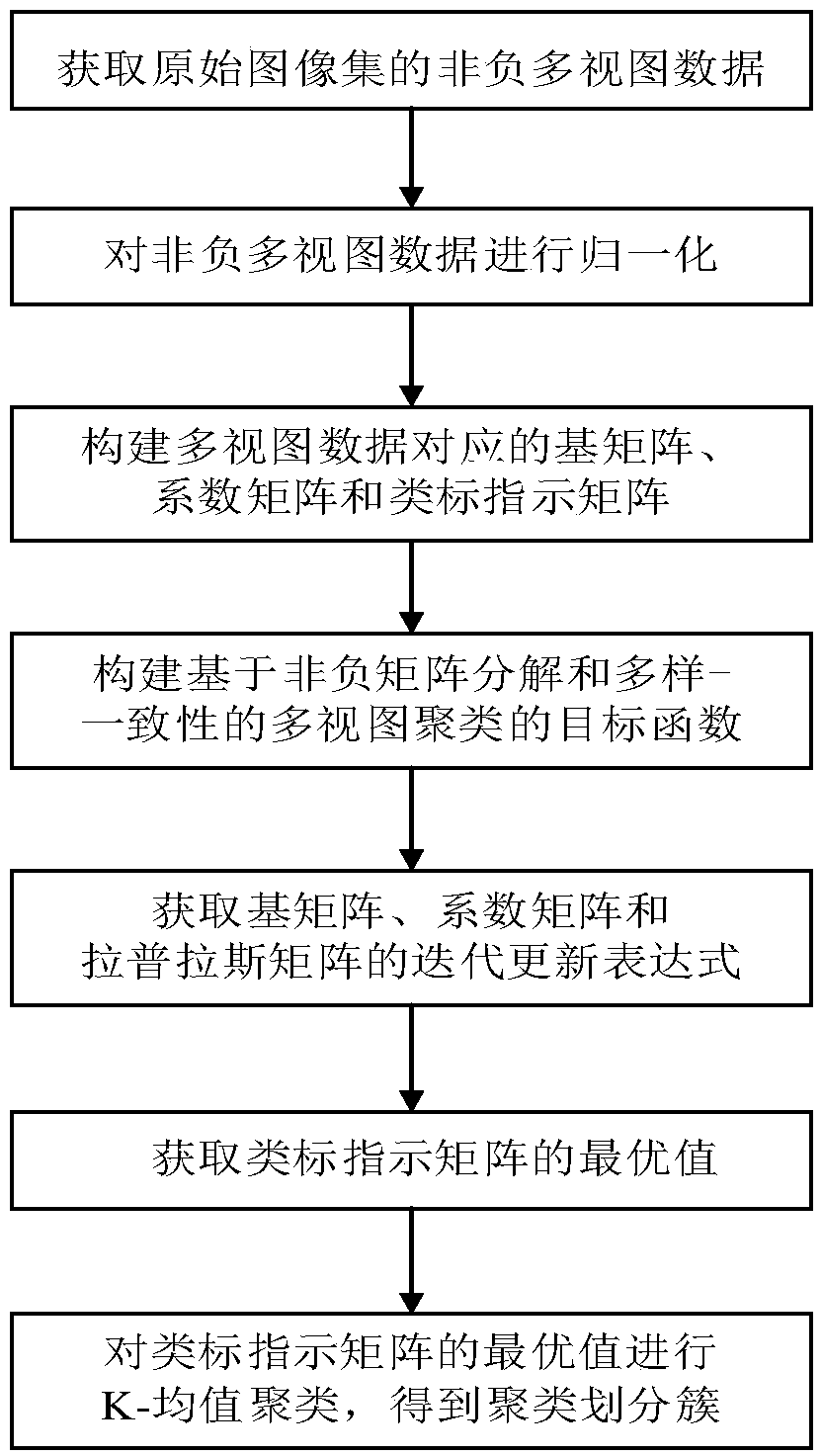
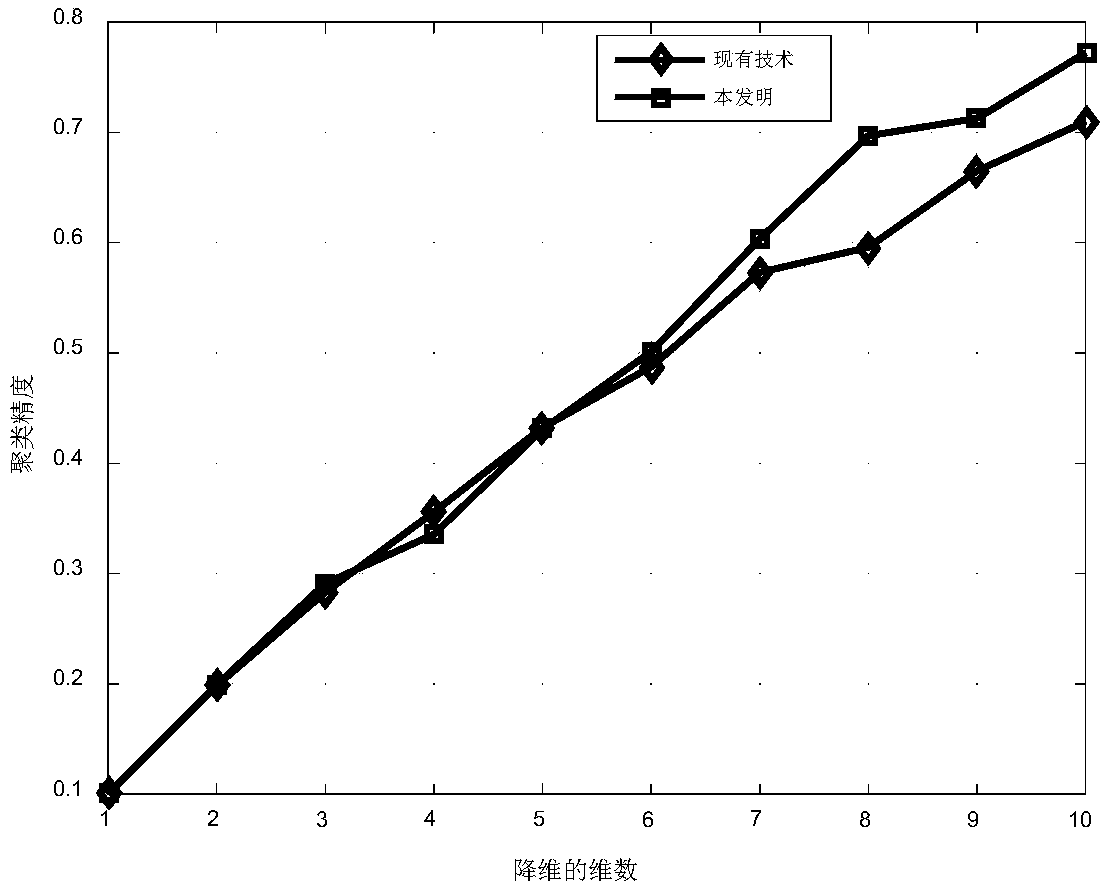
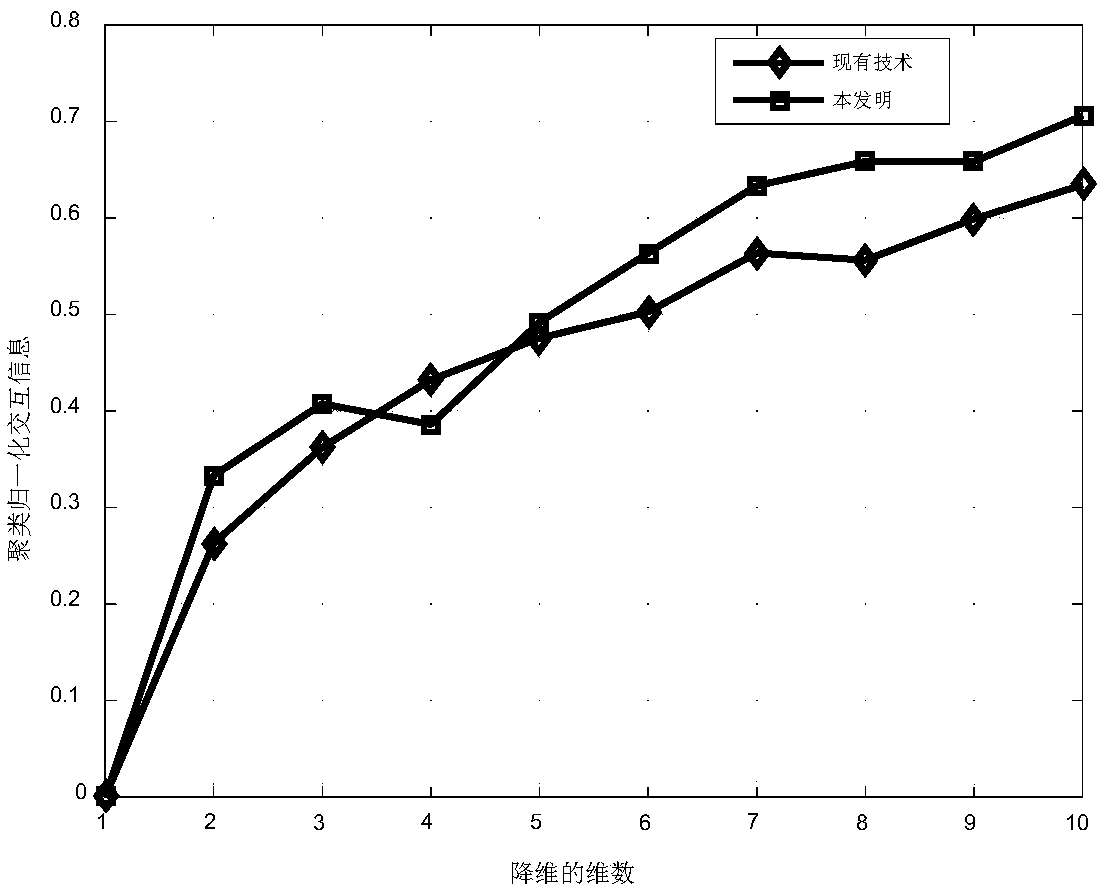
InactiveCN108776812AHigh precisionCharacter and pattern recognitionInformation analysisInvestment analysis
The present invention provides a multi-view clustering method based on non-negative matrix factorization and diversity-consistency. The technical problem is solved that the clustering precision and the normalization interaction information are low in a current multi-view clustering method. The method comprises the steps of: obtaining normalization non-negative multi-view data of an original imageset; constructing a base matrix, a coefficient matrix and a standard-similar indication matrix corresponding to the multi-view data; constructing a target function based on the non-negative matrix factorization and diversity-consistency multi-view clustering; obtaining an iteration updating expression of the base matrix, the coefficient matrix and the Laplacian matrix; obtaining the optimal valueof the standard-similar indication matrix; and performing K-mean clustering for the optimal value of the standard-similar indication matrix, and obtaining a clustering cluster corresponding to the multi-view data. The multi-view clustering method employs expression diversity and standard-similar consistency to learn the complementation and common information in the multi-view data so as to effectively improve the performances of the multi-view clustering, and can be applied to the field of biology information analysis and financial investment analysis, etc.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Human body motion video recognition method based on non-negative matrix factorization
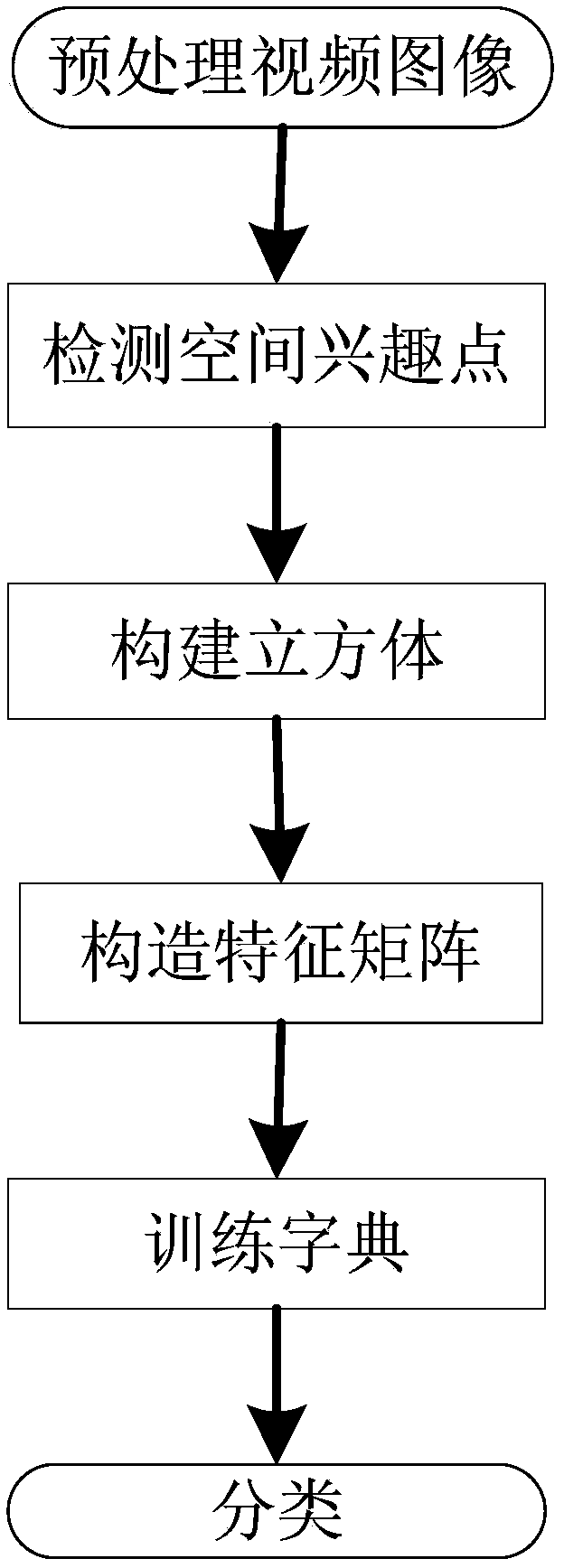
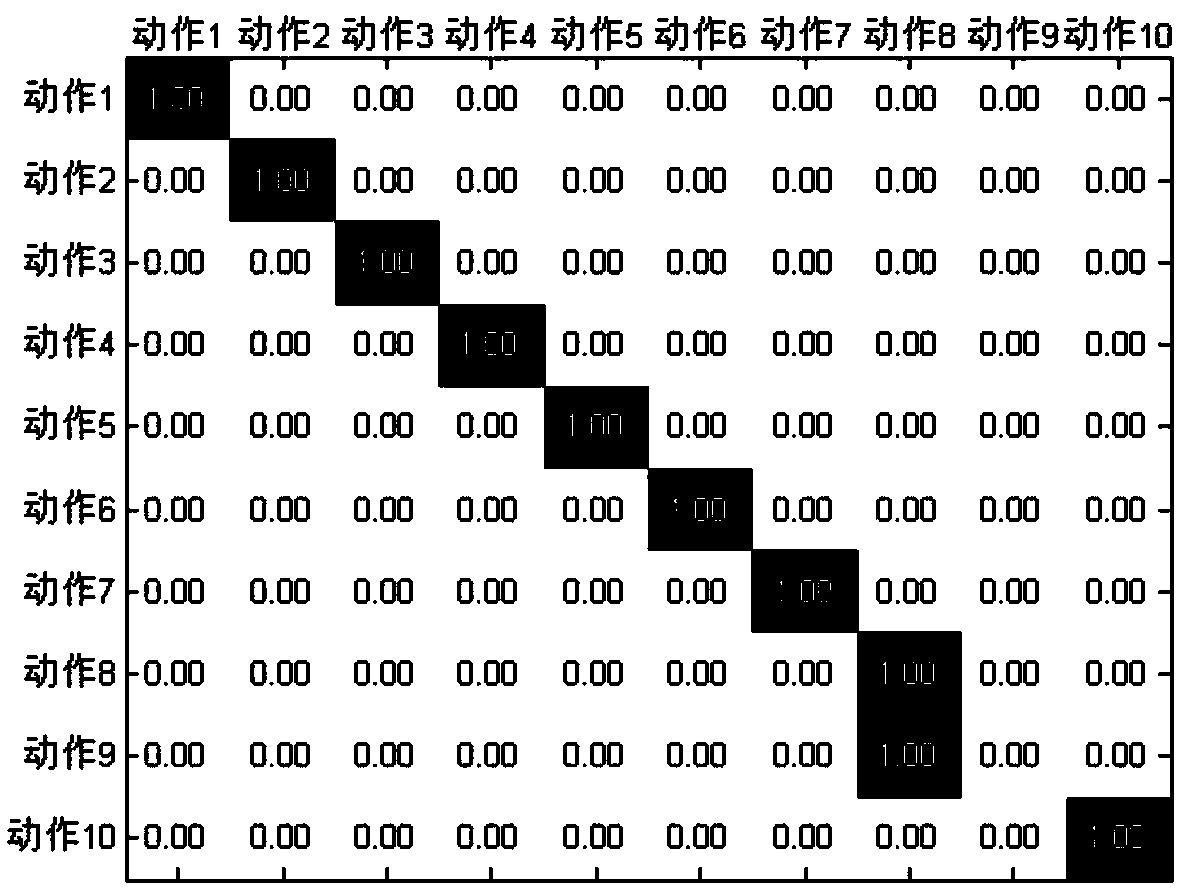
InactiveCN103902989AAccurate extractionImprove recognition rateCharacter and pattern recognitionHuman bodyFeature extraction
The invention discloses a human body motion video recognition method based on non-negative matrix factorization. The human body motion video recognition solves the problems that due to the fact that in the prior art, extraction of characteristics of a motion vehicle is influenced by the background environment, the recognition rate is lowered, and due to the fact that the number of the dimensions of the extracted characteristics is excessively high, the calculation amount is excessively large. The method specifically includes the steps of firstly, preprocessing a data set; secondly, detecting space interest points; thirdly, constructing a cube; fourthly, constructing a characteristic matrix; fifthly, training a dictionary; sixthly, conducting classification. According to the method, the influences of the background environment on characteristic extraction can be effectively eliminated in the human body motion video recognition process, the recognition rate of the human body motion video can be improved, the number of the dimensions of the extracted characteristics is low, and the calculation amount and the complexity in the human body motion video recognition process are reduced.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
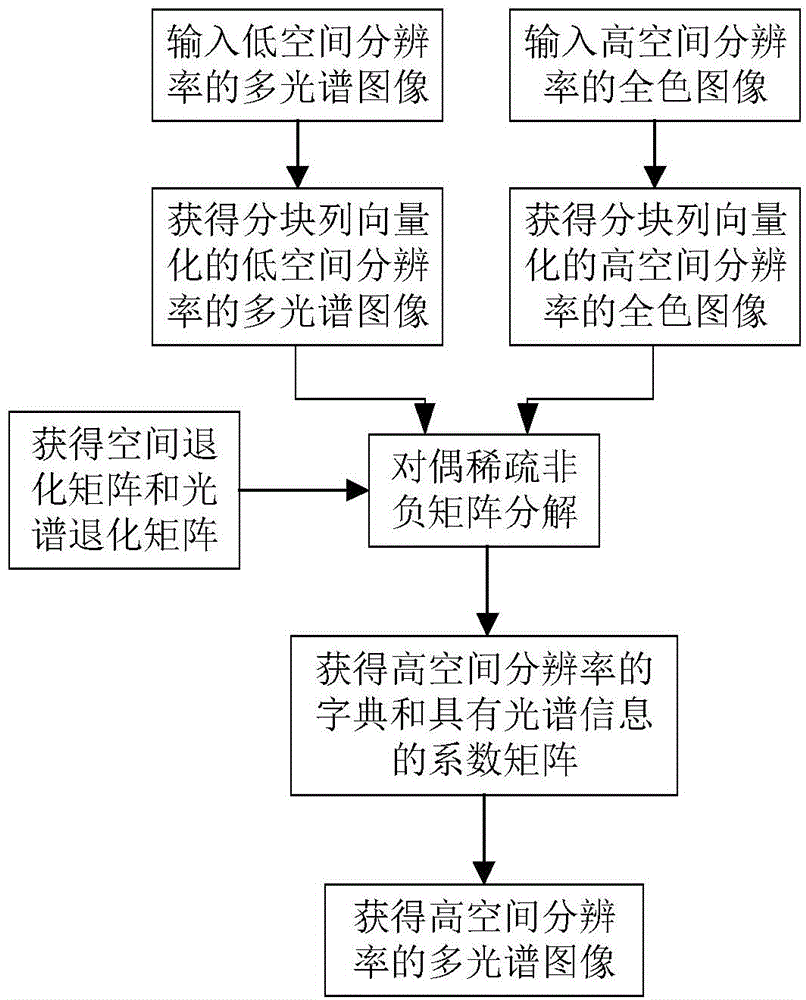
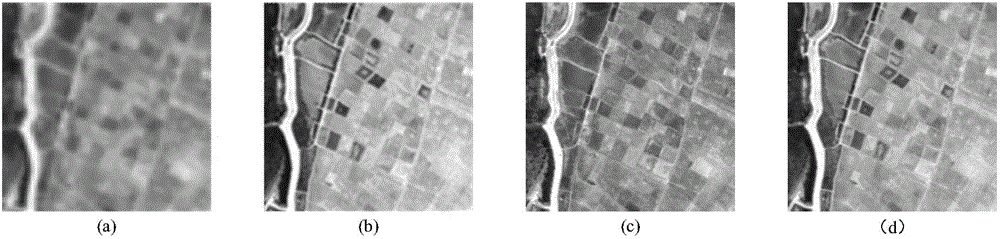
Multispectral image and full-color image fusion method based on dual sparse non-negative matrix factorization
The present invention discloses a multispectral image and full-color image fusion method based on dual sparse non-negative matrix factorization and mainly solves the problems that space information is fuzzy and a spectrum is distorted in the prior art. The multispectral image and full-color image fusion method comprises the steps of: (1) respectively inputting a multispectral image with a low spatial resolution ratio, a full-color image with a high spatial resolution ratio, a spectrum degenerate matrix and a spatial degenerate matrix; (2) respectively carrying out partitioned column vectorization on the multispectral image with the low spatial resolution ratio and the full-color image with the high spatial resolution ratio; (3) carrying out dual sparse non-negative matrix factorization on the images subjected to column vectorization so as to obtain a dictionary with a high spatial resolution ratio and a coefficient matrix with spectral information; and (4) multiplying the dictionary with the high spatial resolution ratio by the coefficient matrix with the spectral information so as to obtain the multispectral image with the high spatial resolution ratio, which is subjected to column vectorization, and restoring the multispectral image with the high spatial resolution ratio, which is subjected to column vectorization, into the multispectral image with the high spatial resolution ratio. According to the multispectral image and full-color image fusion method disclosed by the present invention, the accurate space information and the accurate spectral information can be obtained; and the multispectral image and full-color image fusion method can be used for the fields of remote sensing of object identification, terrain classification, environmental monitoring and the like.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
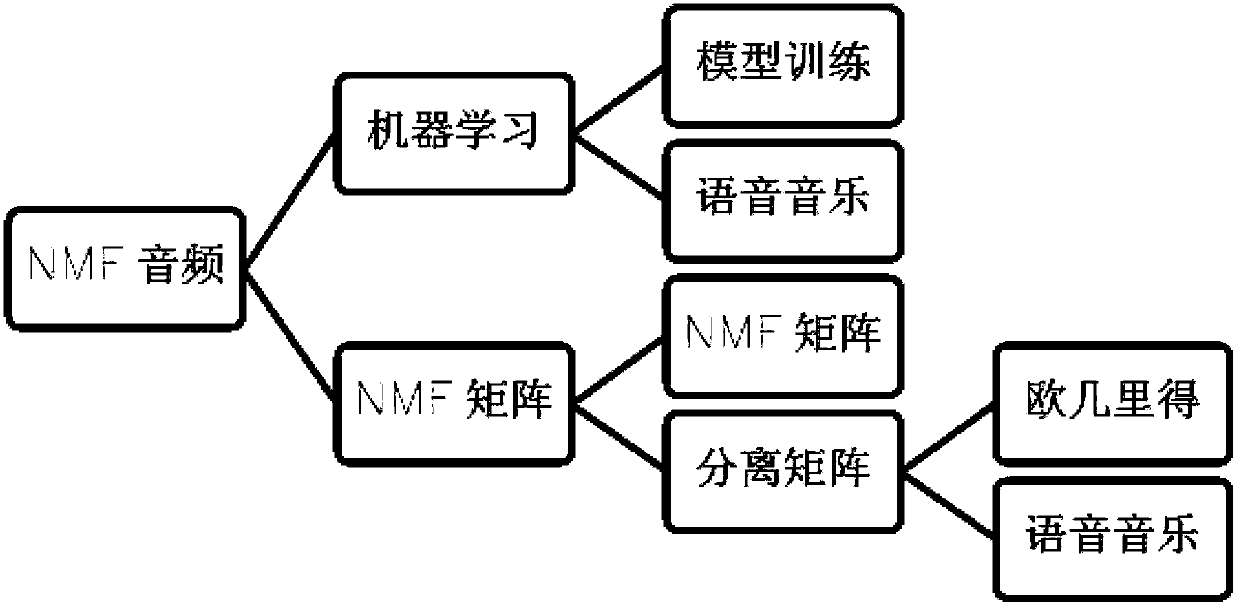
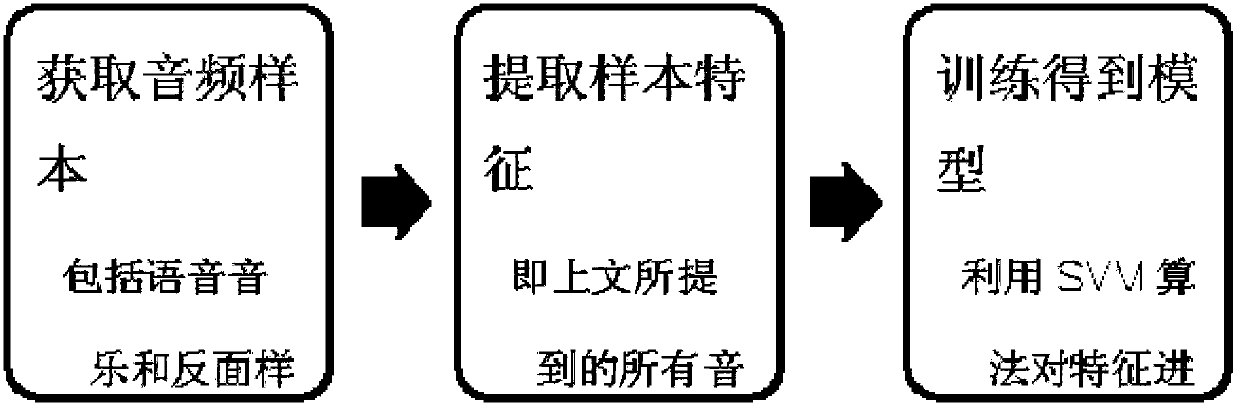
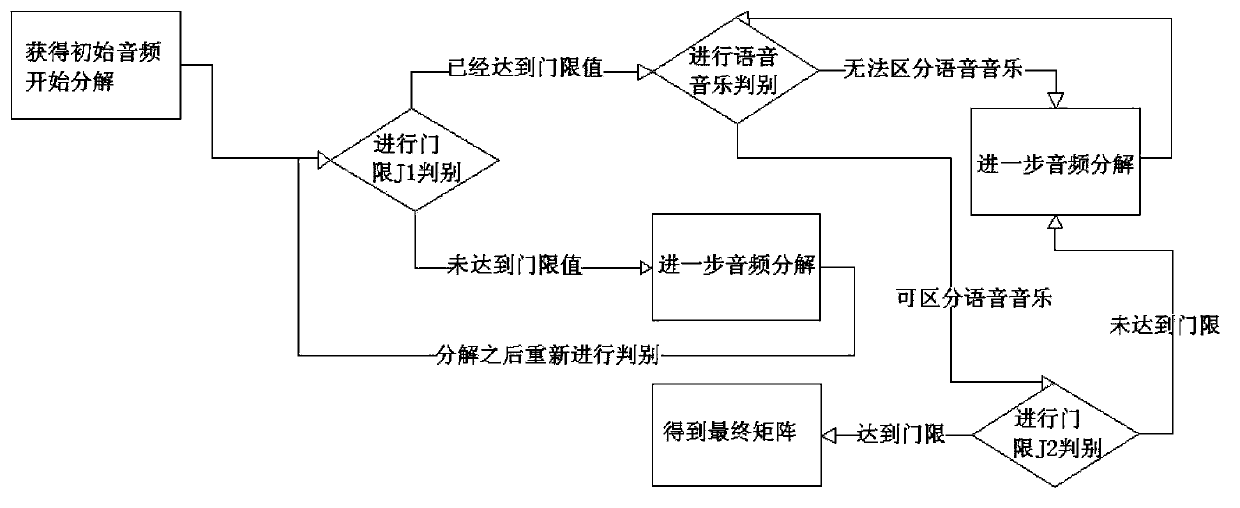
Audio frequency separation method based on NMF non-negative matrix factorization
The invention belongs to the field of voice signal factorization, and specifically relates to an audio frequency separation method based on NMF non-negative matrix factorization. The audio frequency separation method comprises an auxiliary music voice distinguish module and an NMF non-negative matrix factorization module. The method can relatively well separate voice audio frequency and music audio frequency mixed in the audio frequency by introducing the NMF novel mathematic research result and combining the audio frequency characteristic difference of the voice audio frequency and the music audio frequency, thereby obtaining relatively clear music audio frequency and voice audio frequency. By combining the NMF method and machine learning algorithm, the separation work of the audio frequency can be completed efficiently.
Owner:SHANGHAI 8D WORLD NETWORK SCI & TECH
Microscopic image color convolution removal method and cutting method based on non-negative matrix factorization (NMF)
ActiveCN104200428AImprove accuracyFully automatedImage enhancementImage analysisMicroscopic imageInformation processing
The invention discloses a microscopic image color convolution removal method based on non-negative matrix factorization (NMF), and belongs to the image information processing technology filed. The microscopic image color convolution removal method based on the NMF is directed at a tissue microscopic image after dye marking, and uses an NMF method to separate observation channels corresponding to different coloring agents. The invention further discloses a microscopic image cutting method based on the NMF. The microscopic image cutting method based on the NMF is used to cut the image based on the observation channels separated through the NMF method, not only can achieve rapid and completely automatic image processing, but also obtain an accurate image cutting result, and provides accurate basis for subsequent cell detection and pathological diagnostic analysis. Compared with the prior art, the microscopic image color convolution removal method and the microscopic image cutting method based on the NMF can effectively improve microscopic image cutting accuracy, save computation time, and obtain the microscopic image good in visual effect.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF INFORMATION SCI & TECH
Method, system and computer program product for breast density classification using parts-based local features
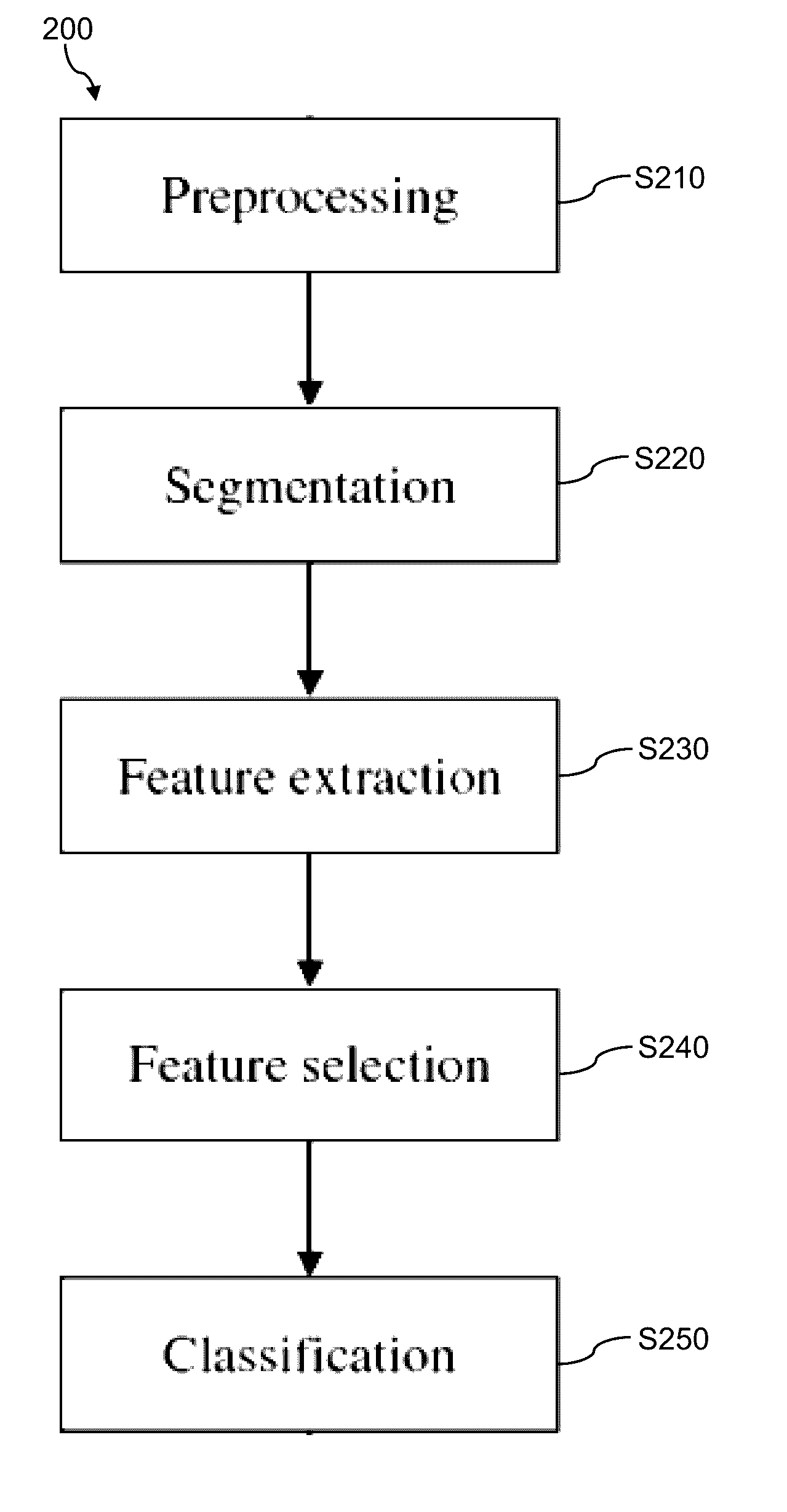
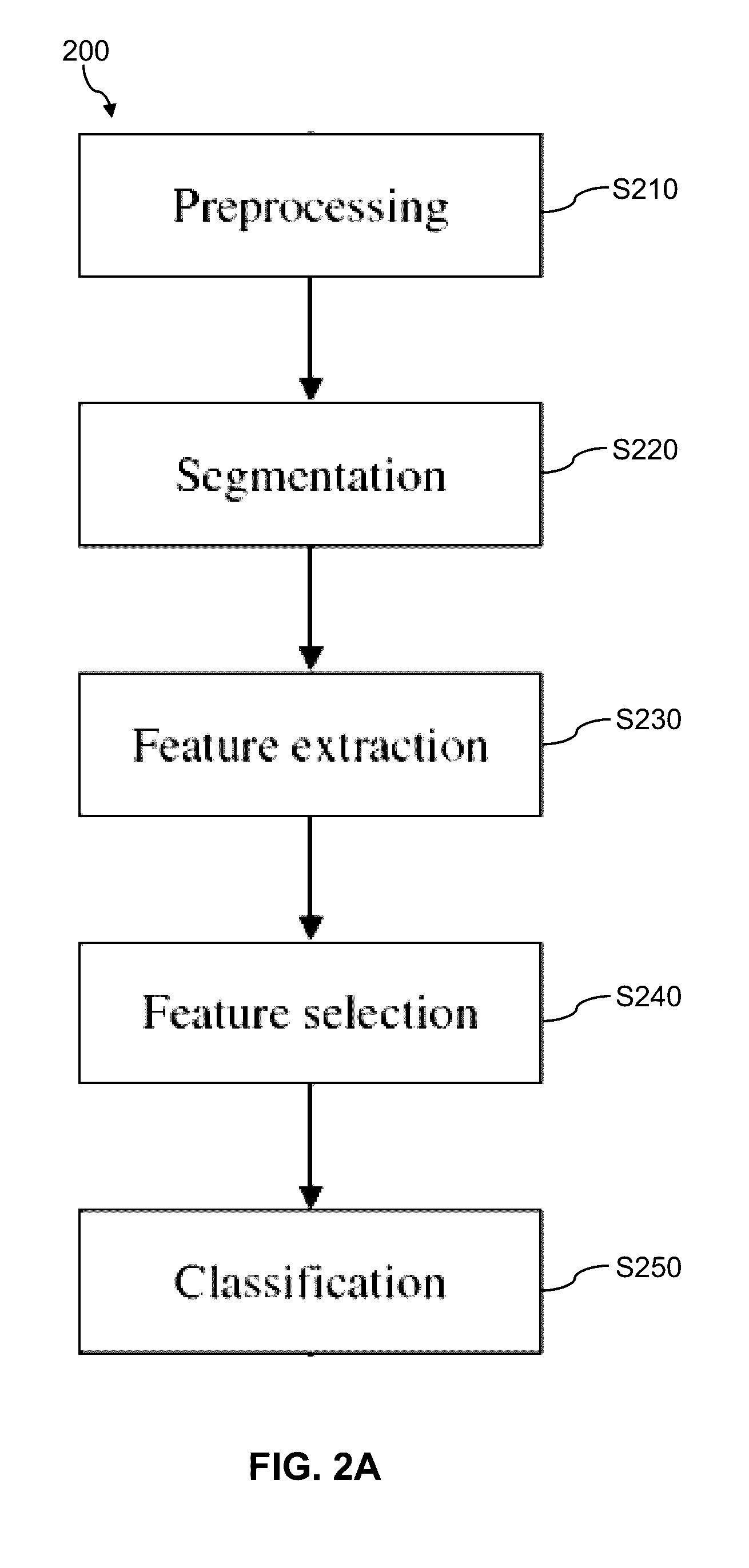
InactiveUS20160314579A1Improve accuracyImage enhancementImage analysisPrincipal component analysisClassification methods
An automated content-based image retrieval method, a system and a computer program product for the classification of breast density from mammographic imagery. Raw digital mammogram images taken of patients are initially pre-processed to remove noise and enhance contrast, then subjected to pectoral muscle segmentation to produce region of interest (ROI) images. The ROI images are then decomposed using non-negative matrix factorization (NMF), where a non-negative sparsity constraint and reconstruction quality measures are imposed on the extracted and retained first few NMF factors. Based on the retained NMF factors, kernel matrix-based support vector machines classify the mammogram images binomially or multinomially to breast density categories. Methods of assessing and comparing the NMF-based breast classification method to principal component analysis or PCA-based methods are also described, and the NMF-based method is found to achieve higher classification accuracy and better handling of invariance in the digital mammogram images because of its parts-based factorization.
Owner:KING FAHD UNIVERSITY OF PETROLEUM AND MINERALS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com